Device and method for detecting nucleic acid by isothermal amplification technology
A nucleic acid and storage chamber technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid detection devices using constant temperature amplification technology, can solve the problems of harsh reagent storage conditions, easy attenuation, unstable fluorescent signals, etc. stable output
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
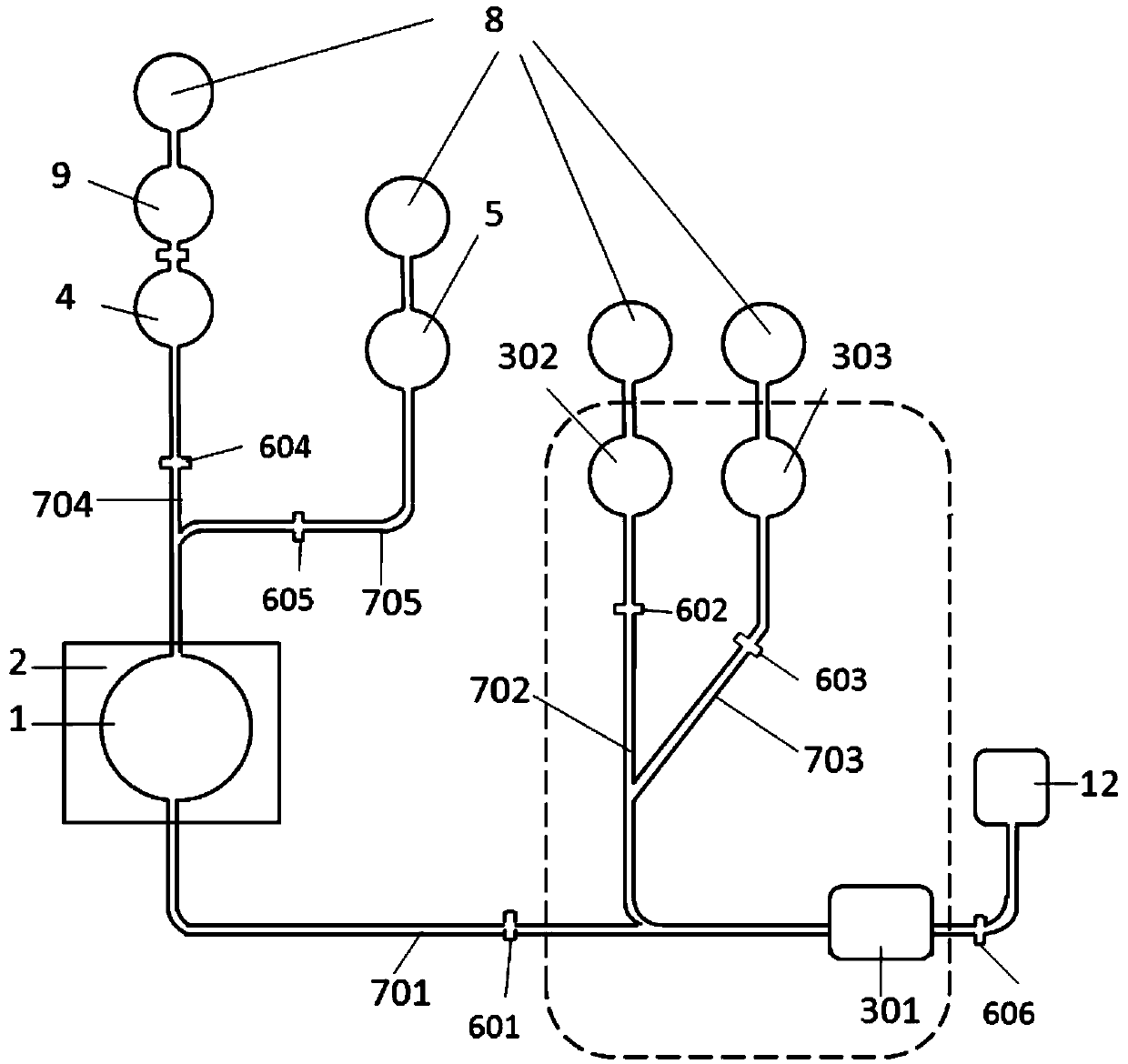
[0038] A nucleic acid detection device according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a sample processor and a magnetic sensitive detector; the structure of the sample processor is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it includes a microfluidic channel 1, a thermostat 2, a capture chip storage chamber 301, a DNA modified magnetic bead storage chamber 302 and a cleaning solution storage chamber 303;
[0039] A reagent inlet and a reagent outlet are provided on the micro-flow channel 1; a temperature controller 2 is provided on the micro-flow channel 1;
[0040] The inlet of the capture chip storage chamber 301 communicates with the reagent outlet of the microfluidic cell 1 through the first microchannel 701, communicates with the DNA modification magnetic bead storage chamber 302 through the second microchannel 702, and stores it with the cleaning solution through the third microchannel 703. The chamber 303 communicates; the first microchannel 701 is provided with a fir...
Embodiment 2
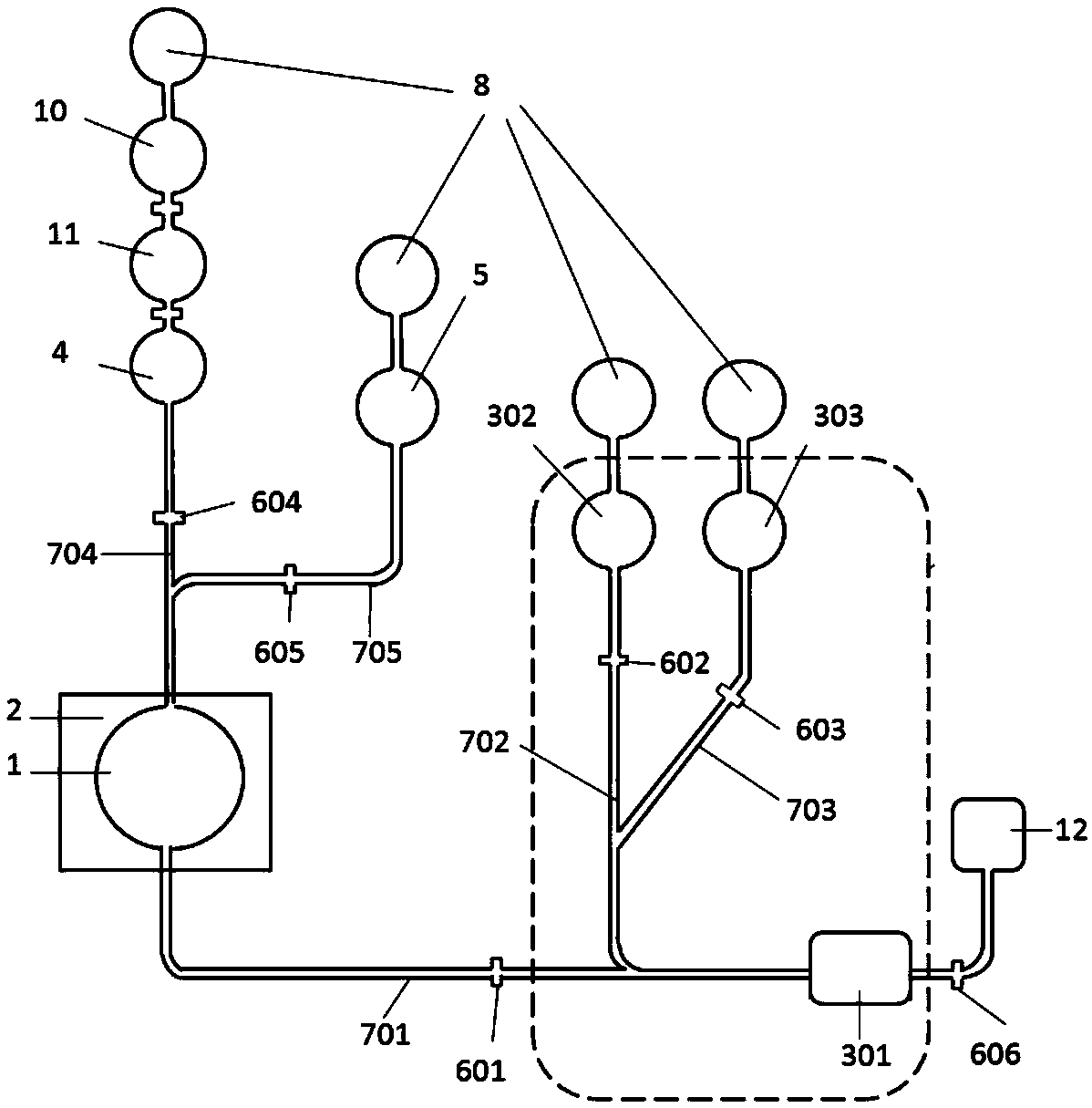
[0061] A device for detecting nucleic acid according to an embodiment of the present invention differs from Embodiment 1 only in that the sample processor is different. The sample processor of the device for detecting nucleic acid in this embodiment is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the difference between it and the sample processor of Example 1 is: the sample processor of the device for detecting nucleic acid in this embodiment does not include a DNA extraction chamber 9 with a built-in DNA extraction solution, but the device for detecting nucleic acid in this embodiment The sample processor also includes an RNA extraction chamber 10 and a reverse transcription reagent storage chamber 11 with a built-in RNA extraction solution, and the reverse transcription reagent storage chamber 11 communicates with the reagent outlet of the RNA extraction chamber 10 and the reagent inlet of the DNA holding chamber 4 to be tested respectively; And in this embodiment, the pressurizer 8 is co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com