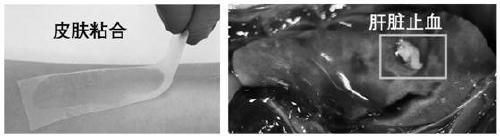
Biological adhesive based on biological engineering protein and preparation method of biological adhesive
A bioadhesive, bioengineering technology, applied in the preparation of protein adhesives, animal glue or gelatin, adhesive types, etc., can solve the lack of non-invasive technology, fixation and bone atrophy, poor bone healing, etc. problems, achieve the effects of no special equipment, low cost, good biocompatibility and degradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] The present invention provides a kind of preparation method of bioadhesive based on bioengineering protein, comprises the following steps:
[0034] A) respectively dissolving the positively charged elastin-like protein and the alkyl-type anionic surfactant in ultrapure water to obtain an elastin-like protein solution and a surfactant solution;
[0035] The alkyl anionic surfactant comprises sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and / or sodium dodecylsulfonate;
[0036] B) adding the surfactant solution dropwise into the elastin-like protein solution, and mixing uniformly to obtain a binder solution;
[0037] C) centrifuging the adhesive solution and then freeze-drying to obtain a bioadhesive.
[0038] In the present invention, the type, source and amount of the positively charged elastin-like and alkyl anionic surfactants are the same as those of the above-mentioned positively charged elastin-like and alkyl anionic surfactants. The types, sources and dosages are the same and ...
Embodiment 1
[0046] Transform the positively charged elastin-like ELP vector plasmid into Escherichia coli expression strain BL21DE3, pick a single clone colony, and culture overnight with LB culture medium; add the overnight activated expression seed liquid to TB medium until the bacterial liquid reaches OD600 When the value is 0.8, the inducer isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside is added and the temperature is lowered to 30 degrees for overexpression. After induction for 12 hours, collect the bacterial cells, resuspend them with lysis buffer, add protease inhibitors, DNase, and lysozyme, break the bacterial cells with a high-pressure crusher, centrifuge at a speed of 10,000 rpm or more, collect the supernatant, and purify by HPLC. Charged elastin-like ELP.
[0047] Take 11 mg of ELP protein and 7.5 mg of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and add them into 50 μL of ultrapure water respectively. The surfactant aqueous solution was added dropwise to the ELP protein aqueous solution, shaken a...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Take 8.7 mg of the ELP protein prepared in Example 1 and 6 mg of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, and add them into 50 μL of ultrapure water respectively. The surfactant aqueous solution was added dropwise to the ELP protein aqueous solution, shaken and centrifuged for 10 minutes, and the precipitate layer was left to freeze-dry for 20 minutes to obtain the ELP adhesive.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com