Preparation methods for high capacity biomass hard carbon anode material of sodium ion battery
A technology for sodium ion batteries and negative electrode materials, which is applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, electrochemical generators, etc., can solve problems such as being unsuitable for large-scale production, difficult to guarantee stability, and long process processing, and achieve a suitable scale Chemical production, good morphology and pore structure, mild and controllable preparation conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
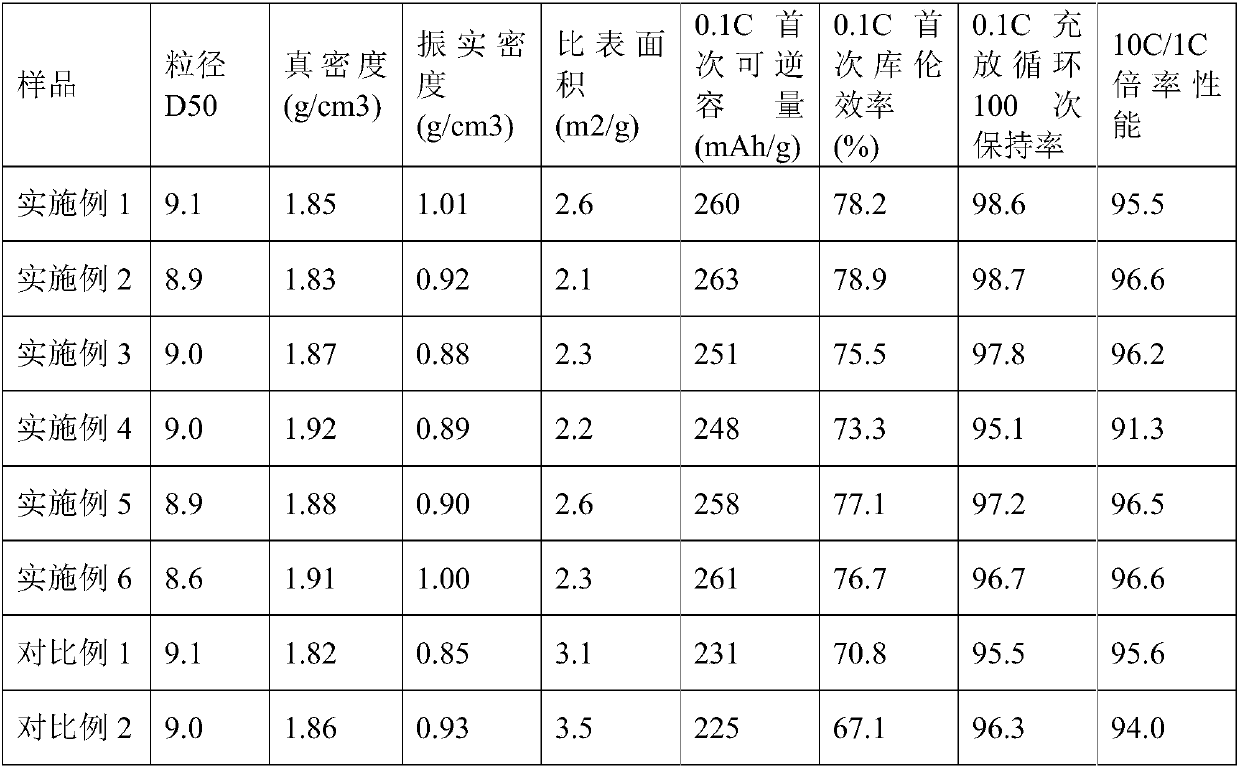
Embodiment 1
[0032] 1. Take 1000g of rice starch crushed and sieved to a volume average particle size of 10 μm;
[0033] 2. Feed rice starch and 150g of ammonium chloride into a stirring mixer and mix for 10 minutes at a speed of 1000r / min to obtain a mixture; put the obtained mixture in a blast drying oven and dehydrate and solidify at 150°C for 6 hours to obtain The cured rice starch precursor;
[0034] 3. Add deionized water and 100 g of phosphoric acid to the cured rice starch precursor, and prepare the solidified material into a slurry with a solid content of 50% in a high-speed mixing mixer, and then place it in a blast drying oven at 150 ℃ drying to completely remove water, obtain the modified rice starch precursor after cooling;
[0035] 4. Put the modified rice starch precursor into the pit furnace and raise the temperature at 2°C / min to 600°C under the protection of nitrogen for pre-carbonization for 1 hour. After cooling down to room temperature and discharging, use jet milling...
Embodiment 2
[0038] 1. Take 1000g of rice starch crushed and sieved to a volume average particle size of 10 μm;
[0039] 2. Feed rice starch and 200g of ammonium chloride into a stirring mixer and mix at 1000r / min for 10 minutes to obtain a mixture; react the obtained mixture in a blast drying oven at 150°C for 6 hours to obtain solidified Rice starch precursor;
[0040] 3. Add deionized water and 100 g of phosphoric acid to the cured rice starch precursor, and prepare the solidified material into a slurry with a solid content of 50% in a high-speed mixing mixer, and then place it in a blast drying oven at 150 ℃ drying to completely remove water, obtain the modified rice starch precursor after cooling;
[0041] 4. Put the modified rice starch precursor into the pit furnace and raise the temperature at 2°C / min to 600°C under the protection of nitrogen for pre-carbonization for 1 hour. After cooling down to room temperature and discharging, use jet milling to adjust the particle size to 9 μ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] 1. Take 1000g of rice starch crushed and sieved to a volume average particle size of 10 μm;
[0045]2. Feed rice starch and 150g of ammonium chloride into a stirring mixer and mix at 1000r / min for 10 minutes to obtain a mixture; react the obtained mixture in a blast drying oven at 150°C for 6 hours to obtain cured rice starch precursor;
[0046] 3. Add deionized water and 50 g of phosphoric acid to the cured rice starch precursor, and prepare the solidified product into a slurry with a solid content of 50% in a high-speed mixer, and then place it in a blast drying oven at 150 ℃ drying to completely remove water, obtain the modified rice starch precursor after cooling;
[0047] 4. Put the modified rice starch precursor into the pit furnace and raise the temperature at 2°C / min to 600°C under the protection of nitrogen for pre-carbonization for 1 hour. After cooling down to room temperature and discharging, use jet milling to adjust the particle size to 9 μm to obtain Pr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com