Induction and rapid propagation method of salvia chinensis hairy roots
A hairy root and purple ginseng technology, which is applied in the directions of horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as research gaps in the induction and propagation of purple ginseng hairy roots, so as to improve the induction rate, The effect of protecting the ecological environment and rapid induction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1 Screening and optimization of the optimal induction system for hairy roots of purple ginseng
[0042] 1. Experimental method
[0043] 1.1 Effects of different A. rhizogenes strains and explant types on the induction of hairy roots of purple ginseng
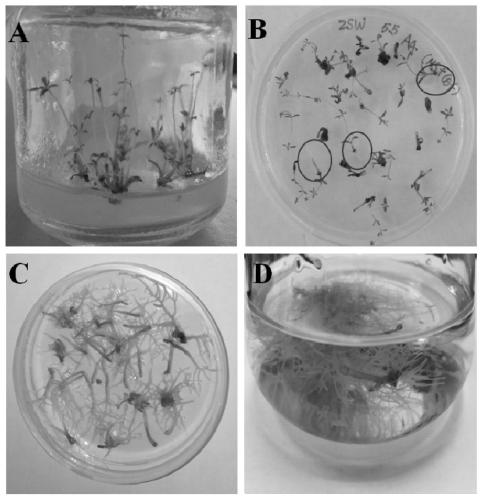
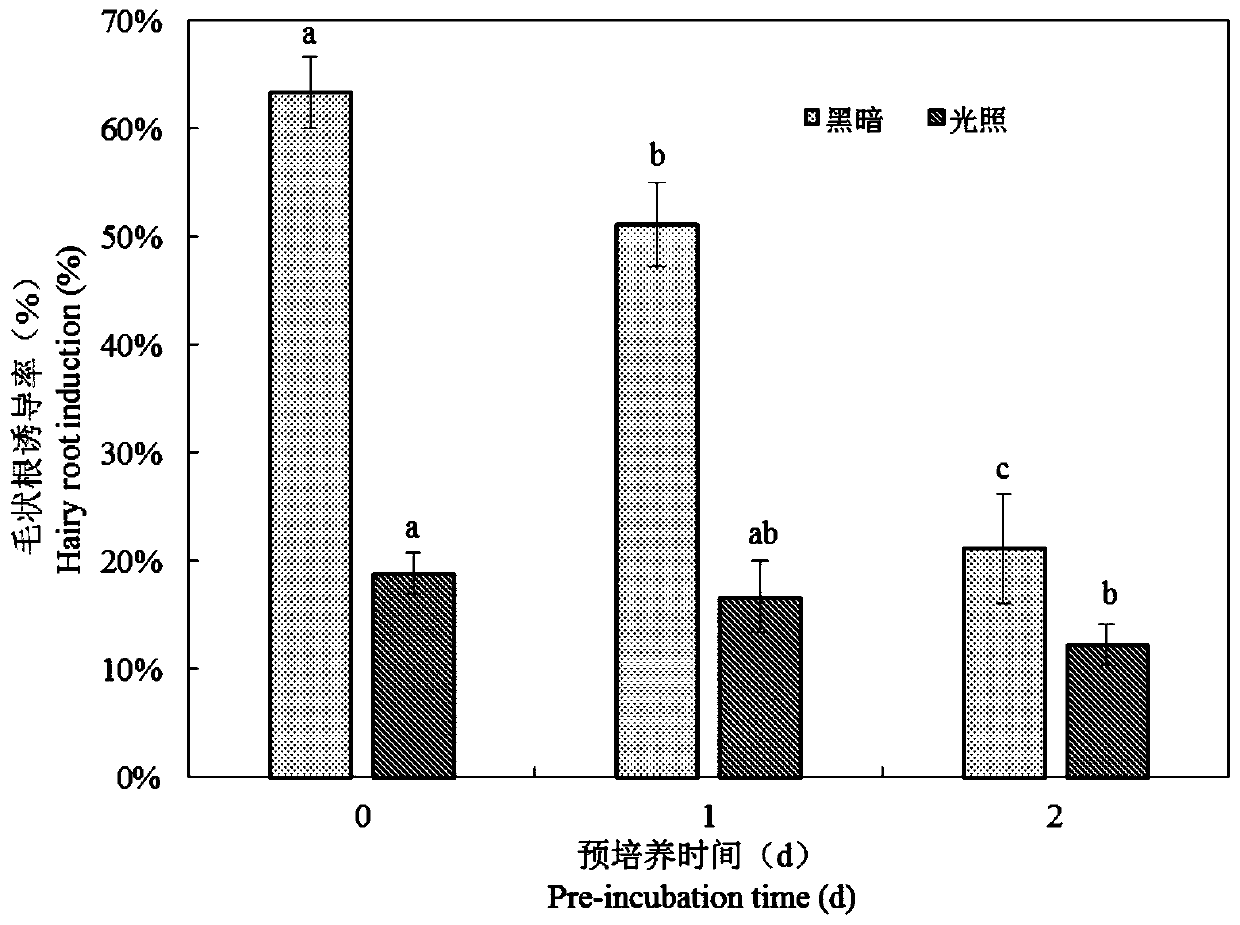
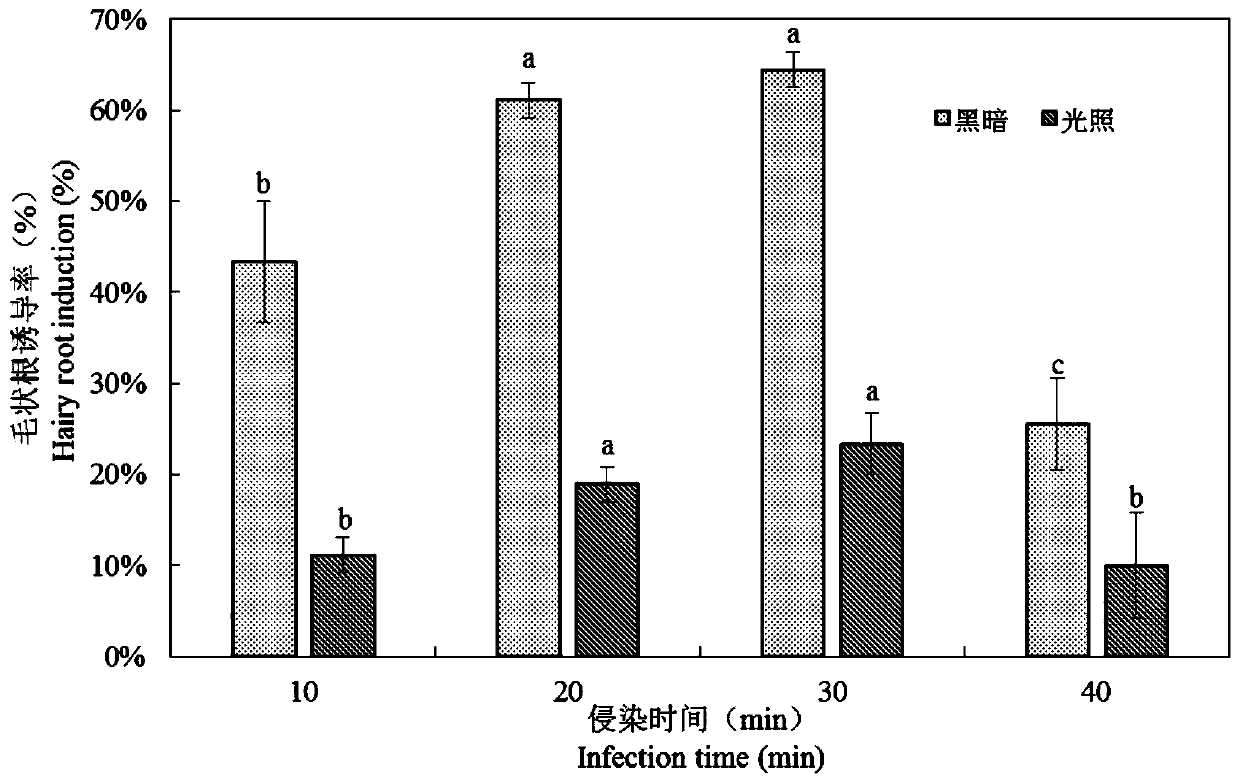
[0044] (1) Obtaining sterile seedlings of purple ginseng tissue culture: Select the nodes, rhizomes and leaves of the young buds of the purple ginseng plant in the current year as explants, shake them in 0.5% sodium hypochlorite for 8 minutes, and then use sterile water to rinse twice, each time 5min times. Then disinfect with 0.1% mercuric chloride for 5 to 8 minutes, and then rinse with sterile water for 4 times, 5 minutes each time. After that, the sterilized explants were evenly spread on the sterilized filter paper, and the residual water on the surface was dried. cm in size, were placed on MS solid medium containing 0.5 mg / L, 1 mg / L and 2 mg / L TDZ, respectively, and placed in a light incubator. About 20d...
experiment example 2
[0067] Experimental Example 2 Molecular detection of hairy roots of purple ginseng induced and propagated by the present invention
[0068] 1. Experimental method
[0069] When A. rhizogenes infects plants to form hairy roots, the rhizogen rol gene in the T-DNA region of the Ri plasmid of A. rhizogenes A4 is transferred into the plant genome, and finally hairy roots are induced. In order to confirm whether the induced roots are hairy roots, in addition to morphological observation and distinction, it is also necessary to perform molecular level detection on the hairy roots to determine whether the rol gene is inserted into the induced hairy roots.
[0070] After the hairy roots induced in Experimental Example 1 grew to a length of 1 to 3 cm, the genomic DNA of 3 randomly selected hairy roots of purple ginseng was extracted using the plant genomic DNA extraction kit of Beijing Qingke Xinye Biotechnology Co., Ltd., The rol genes (rolB and rolC genes) contained in hairy roots we...
experiment example 3
[0086] Experimental Example 3 LC-MS detection of RAs in the hairy roots of purple ginseng induced and propagated by the present invention
[0087] 1. Experimental method
[0088] After the hairy roots of purple ginseng were cultured in MS liquid medium for 60 days, LC-MS was used to detect whether the hairy roots contained RAs.
[0089] Weigh 1 g of the hairy roots dried to constant weight obtained in Experimental Example 1 and place them in a 25 mL conical flask with a stopper, pipette 10 mL of 83% methanol to soak overnight, ultrasonically treat at room temperature for 86 min, and extract 3 times. The solution was transferred and combined into an EP tube, centrifuged at 13,500 × g for 5 min, and the supernatant was transferred to a new EP tube for use. 1 mL of the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm nylon filter for UPLC-MS detection.
[0090] Based on the structural characteristics and mass spectrometry fragmentation rules of RAs, Waters ACQUITY UPLC H Classsystem ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com