Kit for screening of primary open-angle glaucoma
A kit and reagent technology, applied in the field of SNP, can solve the problem of unseen association between glaucoma and RAMP2 gene mutation site
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0032] Embodiment Kit and method of use of the present invention
[0033] All components, content and method of use in the kit of the present invention are as follows:
[0034] 1. PCR amplification reagent (50 people):
[0035] The PCR amplification reagent is used to amplify a DNA sequence where the SNP site is located, and its composition is shown in Table 1.
[0036] Table 1 PCR amplification reagents
[0037] The PCR mixture in Table 1 includes Taq enzymes, dNTPs, magnesium ions and other components required for conventional PCR;
[0038]
[0039] The primer pair information is shown in Table 2.
[0040] Table 2 Primers used in RAMP2 gene amplification
[0041]
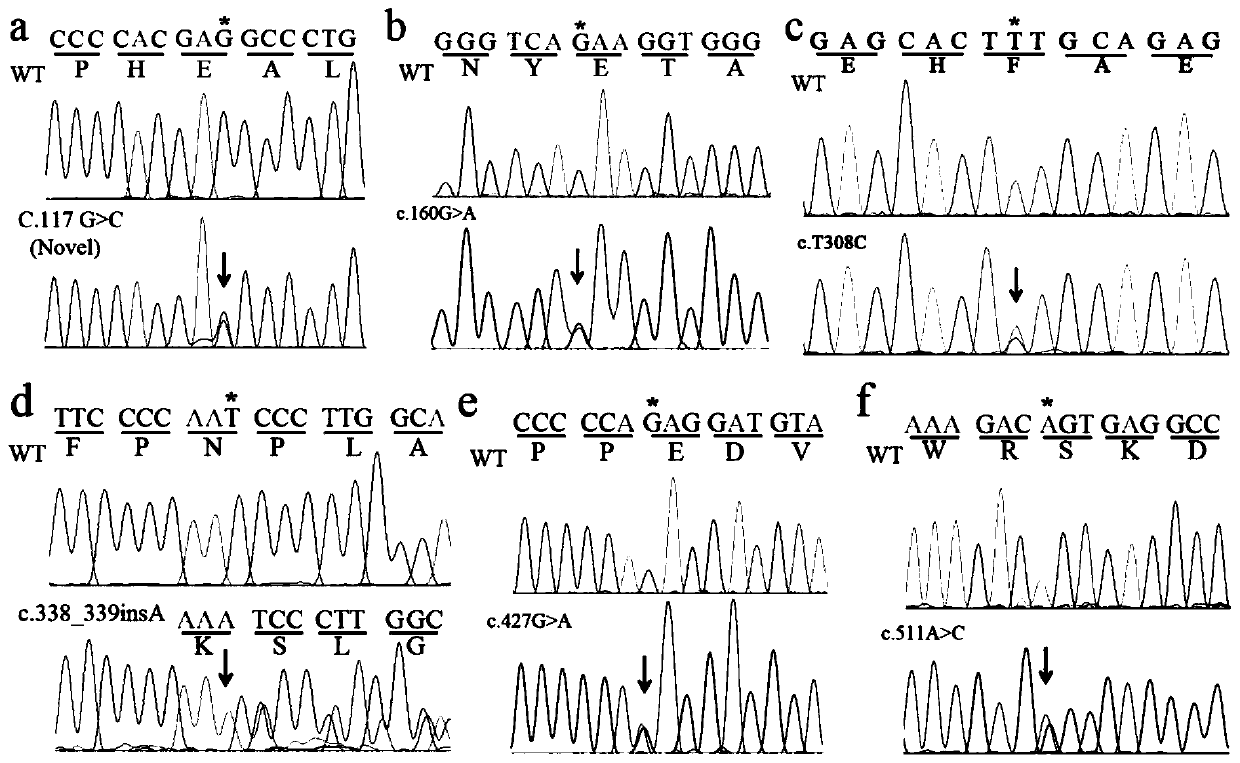
[0042] Attachment: Primer-1F / R primer amplification: Glu39Asp (c.117G>C), Glu54Lys (c.160G>A)
[0043]Primer-2F / R primer amplification: Phe103Ser(c.308T>C), Asn113Lysfs*10(c.338_339insA), Glu143Lys (c.427G>A), Ser171Arg(c.511A>C)
[0044] 2. RAMP2 gene variation typing detection reagent (50 people):
...
experiment example 1
[0076] Screening of experimental example 1 mutation site
[0077] 1. Method
[0078] DNA was extracted from 4763 POAG patients and 10953 healthy controls. Through next-generation sequencing technology, using Illumina TruSeq enrichment capture, HiSeq 2000 / 2500 sequence generator targeted screening of POAG candidate genes, so that the genomic DNA of each individual is enriched in the library. Libraries were sequenced using an automated Illumina HiSeq 2000 / 2500 sequencer. The sequence results were aligned with the sequence of UCSC hg19 (http: / / genome.ucsc.edu / ) using BWA-MEM (https: / / github.com / lh3 / bwa). SNPs and Indels were detected by using two databases, Samtools (http: / / samtools.sourceforge.net / ) and freebayes (https: / / github.com / ekg / freebayes). Based on the information from the RefSeq database, we used the Annovar (http: / / annovar.openbioinformatics.org / en / latest / ) database to classify SNVs into different functional categories based on their genetic location and expected i...
experiment example 2
[0083] Experimental example 2 The specificity test of the kit of the present invention for RAMP2 genotyping detection
[0084] 1. Method
[0085] The mutation sample DNA involved in Table 2 in Experimental Example 1 and the DNA of 20 healthy subjects were used as experimental materials, and the kits in the examples were used to perform detection according to the above-mentioned experimental method.
[0086] 1) DNA extraction
[0087] Take 2ml of whole blood (EDTA anticoagulated) from the patient, and extract its genomic DNA.
[0088] 2) Amplify the DNA fragment containing the detected SNP site by PCR, and the PCR amplification system of each mutation site is as follows:
[0089]
[0090]
[0091] Reaction conditions:
[0092]
[0093] PCR product detection:
[0094] Use 2% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the PCR product, observe the effect of the PCR reaction, and determine the amount of it added as a template in subsequent reactions.
[0095] 3) Sanpshot t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com