CAR-T cell containing unstable structural domain, preparation method thereof and method for adjusting functions of CAR-T cell
A technology for stabilizing structures and cells, applied in the fields of immunology and cell biology, can solve problems such as difficulty in application, lack of adjustability, and inability to precisely regulate the expression level of cytokines in the time of cell therapy, and achieve steps that are easy to operate and process little effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The present invention also includes a method for preparing CAR-T cells containing an unstable domain, comprising the following steps:
[0031] ①The gene encoding the unstable domain is connected to the end of the CAR gene to construct a fusion gene; specifically, the gene encoding the unstable domain is placed at the 3' end of the CAR gene and connected to form a fusion gene;
[0032] ② Insert the fusion gene clone obtained in step ① into the lentiviral plasmid;
[0033] ③Packing the virus and preparing the lentivirus carrying the fusion gene;
[0034] ④ Infect T cells with the lentivirus obtained in step ③ and amplify them.
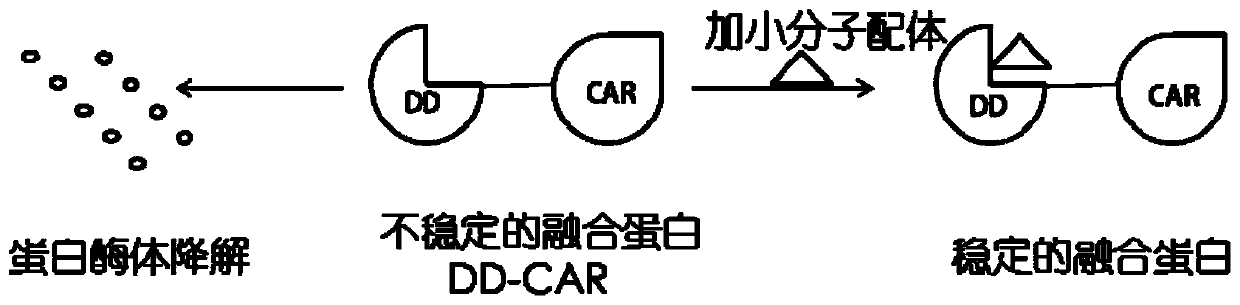
[0035] The invention also discloses a method for regulating the function of CAR-T cells containing an unstable domain, adding a small molecule compound corresponding to the unstable domain; the amount of the small molecule compound added is 0-1000 μmol / L. Such as figure 1 as shown, figure 1 The triangle in is a small molecular compound, which ...
Embodiment 1
[0045] Example 1 Preparation of DHFR-CD19CAR-T cells
[0046] 1. Whole-gene synthesis of the fusion gene of DHFR and CD19CAR
[0047] The unstable domain DD selects the unstable domain of dihydrofolate reductase (Dihydrofolate reductase), referred to as DHFR; its small molecule compound ligand is trimethoprim (TMP)
[0048] The sequence of DHFR is SED ID NO: 1, the transmembrane region, co-stimulatory signal region, and CD3ζ sequence of CD19CAR are SED ID NO: 2, according to figure 2 The positional relationship of the ScFV sequence, the transmembrane region, the co-stimulatory signal region, and the CD3ζ sequence were connected to construct a CD19CAR, whose sequence is SEQ ID NO: 3;
[0049] The fusion gene of DHFR and CD19CAR is synthesized from the entire gene, so that the upstream restriction site of the fusion gene is XbaI, and the downstream restriction site is BamHI; the sequence of the fusion gene (DHFR-CD19CAR) is SEQ ID NO: 4; in this fusion gene, The DHFR encoding...
Embodiment 2
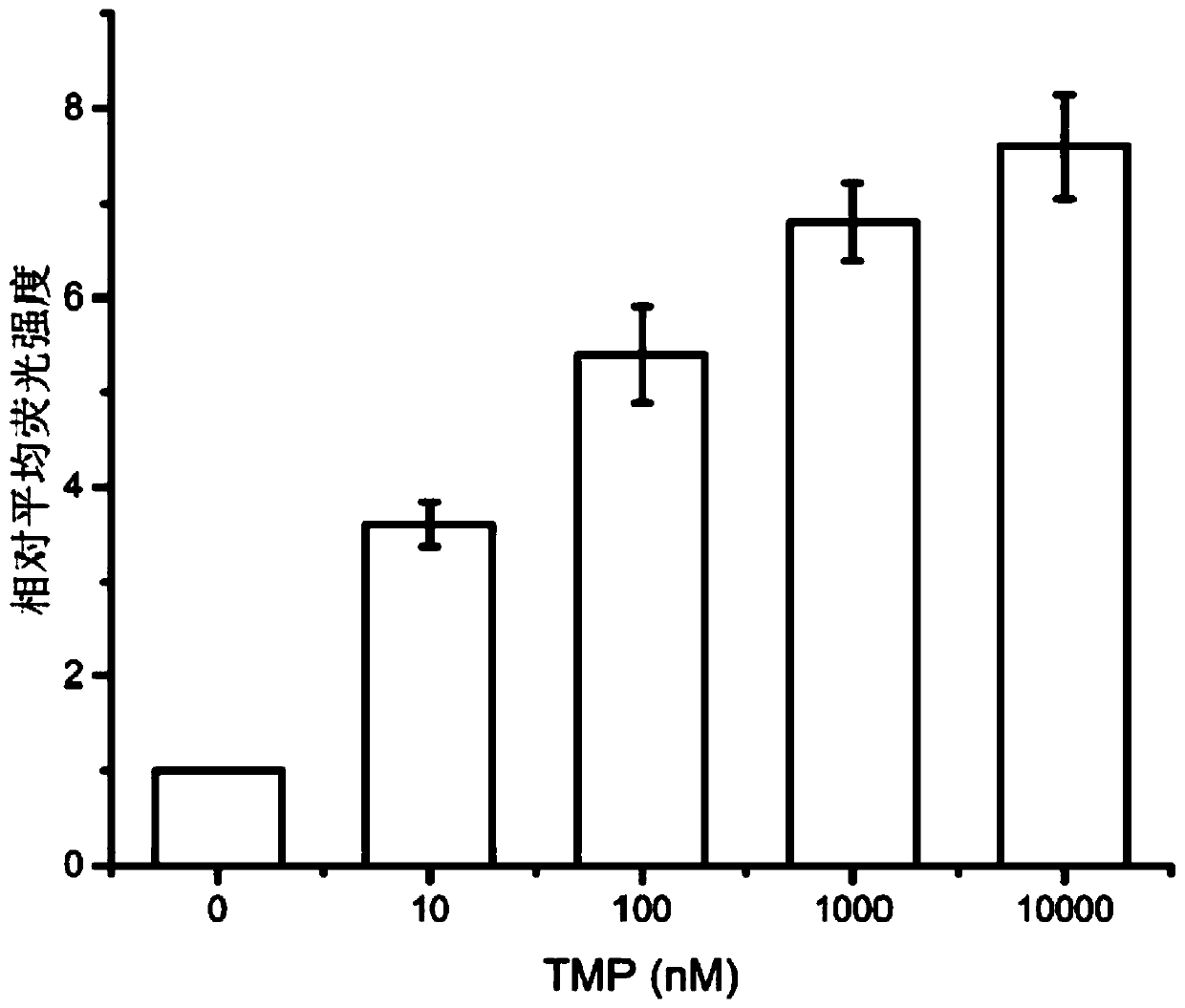
[0100] Using TMP to regulate the number of CAR molecules on the membrane surface of DHFR-CD19CAR-T cells prepared in Example 1
[0101] Take the DHFR-CD19CAR-T cells constructed in Example 1, place them in a 24-well plate, and add DHFR ligand-trimethoprim to the final concentrations of 0nM and 10nM, respectively, for 5*10^5 CAR-T cells per well , 100nM, 1000nM, 10000nM; 3 parallels in each group; cultivated for 24h;
[0102] Take biotin-labeled CD19 protein (Biotinylated Human CD19, Fc Tag, ultrasensitivity (primary amine labeling), ACROBiosystems, Cat. No. CD9-H8259), FITC-labeled streptavidin (FITC-SA, Biolegend, Cat. No.405201), perform flow cytometric detection according to the method in the corresponding instructions, and measure the average fluorescence intensity of the CAR-positive cell population. The more CAR molecules on the membrane surface, the stronger the fluorescence intensity.
[0103] Such as image 3 As shown, the average fluorescence intensity increases wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com