Method of electrolyzing anode to leach vanadium in normal temperature saturated oxalic acid solution
A technology of oxalic acid solution and anode electrolysis, applied in the field of electrochemistry, can solve the problems of increasing production costs, increasing production costs, strong corrosion, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing pollution, reducing energy consumption, and simple components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Using vanadium trioxide and ferric oxide as the initial raw materials, they were calcined at 1200°C for 48 hours in a reducing atmosphere to obtain Fe 2 VO 4 .
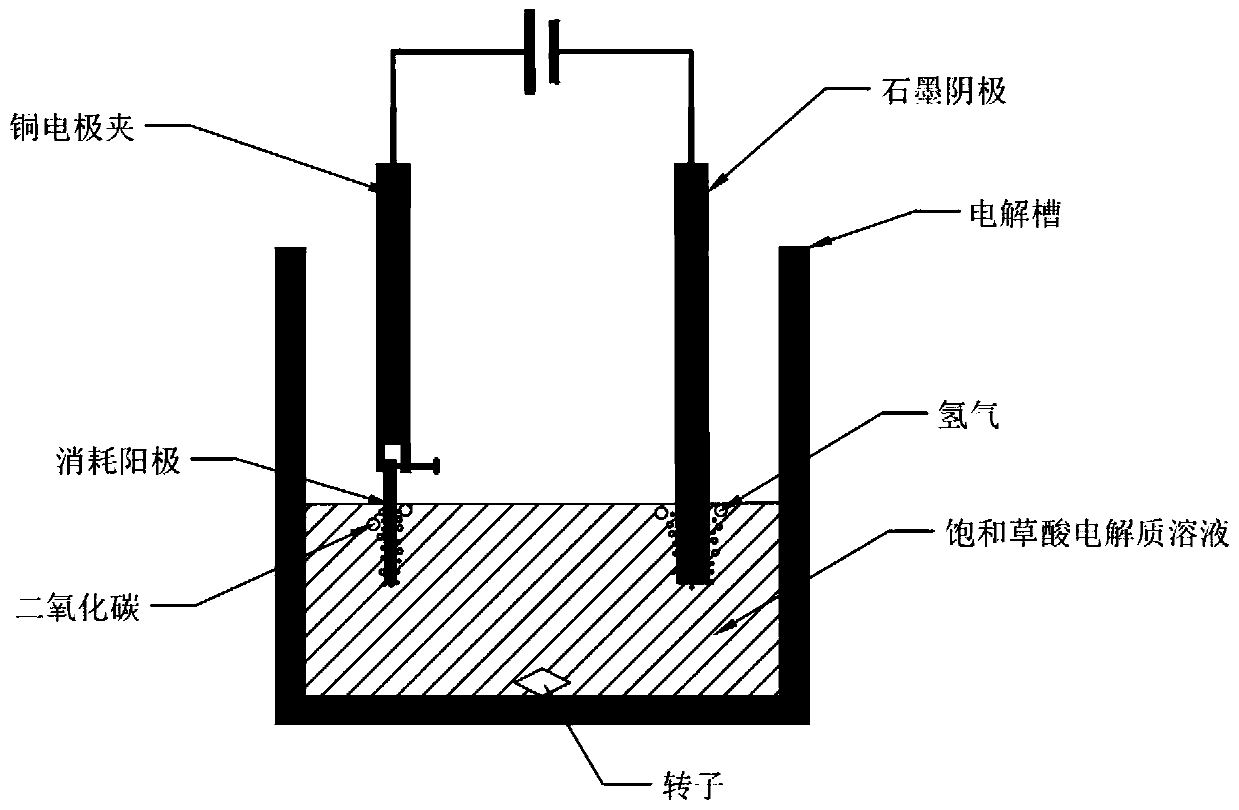
[0033] (2) Using the pure vanadium-iron spinel obtained in step (1) as a raw material to make an anode, the diameter of the anode is 10mm, and the thickness is about 3mm.
[0034] (3) The electrolytic reaction is carried out in an electrolytic cell at normal temperature and pressure. The cathode material of the electrolytic cell is a graphite rod with a diameter of 6mm, the center distance between the anode and the cathode is 5cm, and the electrolytic solution is a saturated oxalic acid solution.
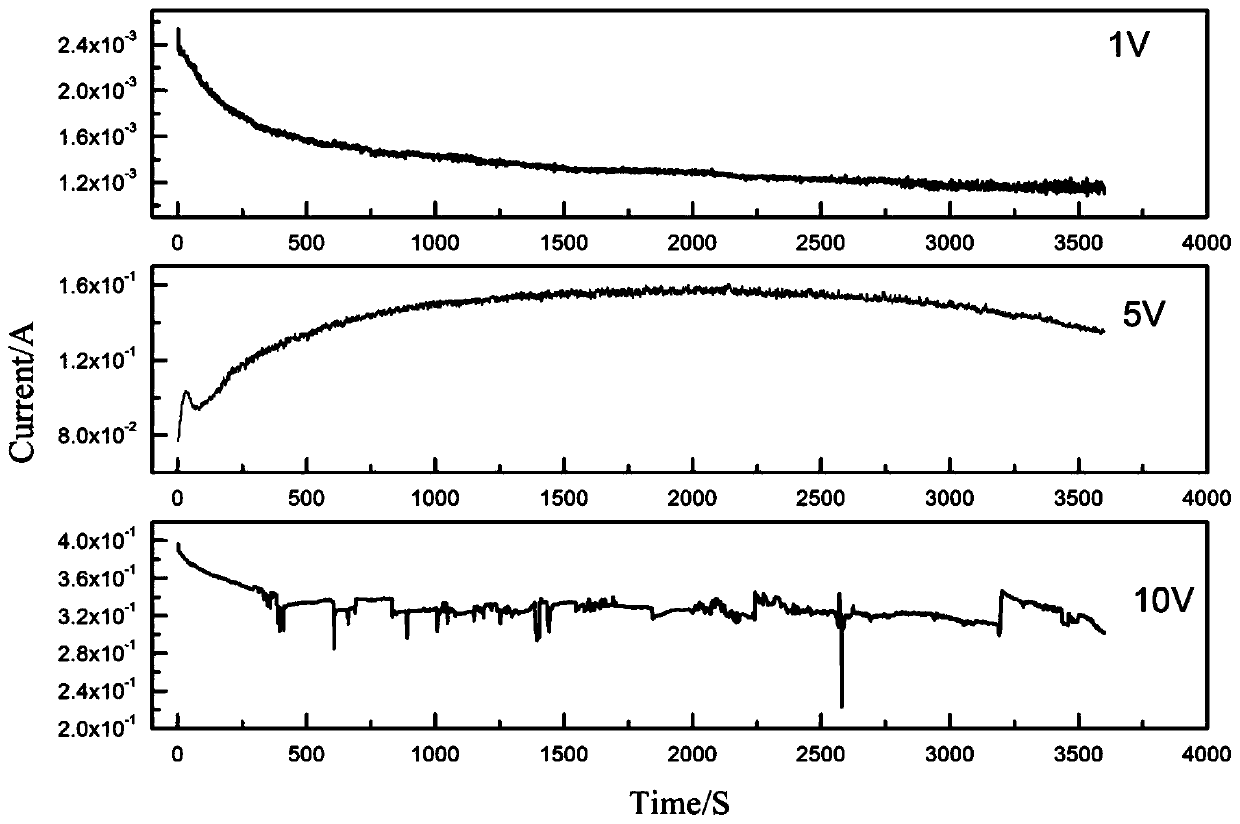
[0035] (4) The cell voltage is selected as 1V, the electromagnetic stirring speed is 500r / min, the electrolysis temperature is room temperature, and the electrolysis reaction is selected as 1h.
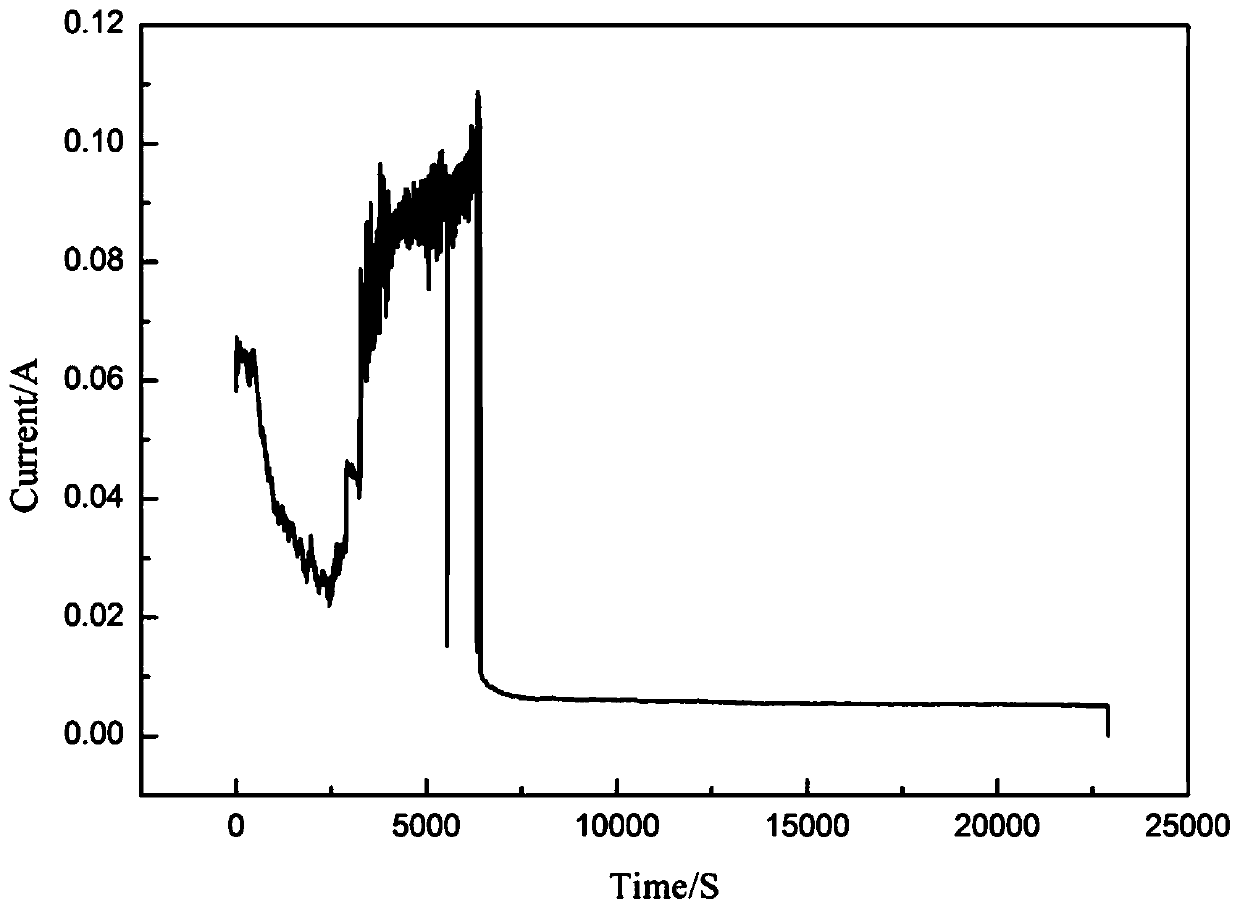
[0036] (5) After the electrolysis reaction, solid-liquid separation was carried out, and finally the concentration o...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Using vanadium trioxide and ferric oxide as the initial raw materials, they were calcined at 1200°C for 48 hours in a reducing atmosphere to obtain Fe 2 VO 4 .
[0039] (2) Using the pure vanadium-iron spinel obtained in step (1) as a raw material to make an anode, the diameter of the anode is 10mm, and the thickness is about 3mm.
[0040] (3) The electrolytic reaction is carried out in an electrolytic cell at normal temperature and pressure. The cathode material of the electrolytic cell is a graphite rod with a diameter of 6mm, the center distance between the anode and the cathode is 5cm, and the electrolytic solution is a saturated oxalic acid solution.
[0041] (4) The cell voltage is selected as 5V, the electromagnetic stirring speed is 500r / min, the electrolysis temperature is room temperature, and the electrolysis reaction is selected as 1h.
[0042] (5) After the electrolysis reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and the concentratio...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Using vanadium trioxide and ferric oxide as the initial raw materials, they were calcined at 1200°C for 48 hours in a reducing atmosphere to obtain Fe 2 VO 4 .
[0045] (2) Using the pure vanadium-iron spinel obtained in step (1) as a raw material to make an anode, the diameter of the anode is 10mm, and the thickness is about 3mm.
[0046] (3) The electrolytic reaction is carried out in an electrolytic cell at normal temperature and pressure. The cathode material of the electrolytic cell is a graphite rod with a diameter of 6mm, the center distance between the anode and the cathode is 5cm, and the electrolytic solution is a saturated oxalic acid solution.
[0047] (4) The cell voltage is selected as 10V, the electromagnetic stirring speed is 500r / min, the electrolysis temperature is room temperature, and the electrolysis reaction is selected as 1h.
[0048] (5) After the electrolysis reaction is finished, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and finally the con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com