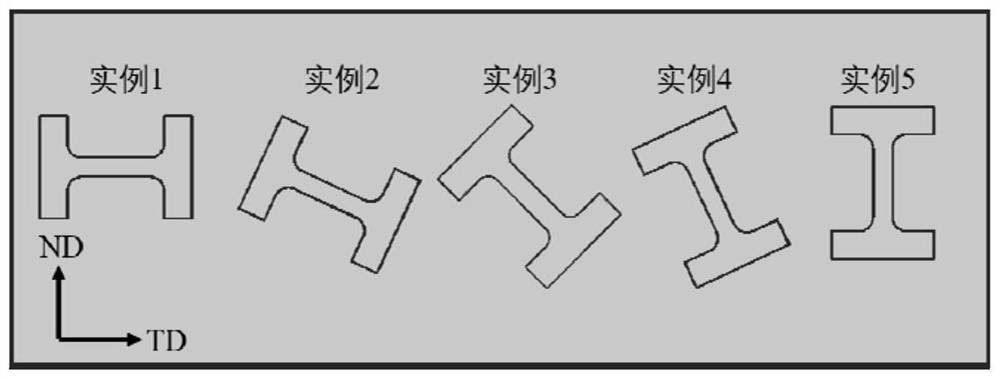
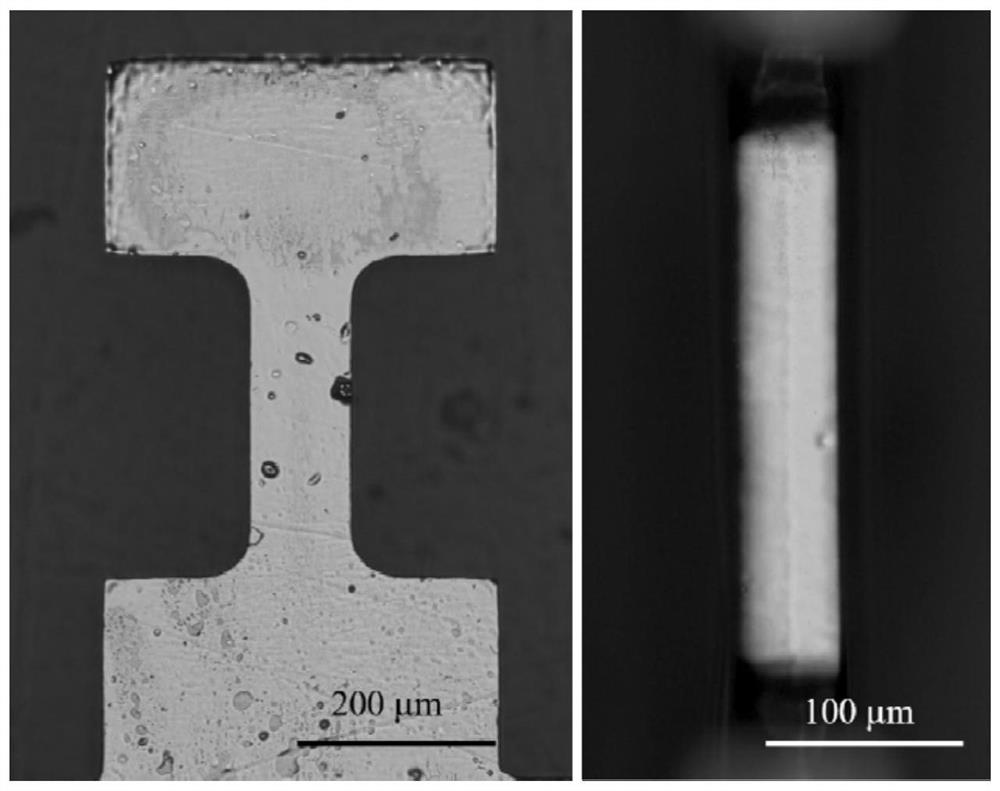
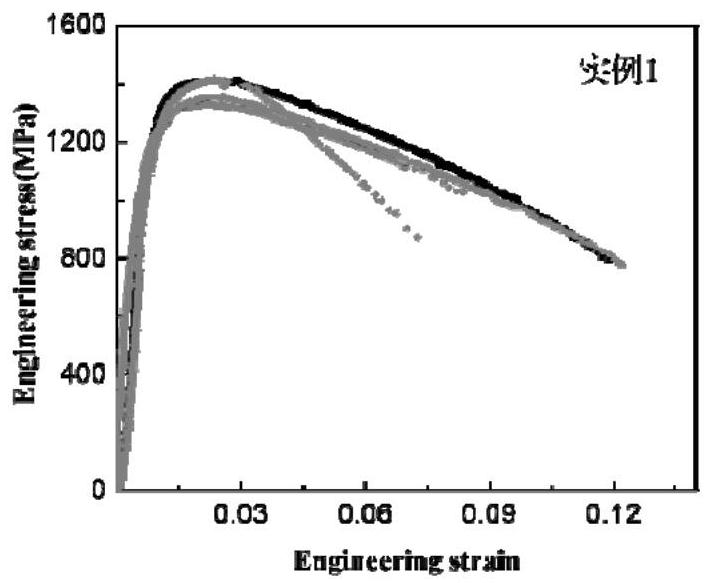
A method for preparing multi-oriented mesoscopic tensile samples based on femtosecond laser processing
A femtosecond laser processing and sample preparation technology, applied in the field of multi-oriented mesoscopic tensile sample preparation, can solve the problem that the intrinsic properties of the material cannot be well reflected, the sample size cannot meet the mechanical experiments, processing efficiency and cost constraints, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of reducing processing costs, shortening time-consuming, and improving processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Step 1: Cut a thin slice with a thickness of 1mm on the TD-ND cross-section of the nanosheet nickel sample with a wire cutting device, and use water, ethanol, and acetone to clean the thin slice ultrasonically in order to remove residual stains on the sample surface;
[0030] Step 2: Use #600, #800, #1200, #2000, #4000 sandpaper to mechanically thin the slices obtained in step 1 in turn. During the grinding process, do not apply too much force and add a small amount of water continuously to reduce grinding The heat generated in the process affects the sample. Use the cross method to uniformly thin both sides of the sheet until the thickness is reduced to 50 μm, and there is no obvious scratch on the surface of the sheet. Once again, the thinned sample was ultrasonically cleaned with water, ethanol, and acetone to remove residues on the surface of the sample;
[0031] Step 3: Glue both ends of the clean paper to the glass slide, and place the thin slice obtained in Step...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Step 1: Cut a thin slice with a thickness of 1mm on the TD-ND cross-section of the nanosheet nickel sample with a wire cutting device, and use water, ethanol, and acetone to clean the thin slice ultrasonically in order to remove residual stains on the sample surface;
[0038] Step 2: Use #600, #800, #1200, #2000, #4000 sandpaper to mechanically thin the slices obtained in step 1 in turn. During the grinding process, do not apply too much force and add a small amount of water continuously to reduce grinding The heat generated in the process affects the sample. Use the cross method to uniformly thin both sides of the sheet until the thickness is reduced to 50 μm, and there is no obvious scratch on the surface of the sheet. Once again, the thinned sample was ultrasonically cleaned with water, ethanol, and acetone to remove residues on the surface of the sample;
[0039] Step 3: Glue both ends of the clean paper to the glass slide, and place the thin slice obtained in Step...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Step 1: Cut a thin slice with a thickness of 1mm on the TD-ND cross-section of the nanosheet nickel sample with a wire cutting device, and use water, ethanol, and acetone to clean the thin slice ultrasonically in order to remove residual stains on the sample surface;
[0046] Step 2: Use #600, #800, #1200, #2000, #4000 sandpaper to mechanically thin the slices obtained in step 1 in turn. During the grinding process, do not apply too much force and add a small amount of water continuously to reduce grinding The heat generated in the process affects the sample. Use the cross method to uniformly thin both sides of the sheet until the thickness is reduced to 50 μm, and there is no obvious scratch on the surface of the sheet. Once again, the thinned sample was ultrasonically cleaned with water, ethanol, and acetone to remove residues on the surface of the sample;
[0047] Step 3: Glue both ends of the clean paper to the glass slide, and place the thin slice obtained in Step...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com