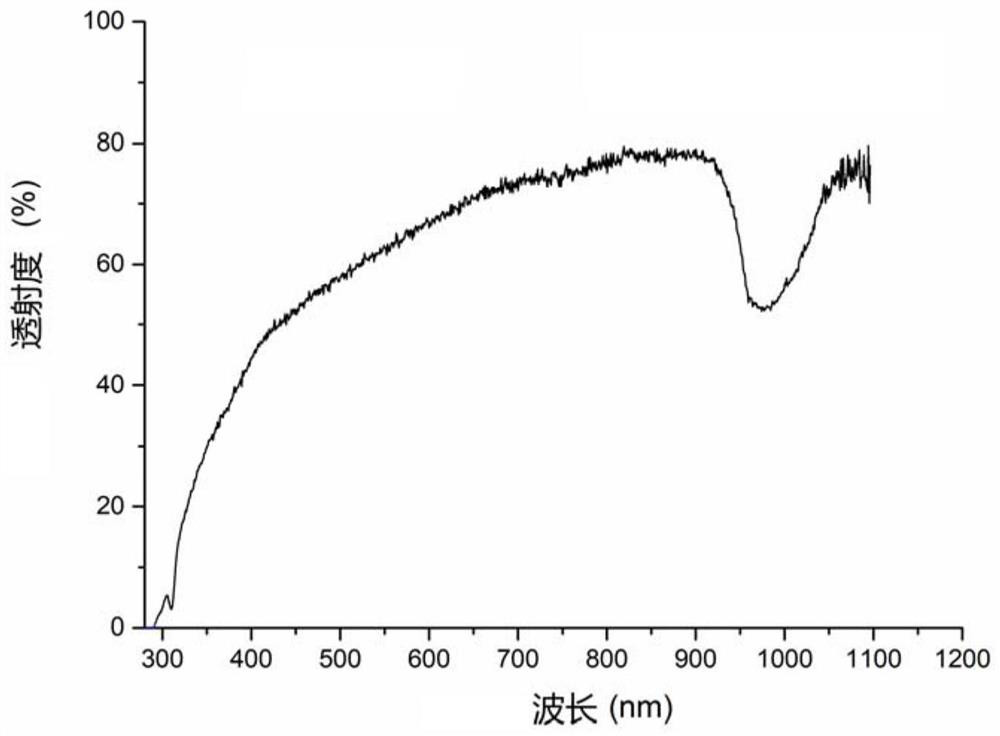
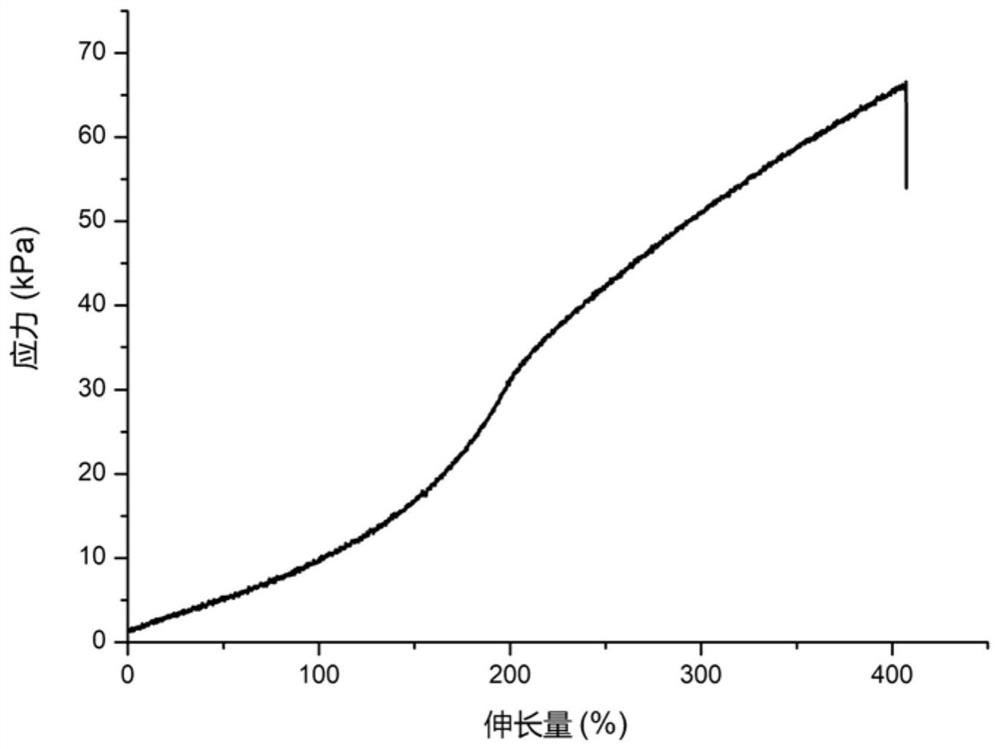
Thixotropic photocurable hydrogel and its preparation method and application
A light-curing and hydrogel technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, can solve the problems of only printing thin walls, the model is difficult to fix, the medium cannot be cured, etc., to increase the transparency, avoid whitening, and improve the degree of mixing. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Mix 2 g of Carbopol940 rheology modifier with 1000 mL of deionized water, neutralize with sodium hydroxide solution during mixing, measure the mixture with a pH meter, stop titration when the mixture is completely mixed and becomes neutral, and obtain mixture A;
[0033] (2) Add 200 g of acrylamide monomer to 700 g of mixture A, mix briefly, add 1.25 g of polyethylene glycol 400 diacrylate, and continue mixing with a mechanical stirrer for 15 minutes to obtain mixture B;
[0034] (3) 0.1g TPO photoinitiator (liquid state, free radical type), drop in 700g mixture B, use mechanical stirrer to stir 2 hours under the dark condition, the gained mixture is standby after vacuum defoaming under the air pressure 250Pa;
[0035] (4) Take out the printed container, and use a 405nm, 100w near-ultraviolet light source to irradiate for 3 minutes at a distance of 5cm for curing to obtain a thixotropic photocurable hydrogel.
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Mix 0.5g Carbopol940 rheology modifier with 1000mL deionized water, use sodium hydroxide solution to neutralize during mixing, use pH meter to measure the mixture, stop titration when the mixture is completely mixed and appears neutral, and obtain mixture A;
[0038] (2) Add 250 g of acrylamide monomer to 1000 g of mixture A, mix briefly, add 1.25 g of polyethylene glycol 400 diacrylate, and continue mixing with a mechanical stirrer for 15 minutes to obtain mixture B;
[0039] (3) 0.5g TPO photoinitiator (liquid state, free radical type), drop in 1000g mixture B, use mechanical stirrer to stir 2 hours under dark condition, the gained mixture is standby after vacuum defoaming under the air pressure 0.5Pa;
[0040] (4) Take out the printed container and irradiate it with 460nm, 100w near-ultraviolet light at a distance of 5cm for 1 minute for curing to obtain a thixotropic photocurable hydrogel.
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Mix 1 g of Carbopol940 rheology modifier with 1000 mL of deionized water, neutralize with sodium hydroxide solution during mixing, measure the mixture with a pH meter, stop titration when the mixture is completely mixed and becomes neutral, and obtain mixture A;
[0043] (2) Add 225 g of acrylamide monomer to 905 g of mixture A, mix briefly, add 1.25 g of polyethylene glycol 400 diacrylate, and continue mixing with a mechanical stirrer for 15 minutes to obtain mixture B;
[0044] (3) 0.2g TPO photoinitiator (liquid state, free radical type), drop in 500g mixture B, use mechanical stirrer to stir 5 hours under the dark condition, the vacuum defoaming of gained mixture air pressure 500Pa is standby after defoaming;
[0045](4) Take out the printed container and irradiate it with 350nm, 80w ultraviolet light at a distance of 5cm for 5 minutes for curing to obtain a thixotropic photocurable hydrogel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com