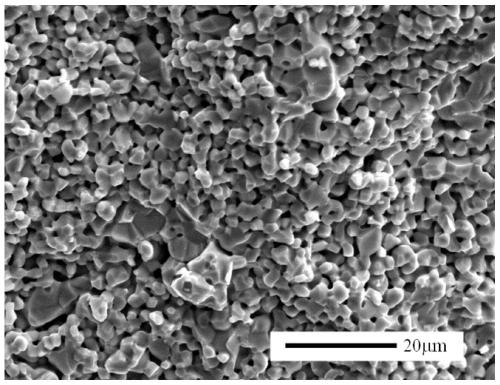
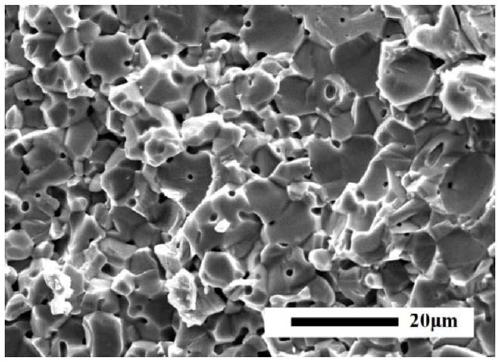
Ti-Fe based porous hydrogen evolution cathode material and preparation method and application
A hydrogen evolution cathode and porous material technology, applied in the direction of electrodes, electrode shape/type, electrolysis process, etc., can solve the problems of easy dissolution and damage of components, and achieve the protection of electrode materials, large hydrogen storage capacity, and reduction of hydrogen evolution over-points. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Step 1: Mix titanium sponge, iron filings, and chromium powder at a molar ratio of 1:0.9:0.1, put it into a vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace, and repeatedly smelt it three times in a high-purity argon environment, and place it in a water-cooled copper crucible Pouring, get Ti 50 Fe 45 Cr 5 alloy.
[0033] Among them, the hydrogen absorption and desorption performance test of the alloy was carried out on a Sievert-type gas reaction controller, evacuated at 473K for 30 minutes, and then absorbed hydrogen at 298K and 5MPa initial hydrogen pressure for 20 minutes, and then raised the temperature to 473K and evacuated , so repeated 3 times to complete the activation process of the alloy. The alloy is tested for hydrogen absorption and desorption under the condition of 298K. Under the hydrogen pressure of 5MPa, the hydrogen absorption and absorption capacity of the alloy, and the hydrogen desorption capacity of the alloy are the difference between the hydrogen ab...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Step 1: Mix titanium sponge, iron filings, and manganese powder at a molar ratio of 1:0.8:0.2, put it into a vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace, and repeatedly smelt it three times in a high-purity argon environment, and place it in a water-cooled copper crucible Pouring, get Ti 50 Fe 40 mn 10 alloy. The hydrogen absorption and desorption performance test of the alloy is the same as in Example 1, and the test results show that the obtained Ti 50 Fe 40 mn 10 The effective hydrogen desorption capacity of the alloy is 1.65wt%.
[0039] Step 2: The obtained alloy is mechanically ground into powder with a particle size of about 1-20 μm. Ti 50 Fe 40 mn 10 The alloy powder is pressed and formed, the pressing pressure is 200MPa, the holding time is 1min, and then sintered in the argon atmosphere, the temperature is 900°C, the time is 1h, and Ti is obtained after cooling in the furnace. 50 Fe 40 mn 10 porous alloy substrate.
[0040] Step 3: Take Ti 50 Fe ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Step 1: Mix titanium sponge, iron filings, and manganese powder at a molar ratio of 1:0.8:0.2, put it into a vacuum non-consumable electric arc furnace, and repeatedly smelt it three times in a high-purity argon environment, and place it in a water-cooled copper crucible Pouring, get Ti 50 Fe 40 mn 10 alloy. The hydrogen absorption and desorption performance test of the alloy is the same as in Example 1, and the test results show that the obtained Ti 50 Fe 40 mn 10 The effective hydrogen desorption capacity of the alloy is 1.65wt%.
[0044] Step 2: The obtained alloy is mechanically ground into powder with a particle size of 1-20 μm. Ti 50 Fe 40 mn 10 The alloy powder is pressed and formed, the pressing pressure is 200MPa, the holding time is 1min, and then sintered in the argon atmosphere, the temperature is 900°C, the time is 1h, and Ti is obtained after cooling in the furnace. 50 Fe 40 mn 10 porous alloy substrate.
[0045] Step 3: Take Ti 50 Fe 40 mn ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com