Microalgae light-harvesting protein NoHLR1 gene and application thereof
A light protein and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Preparation of Nannochloropsis mutants knocked out of light-harvesting protein NoHLR1
[0047] 1. Bacterial strains and their cultivation: Nannochloropsis grows in F2 solid medium and F2 liquid medium.
[0048] 2. The resistance gene tag method was used to construct a saturated mutant library of Nannochloropsis, using hygromycin resistance tags, bleomycin resistance tags, etc. According to molecular biology techniques familiar to those skilled in the art, the resistance tag is amplified, and the fragment containing the screening marker is cut with an appropriate restriction endonuclease, and Nannochloropsis is transformed.
[0049] 3. Electrotransform Nannochloropsis cells, and introduce the fragment containing the resistance tag into the cells. That is, 0.5 micrograms of linearized plasmid and 6 million algal cells were placed in a 0.2cm electroporation cell (Bio-Rad), and 2.2kV pulsed (Bio-Rad electroporation instrument, 50μF).
[0050] 4. According to the...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Cloning of the light-harvesting protein NoHLR1 gene
[0056] 1. Extract the total RNA of Nannochloropsis and reverse transcribe to obtain the first strand of cDNA.
[0057] 2. Using the first strand of cDNA as a template and NoHLR1-F and NoHLR1-R as primers, the cDNA sequence of NoHLR1 gene was obtained by PCR amplification reaction.
[0058] The primer sequences are as follows:
[0059] NoHLR1-F: 5'-GACCTCTGAAGTTCCCATATGATGAAAGTCACCGCCGTGCTCT-3'
[0060] NoHLR1-R: 5'-CTGGGATCCCCCGGGCATATGTTAAGAGAAAAGGGGAACACCG-3'
[0061] Use 2×TaqPCCRMasterMix (Takara) for PCR amplification, the reaction system is: 2 μL of cDNA template, 1 μL of primers F and R (10 μmol / L), 25 μL of 2×PCRMasterMix, add ddH 2 0 to 50 μL.
[0062] The PCR amplification program was: denaturation at 94°C for 3 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 55°C for 90 s, extension at 72°C for 2 min, a total of 35 cycles; and finally extension at 72°C for 10 min.
[0063] 3. After the ampl...
Embodiment 3
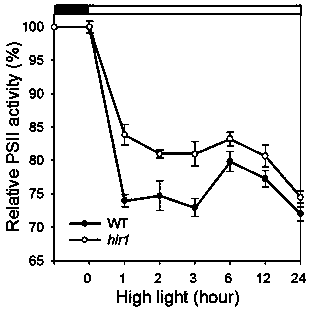
[0065] Expression analysis of embodiment 3 NoHLR1 gene when subjected to high light stress
[0066] Fluorescent quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression of NoHLR1 gene in Nannochloropsis after high light treatment.
[0067] High-light treatment: Dark-adapt the algae cells overnight, then place them in a light incubator for high-light treatment, and collect samples continuously for 48 hours.
[0068] According to the NoHLR1 gene sequence, the following fluorescent quantitative PCR detection primers were designed:
[0069] NoHLR1-QF: 5'-GGACCAGGTCGCCAACCTCAAAT-3'
[0070] NoHLR1-QR: 5'-TCGGACTTGCCCTTGCTAAA-3'.
[0071] Actin-F: GCCGTTATTGGATGGATATG
[0072] Actin-R: ACAACAACTCTCCTTCACA
[0073] Actin was used as an internal reference gene. QuantStudio™qPCR fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument was used to perform fluorescent quantitative PCR, and the reaction program was: 95°C pre-denaturation for 30s; 94°C for 5s, 60°C for 20s, 72°C for 20s, and 45 cycles. Aft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com