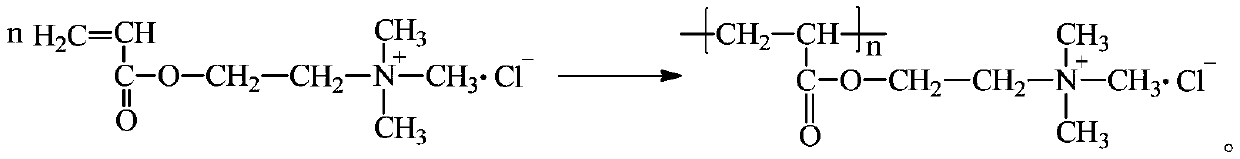
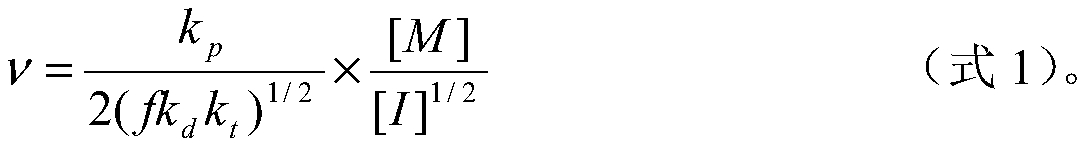Preparation method of PDAC with serialized relative molecular mass and high monomer conversion rate
A technology based on relative molecular weight and monomer conversion rate, which is applied in the field of preparation of water-soluble cationic polymer compounds, can solve the problems that the exothermic heat of the system cannot be dissipated in time, the characteristic viscosity of the product PDAC is low, and the polymerization reaction rate is not stable, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] In the first step, a monomer aqueous solution containing 75% DAC monomer (in terms of mass fraction, the same below) is added to the polymerization reactor. Under the condition of stirring under nitrogen, the average degree of polymerization is 180, accounting for the monomer mass. Triallylamine hydrochloride homopolymer with a fraction of (5.00±0.01)%, a metal chelating agent tetrasodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid solution with a monomer mass ratio of (0.030±0.005)% and a monomer mass Add distilled water to the initiator solution of azobisisobuimidazoline hydrochloride (VA044) with a ratio of (0.85±0.05)% to obtain a reaction solution with a monomer mass fraction of (30.0±2.0)%;
[0033] In the second step, heat the reaction solution to the initiation temperature (35±2)℃, and heat the polymerization reaction for (3.0±0.5)h;
[0034] In the third step, reheat the reaction system to the polymerization temperature (55±2)℃, keep the polymerization reaction for (3.0±0.5)h, ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In the first step, a monomer aqueous solution containing 80% of the DAC monomer is added to the polymerization reactor. Under the condition of stirring with nitrogen, the average degree of polymerization is 140, accounting for (4.50±0.01)% of the monomer mass fraction. Triallylamine hydrochloride homopolymer, the metal chelating agent disodium edetate solution with a monomer mass ratio of (0.010±0.005)% and a monomer mass ratio of (0.43±0.05)% Add distilled water to the initiator solution of azobisisobuimidazoline hydrochloride (VA044) to obtain a reaction solution with a monomer mass fraction of (35.0±2.0)%;
[0038] In the second step, heat the reaction solution to the initiation temperature (35±2)℃, and heat the polymerization reaction for (3.0±0.5)h;
[0039] In the third step, reheat the reaction system to the polymerization temperature (60±2)℃, keep the polymerization reaction (3.0±0.5)h, and stop heating;
[0040] In the fourth step, the reaction product after the two-...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In the first step, a monomer aqueous solution containing 80% of the DAC monomer is added to the polymerization reactor. Under the condition of stirring with nitrogen, the average degree of polymerization is 60, accounting for (3.20±0.01)% of the monomer mass fraction. Triallylamine hydrochloride homopolymer, the metal chelating agent disodium edetate solution with a monomer mass ratio of (0.010±0.005)% and a monomer mass ratio of (0.25±0.05)% Add distilled water to the initiator solution of azobisisobuimidazoline hydrochloride (VA044) to obtain a reaction solution with a monomer mass fraction of (40.0±2.0)%;
[0043] In the second step, heat the reaction solution to the initiation temperature (35±2)℃, and heat the polymerization reaction for (3.0±0.5)h;
[0044] In the third step, reheat the reaction system to the polymerization temperature (60±2)℃, keep the polymerization reaction (3.0±0.5)h, and stop heating;
[0045] In the fourth step, the reaction product after the two-s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com