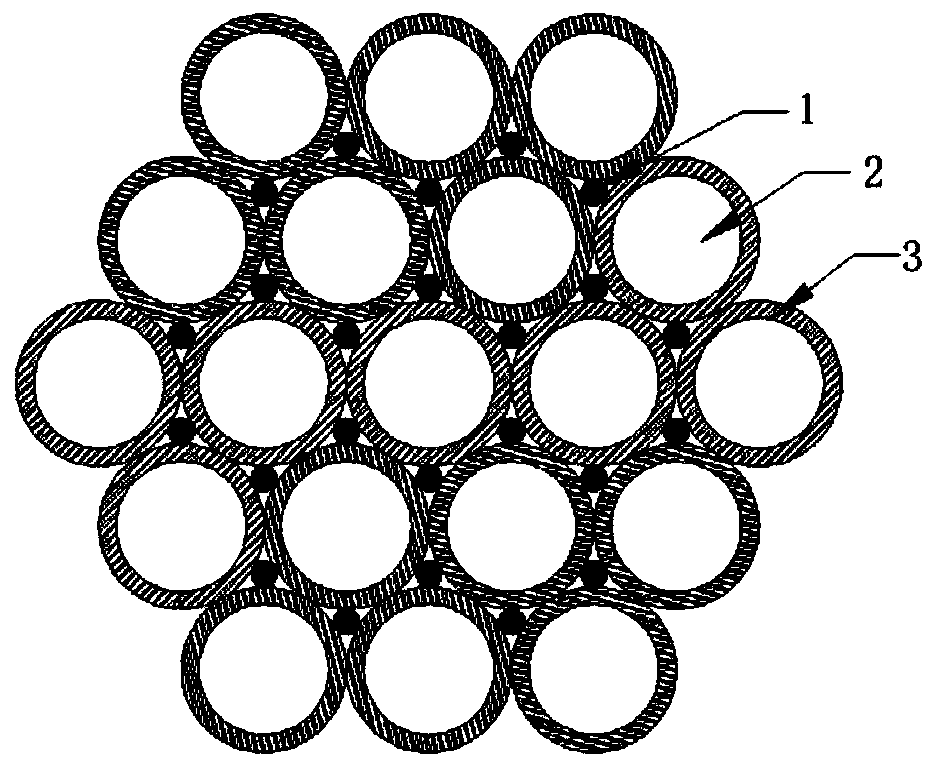
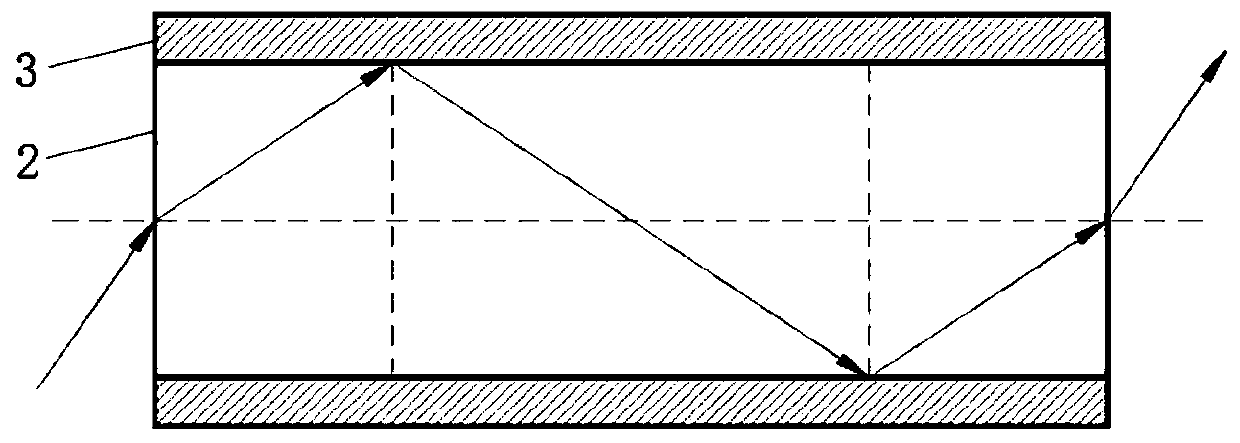
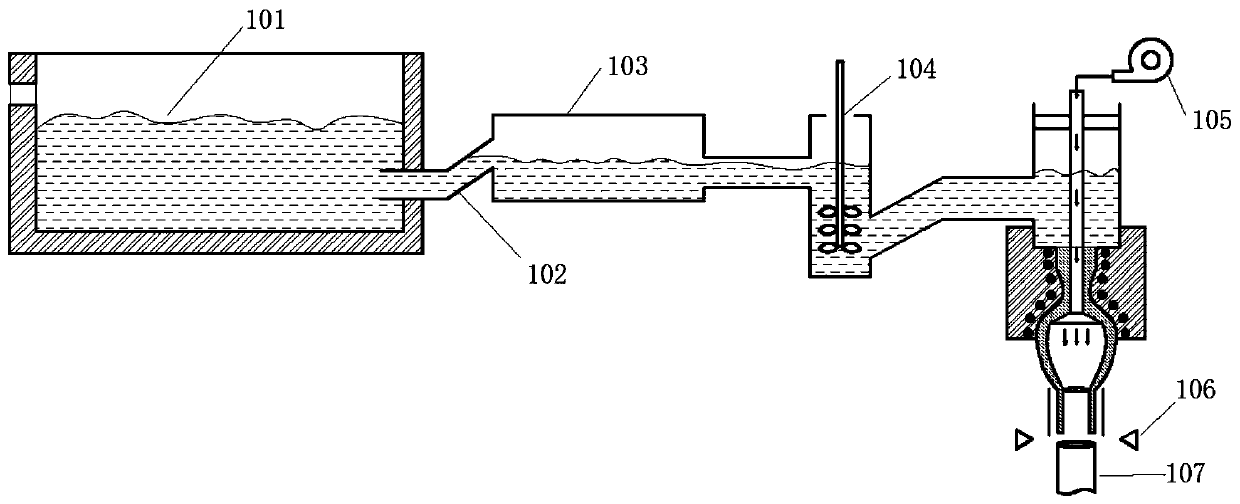
Optical fiber skin layer glass for optical fiber image transmission element and mechanical pipe-drawing forming method of optical fiber skin layer glass
An optical fiber cortex and optical fiber image transmission technology, which is applied in glass forming, glass forming, cladding optical fibers, etc., can solve the problem of the outer diameter dimensional accuracy and wall thickness dimensional accuracy of the cortical glass tube. It can improve the anti-devitrification performance and high temperature viscosity characteristics, increase the lower limit of crystallization temperature, and have excellent anti-devitrification performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] (1) Melting of glass: select raw material by table 1 embodiment 1 glass composition, to the oxide compound of variable price element in the glass raw material such as Fe 2 o 3 etc. are strictly controlled, and the finished glass Fe 2 o 3 If the content is less than 1PPm, weigh quartz sand, aluminum hydroxide, boric acid or boric anhydride, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, calcium carbonate, strontium carbonate, zinc oxide, zirconia, titanium dioxide and antimony trioxide according to the ingredients requirements and mix them evenly , and then melted in the glass melting pool of the electric melting furnace;
[0068](2) Clarification and homogenization: each raw material component is melted at a temperature of 1500° C. for 8 hours. After the raw material is melted into the molten glass, the molten glass flows from the discharge port of the glass melting pool 101 through the upward-inclining feed channel 102 into the clarification tank 103, and control the temper...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The actual composition of the glass refers to Example 2 in Table 1, using the same raw materials and raw material requirements as in Example 1, and adopts melting at 1450°C for 10 hours, clarification and homogenization at 1400°C for 2 hours, and annealing at 580°C. , clarification and annealing process, adopt the test condition identical with embodiment 1, have shown the basic performance of embodiment 2 sample in table 1. (1) The refractive index is 1.52; (2) The average coefficient of linear expansion at 30-300°C is 90×10 -7 / ℃; (3) glass at 10 7.6 The softening temperature at poise is 755°C; (4) The crystallization temperature of the glass is 910°C.
Embodiment 3
[0075] The actual composition of the glass refers to Example 3 in Table 1, using the same raw materials and raw material requirements as in Example 1, and adopts melting at 1600°C for 6 hours, clarification and homogenization at 1300°C for 3 hours, and annealing at 560°C. , clarification and annealing process, adopt the test condition identical with embodiment 1, have shown the basic performance of embodiment 3 sample in table 1. (1) The refractive index is 1.48; (2) The average linear expansion coefficient of 30-300°C is 84×10 -7 / ℃; (3) glass at 10 7.6 The softening temperature at poise is 740°C; (4) the crystallization temperature of glass is 950°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com