High-temperature-resistant Escherichia coli phage and composition, kit and application thereof
A technology of Escherichia coli and phage, applied in the direction of phage, virus/phage, medical raw materials derived from virus/phage, etc., to achieve good high temperature resistance, high stability, and good application and development prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Isolation, preparation and purification of phage
[0039] The source sample of Escherichia coli phage CL9 in the present invention was collected from the sewage of farmers' market in Jiangning District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province, filtered through double-layer filter paper, centrifuged at low speed and normal temperature, and then filtered the supernatant with a 0.22 μm filter membrane.
[0040] Isolation of phage: take 10mL filtered supernatant, add it to 10mL 2 times TSB medium, add 1mL phage host bacteria logarithmic phase bacteria liquid at the same time, place it at 37°C for 6 hours, take the above culture, and put it under the condition of 8000rpm Centrifuge for 10 min, filter the supernatant with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, and set aside. Take 0.5mL of phage host bacteria logarithmic phase bacteria liquid, add 5mL, 48 ℃ semi-solid TSB medium to mix, pour on the TSA plate to prepare a double-layer plate containing the host bacteria. Take 10 μl of th...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: Electron microscope observation of phage
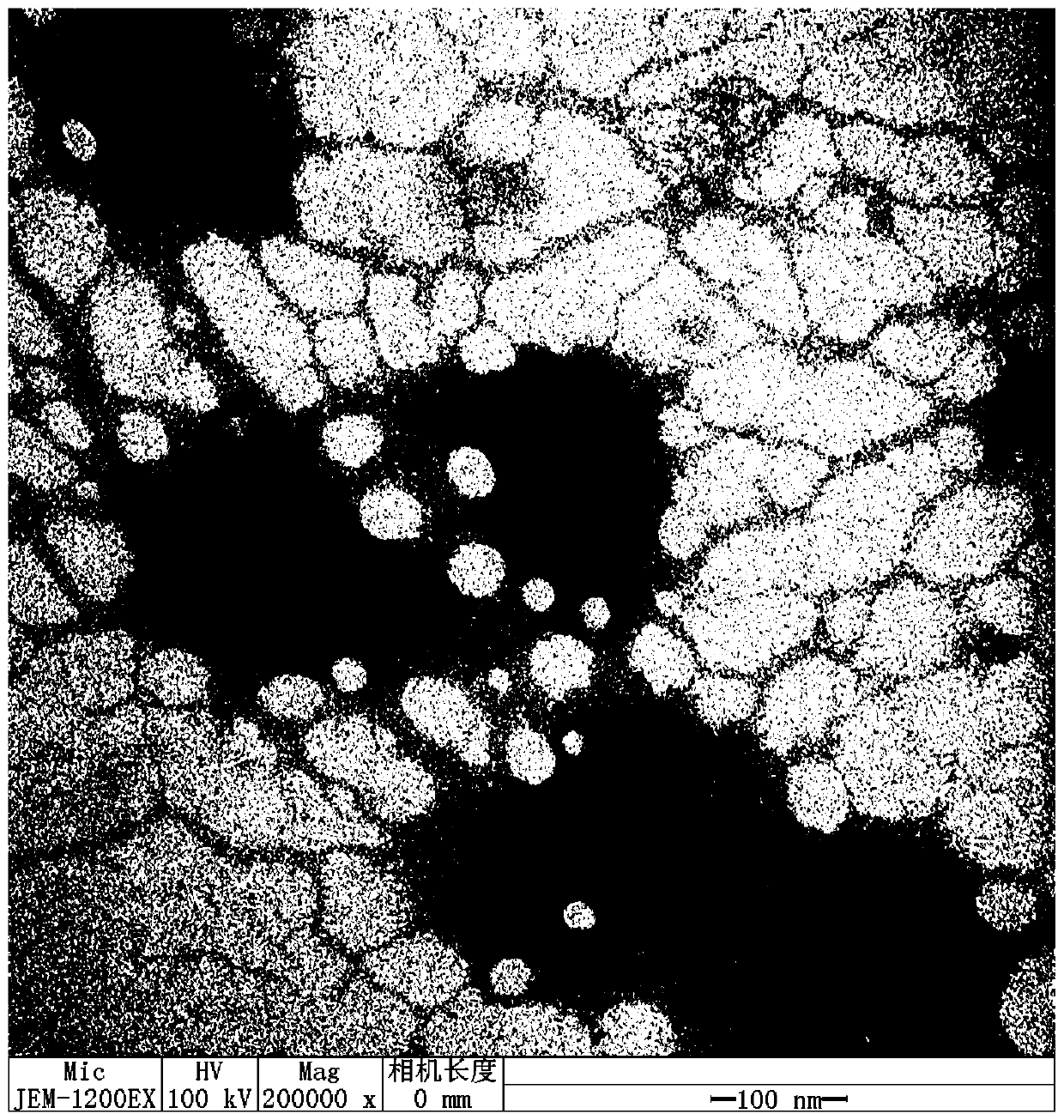
[0043] Take the supernatant of each phage culture obtained in Example 1 for electron microscope observation: take 20 μ L of sample and drop it on the copper grid, wait for its natural precipitation for 15 minutes, absorb excess liquid from the side with filter paper, add 1 drop of 2% phosphotungstic acid (PTA ) on a copper grid, dyed for 10 minutes, sucked the dye solution from the side with filter paper, and observed with an electron microscope after drying: the results are as follows: figure 1 As shown, the morphology of Escherichia coli phage CL9 was found to have a polyhedral head and a long tail, the long diameter L is 50-60nm, the transverse diameter W is 50-60nm, L / WY≈1; the tail length is 60-70nm, 2 to 8 nm wide, with contractile muscle sheaths (see figure 1 ).
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3: Extraction and sequencing of phage genome
[0045] Take 100 mL of each phage prepared in Example 1, add DNaseI and RNaseA at a final concentration of 1 μg / mL, incubate at 37°C for 60 min, add 5.84 g NaCl (final concentration 1 mol / L), dissolve and place in an ice bath for 1 h. Centrifuge at 11,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube. Add solid PEG8000 (final concentration 10%, that is, add 10 g to 100 mL), and after complete dissolution, ice bath for at least 1 h. Centrifuge at 11,000 rpm for 20 min at 4°C, and resuspend the pellet with a small amount of SM solution. Add an equal volume of chloroform and isoamyl alcohol for extraction, shake gently for 30 s, centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 1 min, absorb the supernatant, and repeat the extraction until clarification. Add DNase I and RNase A again to a final concentration of 1 μg / mL, and react at 37°C for 30-60 minutes. Add EDTA to a final concentration of 20 mmol / L (that ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com