Method for rapid aseptic separation of edible fungi haploids
A separation method and haploid technology, which can be applied to microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fungi, etc., can solve the problem of inability to meet the needs of cultivating new varieties of edible fungi, heavy manual picking workload, and successful picking. problems such as low rate, to avoid haploid infection, short incubation period, and simple separation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
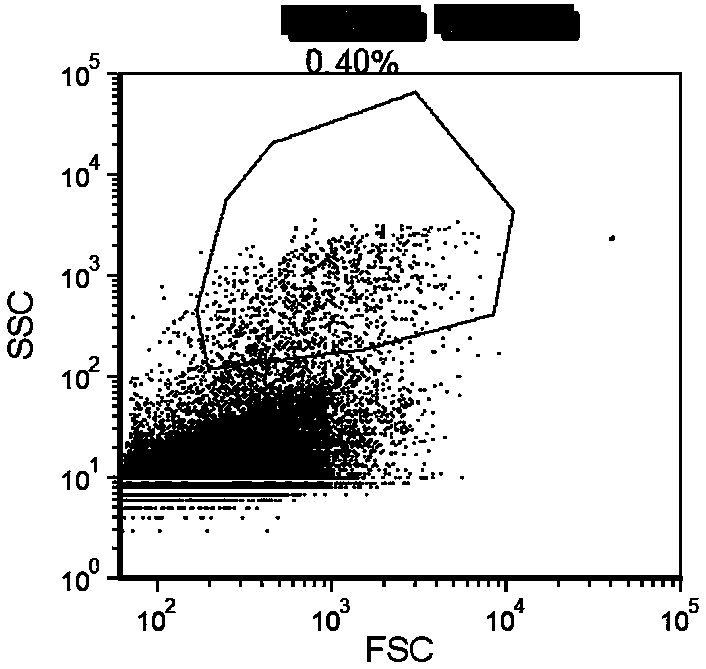
[0025] In the present embodiment, the oyster mushroom mycelium is used as the raw material, and the oyster mushroom mycelium is cultivated and matured in a sterile environment to obtain the mycelial haploid after sorting by flow cytometer, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0026] The first step is to inoculate the oyster mushroom mycelium with good growth conditions into the PDA liquid medium, and then cultivate it in a shaker (the shaker speed is 150rpm) at 25°C for 3 to 5 days, and filter it with 5 layers of sterile lens paper. Collect mature oyster mushroom mycelium;
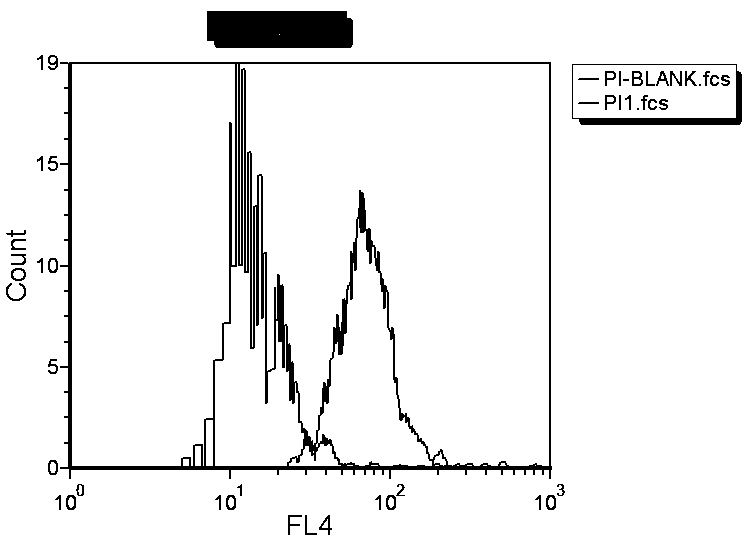
[0027] In the second step, take the mycelium obtained in the first step into a sterile centrifuge tube, add grinding beads to the machine and grind for 120s; add lysate to the triangular flask, transfer the ground mycelium to the triangular flask for lysis for 20 minutes, filter, Add DAPI dye to the filtrate to dye for 10-20min to obtain dyed mycelial liquid;
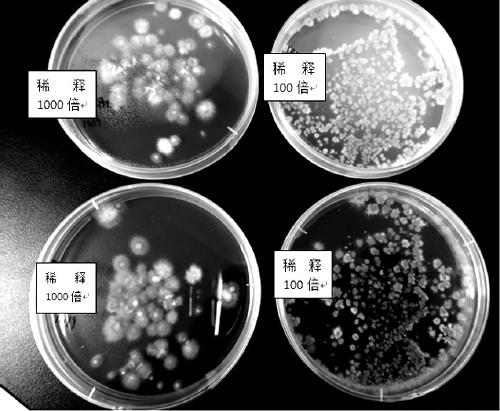
[0028] The third step is to ta...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this example, the oyster mushroom mycelium is used as the raw material, and the oyster mushroom mycelium is first cultured into a mature mycelium, and then the mature mycelium is used to prepare protoplasts, and the protoplasts can be obtained by sorting the protoplasts by a flow cytometer. Body haploid, including the following steps:
[0037] The first step is to inoculate the oyster mushroom mycelium with good growth conditions into the PDA liquid medium, and then cultivate it in a shaker (the shaker speed is 150rpm) at 25°C for 3 to 5 days, and filter it with 5 layers of sterile lens paper. Collect mature oyster mushroom mycelium;
[0038] During the cultivation of oyster mushroom mycelium, the following solutions were prepared:
[0039] P-buffer (ie 0.6M buffer osmotic stabilizer): Weigh 39.35g MgSO 4 , 1.76g of trisodium citrate, dissolved in distilled water and transferred to a 200mL volumetric flask to constant volume, and adjusted to pH 5.5 after constant v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com