Separation and application of lytic escherichia coli phage RDP-EC-16029
A technology of RDP-EC-16029 and Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of microbiology, can solve the problems of stagnant research on bacterial diseases and low acceptance of virus preparations, and achieve good acid-base tolerance and high-efficiency infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Isolation and identification of pathogenic avian Escherichia coli E10
[0035] Sampling was taken from the diseased farm, and the liver of the diseased poultry was taken aseptically, and a line was drawn on the selective medium (MacConkey agar). After culturing at 37°C for 18-24 hours, a round, flat, neat edge, and surface were formed on the medium. Smooth and wet red colonies, pick typical colonies and continue to streak and purify 3 times, then pick a single colony and inoculate in 5mL LB broth, shake and culture at 37°C, 200rpm for 8h to obtain a uniform turbid bacterial suspension. After 16sRNA molecular identification and serotype identification, it was determined to be pathogenic Escherichia coli, named as E10, and stored in a -80°C refrigerator.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Isolation and identification of phage RDP-EC-16029:
[0037](1) Manure treatment: Take manure from the farm, weigh 5g of chicken manure and add it to 10mL of sterile water to soak overnight, then centrifuge the overnight leaching solution at 10,000rpm for 5min, take the supernatant and pass it through a 0.22μm filter, and use the filtrate for later use;
[0038] (2) Preparation of mixed bacterial suspension: Take 0.2mL of bacterial suspension and 0.1mL of filtrate into 5mL of LB broth, culture at 37°C, shake at 200rpm overnight, then centrifuge at 10,000rpm for 5min, and pass the supernatant through a 0.22μm filter. The filtrate is ready for use;
[0039] (3) Separation of bacteriophages: Separation of phages using the double-plate method, take 0.1mL of the filtrate of the mixed bacterial suspension and 0.2mL of the host E. After culturing in a 37°C incubator for 6-8 hours, pick the transparent spot and put it in 1mL of normal saline in a 37°C water bath for ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Electron Microscopic Observation of Phage
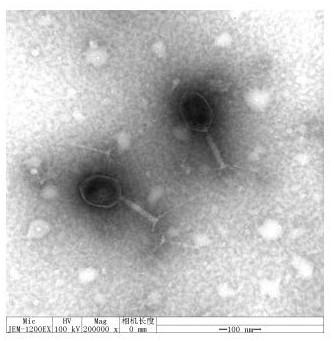
[0042] Take 20 μL of the liquid containing crude phage particles and drop it on the copper grid, let it settle naturally for 15 min, absorb the excess liquid from the side with filter paper, add a drop of 2% phosphotungstic acid (PTA) on the copper grid to stain the phage for 10 min, and then Use filter paper to absorb the staining solution from the side, and observe the phage morphology with an electron microscope after the sample is dry, as shown in figure 1 shown.
[0043] The bacteriophage RDP-EC-16029 has a polyhedral stereosymmetric head, wrapped in nucleic acid, with a diameter of about 70nm, a tail with a length of about 120nm, a tail sheath, and a neck connecting the head and tail. According to the Ninth Report of the International Virus Taxonomy Organization Virus Classification, the bacteriophage is classified as Myoviridae of the order Cauviridae.
[0044] Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of phage R...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com