Method for separating plant antimicrobial peptide, plant antimicrobial peptide and application of plant antimicrobial peptide
A plant antibacterial peptide and antibacterial peptide technology, which is applied in the field of plant antibacterial peptides and plant antibacterial peptides, can solve the problems of unsystematic research on the applicability of antibacterial peptides, the need for further development of plant antibacterial peptides, and the reduction of antibacterial activity, so as to save cumbersome Process, reduced application, effect of improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
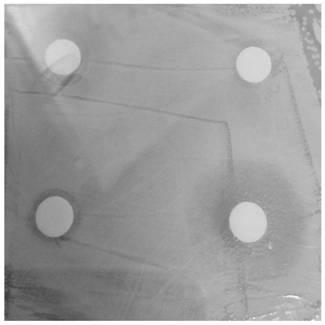
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] A production method for directly extracting antimicrobial peptides from black sesame seeds by using ultrasonic waves:
[0065] 1. Weigh 100g black sesame seeds;
[0066] 2. Add 500 mL of 7% acetic acid solution 5 times the volume of black sesame to black sesame;
[0067] 3. The black sesame and acetic acid solution are sonicated in an ultrasonic generator with a power of 200W-300W and a frequency of 40kHz, and the extraction time is 20min, and the extract is filtered;
[0068] 4. Centrifuge the extract at 4°C for 5 minutes at 10000 rpm, discard the precipitate, so as to harvest the supernatant;
[0069] 5. Heat the extract in a water bath at 80°C for 10 minutes, and then cool to room temperature;
[0070] 6. Dialyze the supernatant for 48 hours and concentrate to obtain a reverse phase chromatography sample;
[0071] 7. Subjecting the reverse phase chromatography sample to reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography, wherein the reverse phase chromatography column is a rev...
Embodiment 2
[0075] A production method for directly extracting antimicrobial peptides from black sesame seeds by using ultrasonic waves:
[0076] 1. Weigh 100g black sesame seeds;
[0077] 2. Add 1000 mL of 5% acetic acid solution 10 times the volume of black sesame to black sesame;
[0078] 3. The black sesame and acetic acid solution are sonicated in an ultrasonic generator with a power of 200W-300W and a frequency of 40kHz, the extraction time is 35min, and the extract is filtered;
[0079] 4. Centrifuge the extract at 4°C for 15 min at 8000 rpm, discard the precipitate, so as to harvest the supernatant;
[0080] 5. Heat the extract in a 60°C water bath for 30 minutes, and then cool to room temperature;
[0081] 6. Dialyze the supernatant for 72 hours and concentrate to obtain a reverse phase chromatography sample;
[0082] 7. Subjecting the reverse phase chromatography sample to reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography, wherein the reverse phase chromatography column is a reverse phas...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A production method for directly extracting antimicrobial peptides from black sesame seeds by using ultrasonic waves:
[0087] 1. Weigh 100g black sesame seeds;
[0088] 2. Add 500 mL of 1% acetic acid solution 20 times the volume of black sesame in the black sesame;
[0089] 3. The black sesame and acetic acid solution are sonicated in an ultrasonic generator with a power of 200W-300W and a frequency of 40kHz, and the extraction time is 10min, and the extract is filtered;
[0090] 4. Centrifuge the extract at 12000 rpm at 4°C for 10 min, discard the precipitate, in order to harvest the supernatant;
[0091] 5. Heat the extract in a water bath at 100°C for 15 minutes, and then cool to room temperature;
[0092] 6. Dialyze the supernatant for 24 hours and concentrate to obtain a reverse phase chromatography sample;
[0093] 7. Subjecting the reverse phase chromatography sample to reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography, wherein the reverse phase chromatography column is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com