Cross-network communication method and address translation equipment
A cross-network and address technology, applied in the field of data communication, can solve problems such as extended user data transmission time and many jump nodes, and achieve the effect of shortening the data transmission path, increasing the speed, and simplifying the proxy server mode
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] In order to understand the content of this plan more clearly, a brief description of the abbreviations and key terms that appear below is given first:
[0062] DNS (Domain Name System, abbreviated as DNS) server: It is a distributed database on the Internet that maps domain names and IP addresses (that is, Internet Protocol Addresses), enabling users to access the Internet more conveniently without having to remember to The IP number string read directly by the machine. The DNS server is used for domain name resolution, and finally obtains the IP address corresponding to the domain name through the domain name for data access.
[0063] SNAT (Source Network Address Translation, abbreviated as SNAT): source address translation, its function is to convert the source address in the data packet to another address.
[0064] DNAT (Destination Network Address Translation, abbreviated as DNAT): Destination address translation, its function is to convert the destination address ...
Embodiment 2
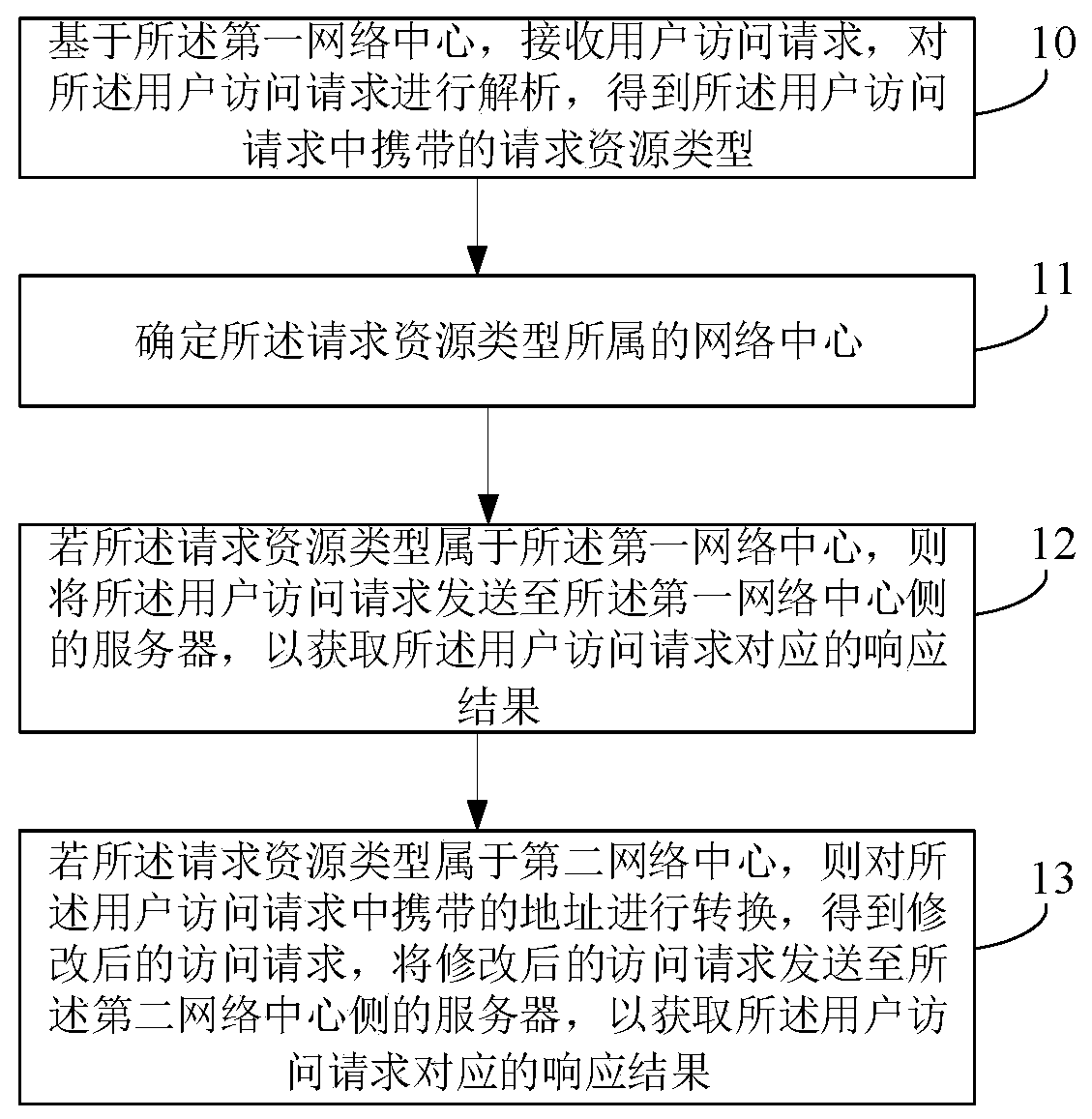
[0107] With reference to Embodiment 1, the following describes the process of cross-network communication for the foregoing method (2), wherein, before obtaining the user access request, it also includes the process of assigning an IP address to the user-side terminal. Specifically, the user-side terminal initiates a network access request, for example, initiates a network access request to the first network center through PPPOE dialing, and the address translation device obtains the access request of the user-side terminal, and then transmits the access request Send to the BARS server on the first network center side. The BARS server at the first network center side responds to the user's access request, and assigns an IP address and an IP address of the DNS server to the user-side terminal for network connection. The address translation device receives the address assigned by the first network center server to the user-side terminal, and feeds back the address to the user-si...
Embodiment 3
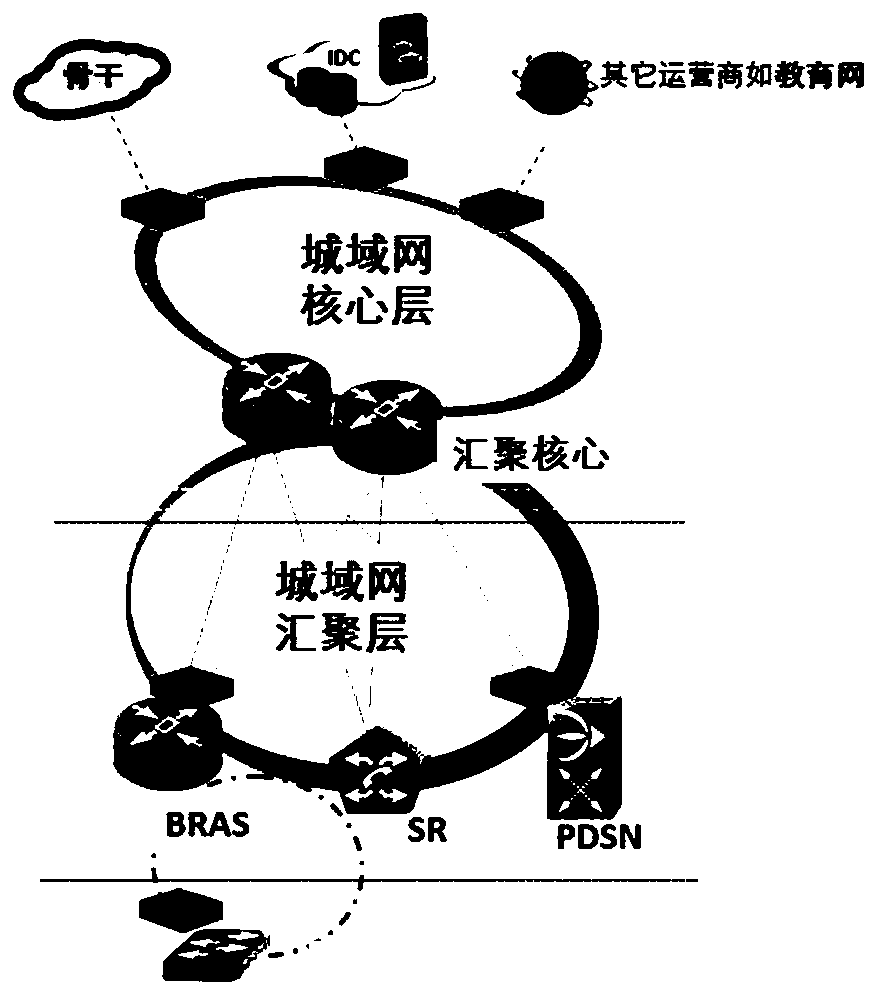
[0115] combine Figure 7 , using a practical application scenario to illustrate one of the implementations of the cross-network communication method of the present invention, here, take the first network center as a network center based on the public network, and the second network center as an example based on an education network explain.
[0116] Wherein, the first source address in the foregoing embodiment is the user-side terminal address, the first target address is the DNS server address of the public network, the second source address is an address that allows access to the education network, and the second target address is the DNS server of the education network address, the third source address is the DNS server address (second target address) of the education network, and the third target address is an address (second source address) that allows access to the education network.
[0117] Wherein, the address conversion device is specifically a DPI device.
[0118]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com