Method for detecting enzymatic activity concentration through combined use of subject and object probes and nanopore technique
A host-guest, active technology, applied in the field of supramolecular chemistry, can solve the problems of strong background interference, low signal characteristics, unfavorable blocking signals and high-sensitivity detection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1D
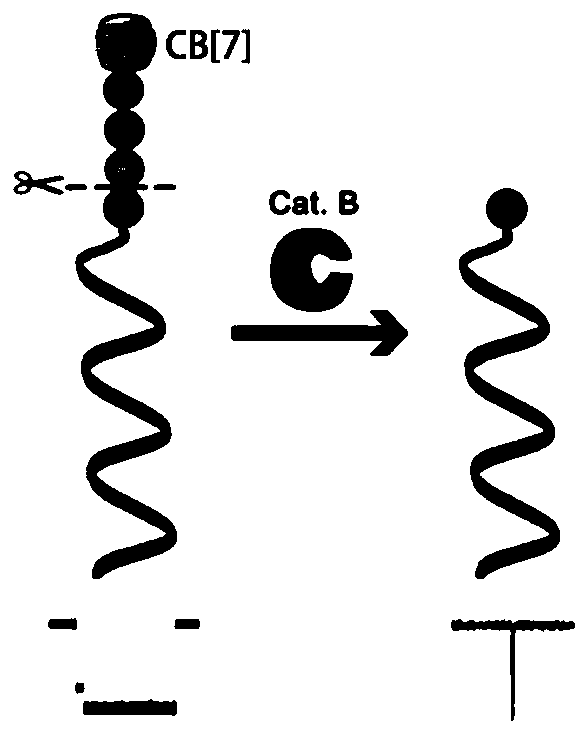
[0063] Example 1 Preparation of DNA-peptide molecular probe
[0064] In this example, two DNA-peptide molecular probes were prepared, and the used DNA molecules and peptide molecules were all commissioned by Sangong Bioengineering (Shanghai) to synthesize. The sequence of the DNA molecule is 5'-CATATTACACTCTCAC GACTC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1), and its 5'end is modified with sulfhydryl groups; the sequence of peptide molecule 1 is LFG K (SEQ ID NO: 2), and the sequence of peptide molecule 2 For FGVCitK (SEQID NO: 3), the side chain of the lysine residue at the carboxyl end of the peptide molecule is modified with 3-maleimidopropionic acid.
[0065] Take 100 μL DNA (100M) and 100 μL peptide molecule 1 (5mM), mix the two evenly and adjust the pH to about 8.0 with ammonia; vortex at room temperature for 4h. The reaction solution was separated and purified by preparative anion exchange chromatography to obtain the desired DNA-peptide molecule 1, which was named as DNA-KGFL probe.
[0066] Take ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Construction of sample cell system
[0068] The sample cell system includes two compartments (cis and trans), the volume of both compartments is 1.0mL, and the two compartments are separated by a 20μm thick PTFE membrane (the middle of the membrane has a diameter of about 100- 150μM hole), use a glass capillary to drop a mixed solution consisting of 1 volume part of n-hexadecane and 10 volume parts of n-pentane into the pores of the polytetrafluoroethylene film (the amount of dripping is about 2 to 3 μL), Then add electrolyte buffer (3M KCl, 10mM Tris, pH 5.0) and 1,2-diphytanyl lecithin (lipids) (1,2-diphytanyl lecithin with phospholipid stock solution) to the two compartments The concentration of the phospholipid stock solution is 10 mg / mL, and the addition amount is about 15 μL; the addition amount of the electrolyte buffer is 1 mL), and mixed with a pipette to make it self-assemble to form a phospholipid bilayer. Then add 1μL of α-hemolysin protein solution ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3 Enzyme activity concentration detection of leucine aminopeptidase
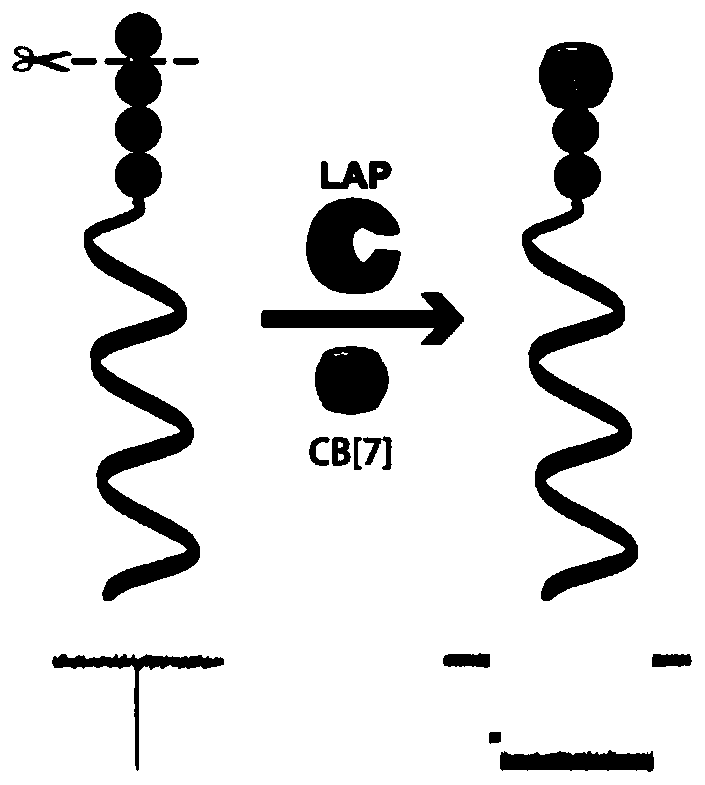
[0073] In this example, the enzyme activity concentration of Leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) was detected. LAP was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, 10 U / mg.
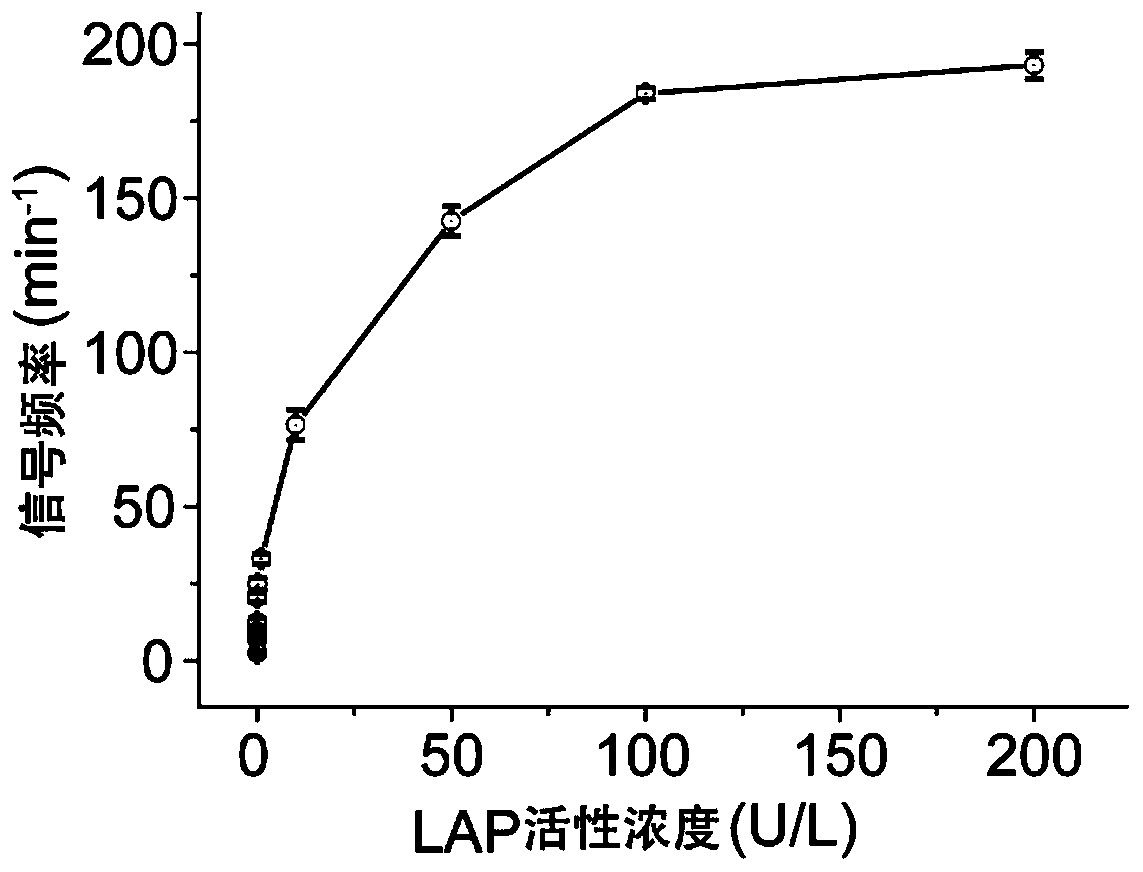
[0074] (1) Take the DNA-KGFL probe (1.23μL, 163.9μM) prepared in Example 1, and then take various concentrations of LAP and mix them in a buffer (10mM PB, pH 7.4), and adjust the total volume to 20μL, so that the final concentration of the LAP to be tested is 3.1×10 -6 , 3.1×10 -5 , 3.1×10 -4 , 3.1×10 -3 , 3.1×10 -2 , 0.31, 3.1, 15.6, 31.2, 46.8, 62.4nM; incubate together at 37°C for 3h, then add 10μL of cucurbit[7]urea (5.0mM), and incubate at 4°C for 2h to prepare the test solution.
[0075] (2) Add the test solution obtained in step (1) to the cis compartment of the sample cell prepared in Example 2, and use a patch clamp amplifier (Axopatch 200B; Axon instruments, Foster City at room temperature of 25±2°C). ,CA) for signal acquisition, the signa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com