A method for producing high-strength copper alloy large-scale ingots by vacuum melting
A technology for vacuum smelting and copper alloys, which is used in the field of vacuum smelting to produce large-scale ingots of high-strength copper alloys. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
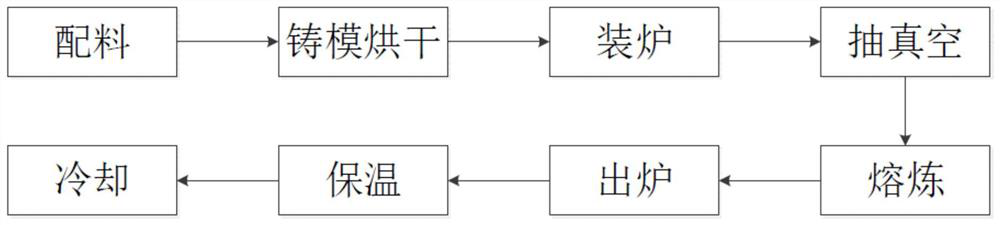
[0026] In this embodiment, a method for producing high-strength copper alloy large-scale ingots by vacuum smelting is obtained by the following method:
[0027] (1) Ingredients: the raw materials used and their proportioning ratio are shown in Table 1,
[0028] Table 1
[0029] Element Grade standard mass percentage Electrolytic copper Cu99.95 GB / T467-2010 76.30% Electrolytic nickel Ni99.95 GB / T6515-2010 14.00% Tin ingots Sn99.95 GB / T 728-2010 9.00% Niobium bar Nb1 GB / T 14842-2010 0.10% Electrolytic manganese JMn98 GB / T 2774-2010 0.60%
[0030] (2) Mold drying: put the cast iron mold into a drying furnace and heat it to 900°C, and dry it for 1 hour;
[0031] (3) Furnace loading: First load tin ingots, cut and pave the entire bottom of the crucible, add electrolytic nickel above the tin ingots, add niobium in the middle of the crucible, and finally add electrolytic copper, electrolytic manganese is added fro...
Embodiment 2
[0040] In this embodiment, a method for producing high-strength copper alloy large-scale ingots by vacuum smelting is obtained by the following method:
[0041] (1) Ingredients: the raw materials used and their proportioning ratio are shown in Table 2,
[0042] Table 2
[0043] Element Grade standard mass percentage Electrolytic copper Cu99.95 GB / T467-2010 76.60% Electrolytic nickel Ni99.95 GB / T6515-2010 15.00% Tin ingots Sn99.95 GB / T 728-2010 8.00% Niobium bar Nb1 GB / T14842-2007 0.20% Electrolytic manganese JMn98 GB / T 2774-2008 0.20%
[0044] (2) Mold drying: put the cast iron mold into a drying furnace and heat it to 800°C, and dry it for 2 hours;
[0045] (3) Furnace loading: First load tin ingots, cut and pave the entire bottom of the crucible, add electrolytic nickel above the tin ingots, add niobium in the middle of the crucible, and finally add electrolytic copper, electrolytic manganese is added fro...
Embodiment 3
[0055] In this embodiment, a method for producing high-strength copper alloy large-scale ingots by vacuum smelting is obtained by the following method:
[0056] (1) Ingredients: the raw materials used and their proportioning ratio are shown in Table 3,
[0057] table 3
[0058] Element Grade standard mass percentage Electrolytic copper Cu99.95 GB / T467-2010 76.45% Electrolytic nickel Ni99.96 GB / T6515-2010 16% Tin ingots Sn99.97 GB / T 728-2010 7% Niobium bar Nb1 GB / T14842-2007 0.15% Electrolytic manganese JMn98 GB / T 2774-2008 0.40%
[0059] (2) Mold drying: put the cast iron mold into a drying furnace and heat it to 700°C, and dry it for 4 hours;
[0060] (3) Furnace loading: First load tin ingots, cut and pave the entire bottom of the crucible, add electrolytic nickel above the tin ingots, add niobium in the middle of the crucible, and finally add electrolytic copper, electrolytic manganese is added from the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com