Method for recovering scandium and vanadium from chlorination-process titanium dioxide wastewater
A technology of titanium dioxide wastewater and chlorination method, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of small specific gravity, few manufacturers adopt, slow phase separation, etc., achieve high-efficiency extraction, simple process operation, and high enrichment multiple Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
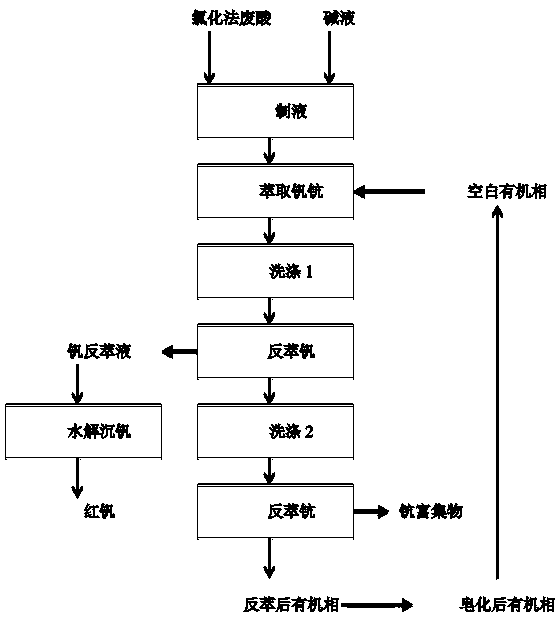
[0024] Such as figure 1 Shown, the method for reclaiming scandium vanadium in the chlorination process titanium white wastewater of the present embodiment comprises the steps:
[0025] 1. Preparation of extraction material liquid of titanium dioxide waste acid by chlorination method: pour 2 / 3 volume of waste acid of titanium dioxide by chlorination method into the liquid preparation barrel (used as a reaction kettle); then use industrial mixed alkali to adjust the pH value to 0.2, and stir React for 2 hours, filter, and the filtrate is the extraction material liquid of titanium white waste acid in the chlorination process. The loss rate of scandium and vanadium in the liquid preparation process is below 1%. Iron 50g / L in the filtrate; Manganese 15g / L; Aluminum 8g / L; Scandium 0.138g / L; Vanadium 1.522g / L; Titanium 0.04g / L;
[0026] 2. Extraction: prepare a composite extractant according to the volume ratio, take 20% diisooctyl phosphate + 2% diisooctyl dithiophosphinic acid + ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] In the method for recovering scandium and vanadium in the chlorination titanium dioxide wastewater of this embodiment, the influence of acidity on the loss of scandium and vanadium is adjusted during the liquid preparation process. Take 600mL of titanium dioxide waste acid from the chlorination process, the initial hydrogen ion concentration is 1.47mol / L, adjust the pH value with industrial mixed alkali (solid), filter and analyze the results:
[0029] name Scandiummg / L Vanadium mg / L Nickel mg / l Titanium mg / l Zirconium mg / l Volume mL filter residue Liquid 139 1527 326 392 355 600 none PH0.20 138 1522 321 40 30 612 8.1g (wet) PH0.87 135 1491 317 22 17 615 16.3g (wet) PH1.47 127 1455 299 14 5 591 21.7g (wet) PH2.13 89 922 293 3 5 576 38.5g (wet) PH2.47 63 813 291 4 5 564 44.1g (wet)
[0030] The amount of filter residue obtained in the liquid preparation process of thi...
Embodiment 3
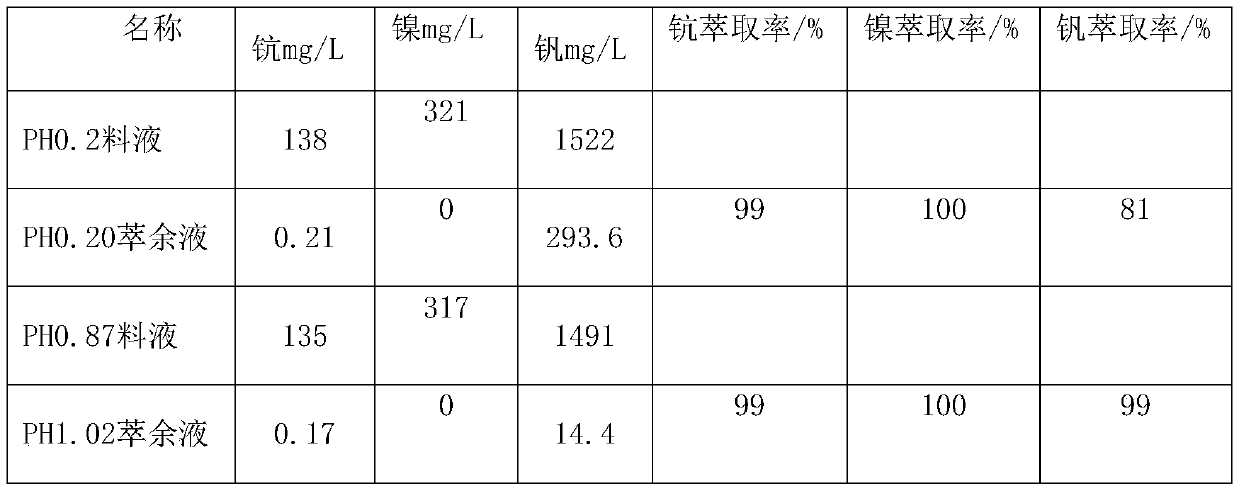
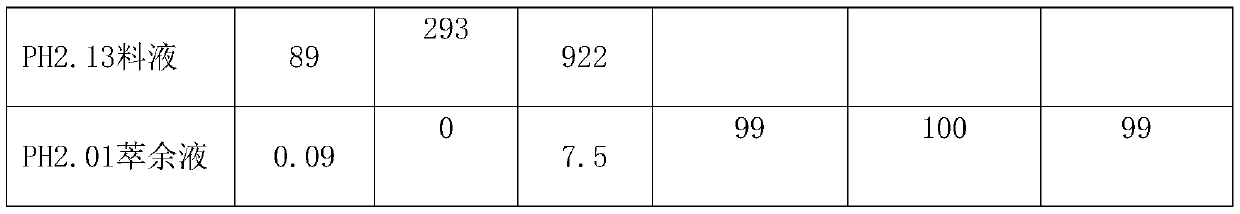
[0032] The method for recovering scandium and vanadium in the chlorination titanium dioxide wastewater of this embodiment, the influence of the acidity of the chlorination titanium dioxide waste acid extraction liquid on the extraction rate during the extraction process. The extractant consists of 15% di-octyl phosphate + 10% di-iso-octyl dithiophosphinic acid + 10% trialkylphosphine oxide + 65% sulfonated kerosene, and the saponification rate is 50%. The extraction ratio O / A=1:1, the feed liquid is the extraction feed liquid of Example 2; the extraction time is 10 min; the number of extraction stages n=1.
[0033]
[0034]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com