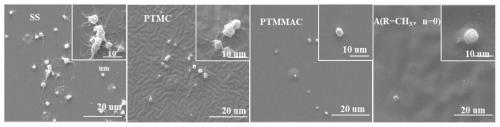
Modified polycarbonate with high anticoagulant activity
A polycarbonate, blood-based technology, applied in the field of polycarbonate modification, can solve the problems of inability to provide reaction sites, low PC grafting rate, unsatisfactory, etc., to achieve improved anticoagulant ability, wide derivatization performance, Research Potential for High Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
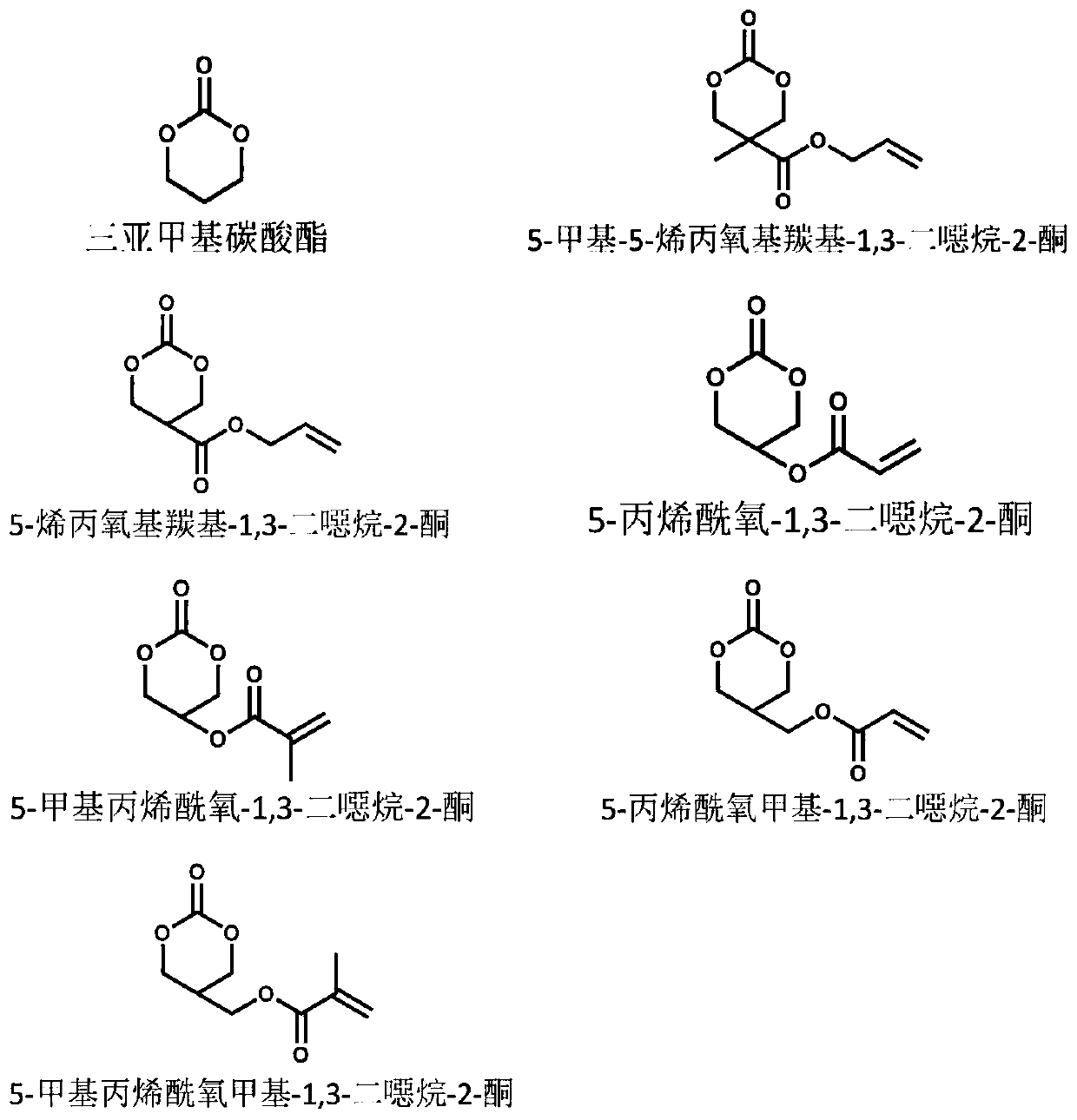
[0016] a. Synthesis of 5-methyl-5-allyloxycarbonyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one (MAC)
[0017] 5-Methyl-5-allyloxycarbonyl-1,3-dioxan-2-one (MAC) was synthesized from 2,2-(bis-hydroxymethyl)propionic acid (bis-HPA). This monomer provides functionalizable double bonds to the side chains of the polycarbonate.
[0018] b. Preparation of random copolymers of TMC and MAC
[0019] Weigh a certain amount of TMC and MAC monomer (molar ratio is 3:1) and a clean and dry magnetic stirrer and place it in a special dry single-necked flask sealed with a rubber stopper, and the reaction device is pumped for half an hour with an oil pump After vacuum, dissolve catalyst and initiator respectively in dry n-hexane and dilute, add stannous octoate (4×10 - 4 mol catalyst), n-octanol (2×10 -5 mol initiator) is injected into the reaction device, pull out the syringe, seal it with vacuum ester, continue vacuuming for one hour, stop vacuuming, and seal. Then, the reaction device was placed in an oil bath and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com