Method for extracting plant pathogenic fungus DNA for PCR detection
A technology for phytopathogenic fungi and mycelium, which is applied in the field of extracting phytopathogenic fungi DNA for PCR detection, can solve the problems of difficulty in high quantification, long extraction process, high price, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Mycelia lysate: 0.5wt.% SDS, 0.1M Tris-HCL (pH9.2), 1.0M NaCl and 10mM EDTA, referred to as STNE Buffer.
[0021] A method for extracting plant pathogenic fungus DNA for PCR detection:
[0022] 1. Sample collection: Use an inoculation needle or a sterile toothpick to scrape the primary mycelium of mung bean size into a PCR tube at the edge of the colony, and use a 96-well PCR tube to process 96 samples at one time.
[0023] 2. DNA release: Add 100 μl STNE Buffer to the mycelia sample tube, treat at 95°C for 10 minutes to promote the release of DNA, vortex or pipette to mix well to obtain crude lysate DNA.
[0024] 3. Template acquisition: After obtaining the crude lysate, dilute it 10 times with sterile water, and add 2 μl of the diluted crude lysate as a template for every 50 μl of PCR system.
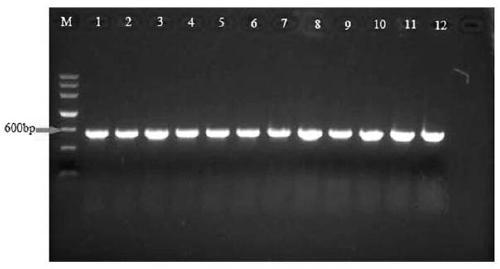
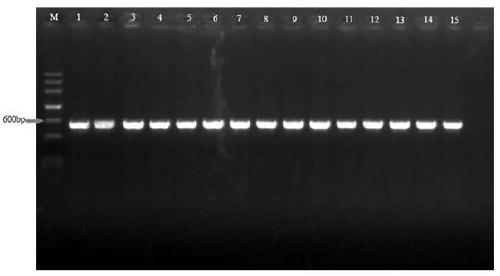
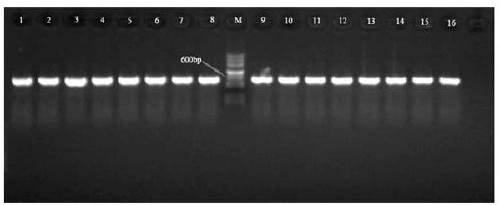
[0025] Three common plant pathogenic fungi, Magnaporthe oryzae ( Magnaporthe oryzae ), Alternaria ( Alternaria alternata ) and Fusarium ( Fusarium graminearum and Fusa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com