Semiconductor device
A semiconductor and N-type semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, diodes, etc., can solve problems such as gate runaway, oxide layer breakdown, failure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
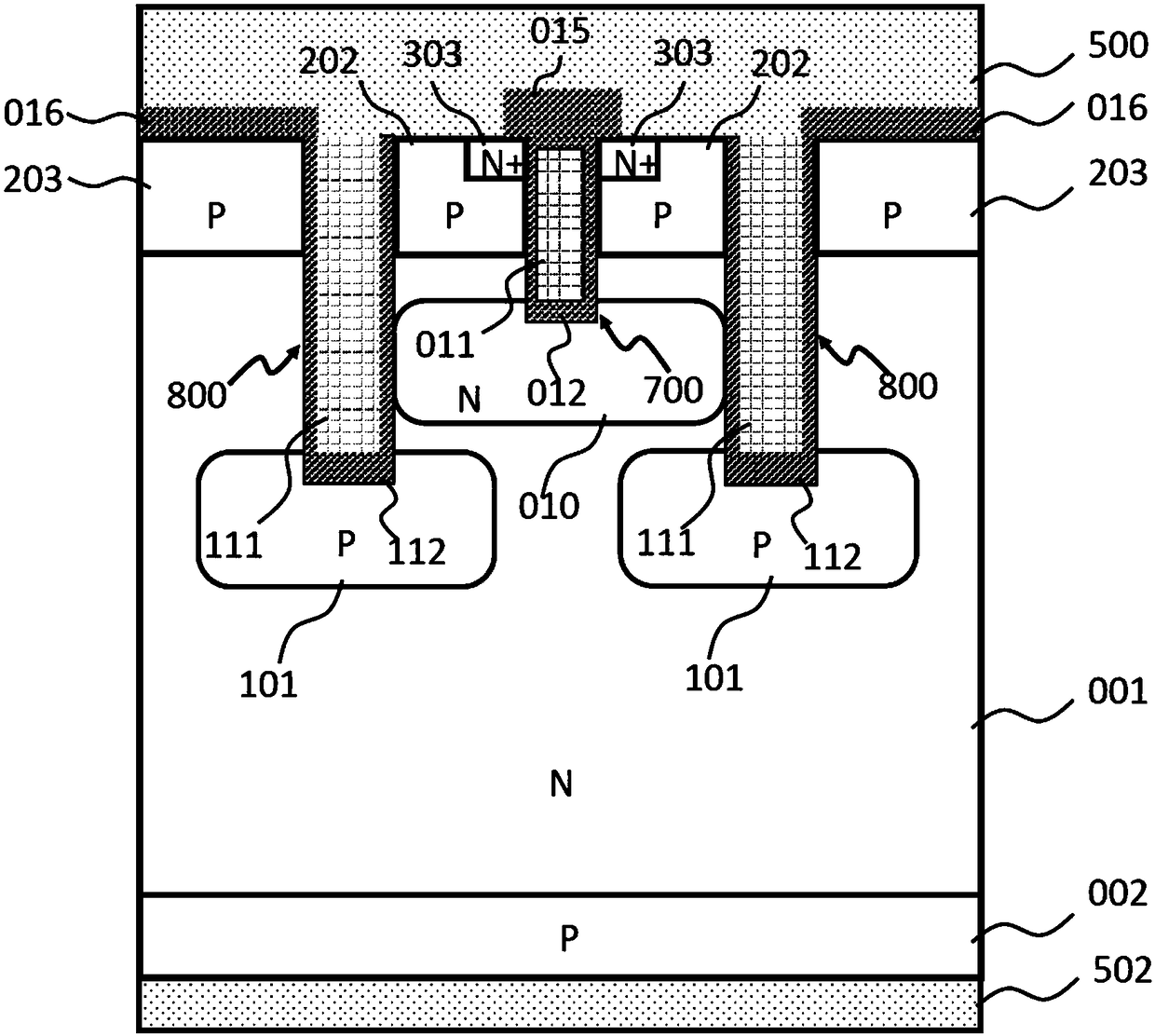
[0056] The MOS-controlled bipolar transistor (MCBT) proposed by the present invention is composed of a plurality of cell units, figure 1A schematic diagram of the cross-sectional structure of one of the cells. The cellular structure uses an N-type substrate 001 as a substrate, a P-type semiconductor region 002, called an anode region, is provided on one side of the N-substrate 001, and at least one first tank unit 700 and At least one second tank unit 800 , wherein the depth of the first tank unit 700 is smaller than that of the second tank unit 800 . At the bottom of the first tank unit 700, there is an N-type carrier barrier region 010 with a higher doping concentration than the N substrate 001, which is called a minority carrier barrier region, and a P-type electric field is provided at the bottom of the second tank unit 800 Shielded area 101. A gate region 011 is provided in the first cell unit 700, and a first medium 012 is provided between the gate region 011 and the N...
Embodiment 2
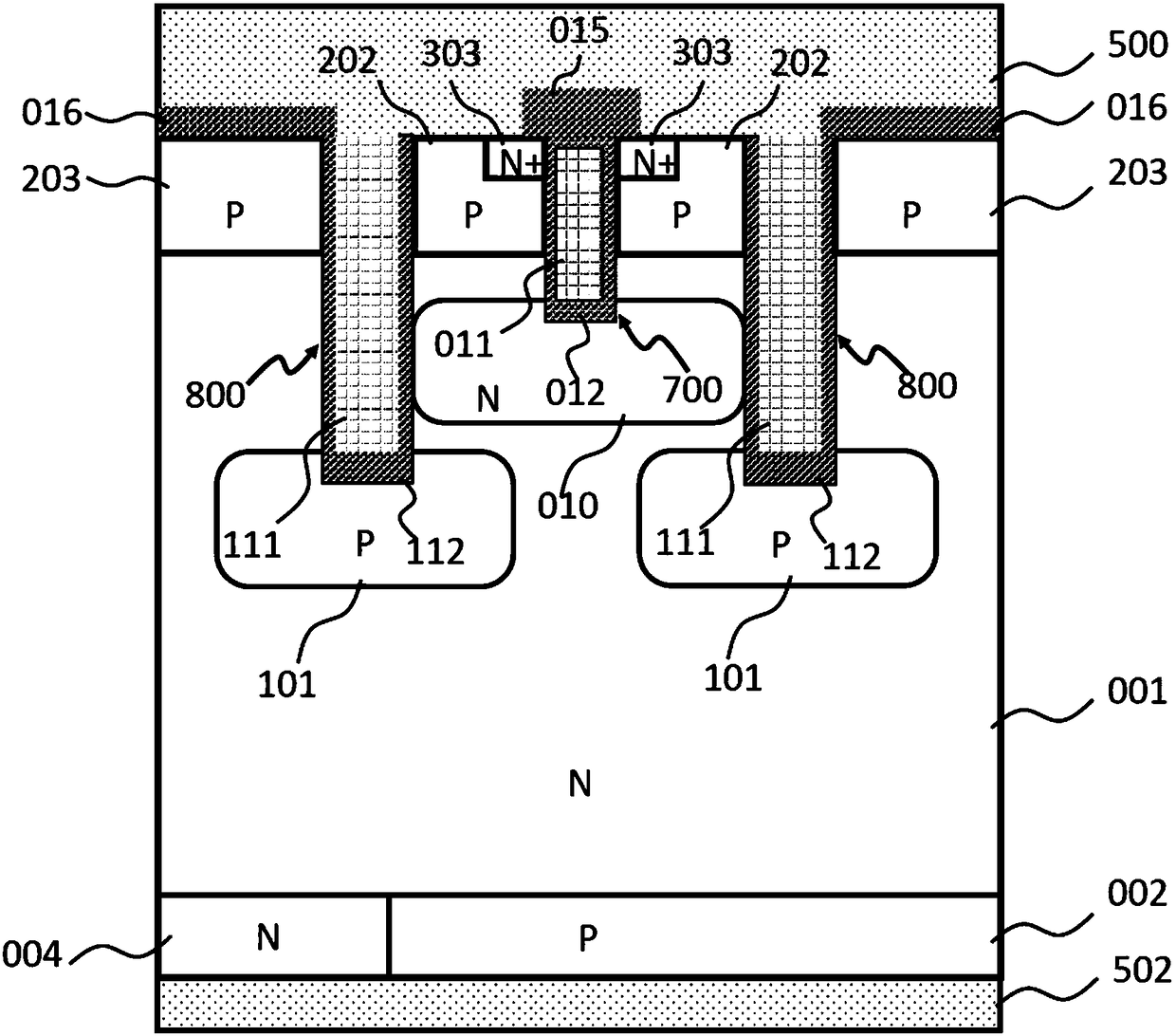
[0069] In the above embodiments, the N-type substrate 001 is non-punch-through, that is, the N-type substrate region 001 will not be fully depleted when the highest voltage is applied between the collector and the emitter. Embodiment 2 provides a PunchThrough or Field Stop cell, the schematic diagram of which is shown in figure 2 shown. There is a first N-type semiconductor region 003 adjacent to the P-type semiconductor region 002 , which is called a field stop region, and the doping concentration of the field stop region 003 is higher than that of the N-type substrate 001 . As the name implies, when the highest voltage is applied between the collector and the emitter, the electric field is cut off in the field stop region 003, and the field stop region 003 will not be completely depleted. The electric field stop structure in Example 2 can obtain a smaller thickness of the N-type substrate 001 than in Example 1.
[0070] Since the thickness of the N-type substrate 001 is r...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3 provides a cell of reverse conduction type (Reverse Conduction), and its structural schematic diagram is as follows image 3 shown. There is a second N-type semiconductor region 004 on the side adjacent to the P-type semiconductor region 002, and both the P-type semiconductor region 002 and the second N-type semiconductor region 004 are in direct contact with the first electrode 502, forming an anode short circuit (Anode Short) structure .
[0073] A P-N-N diode is formed by the P-type source-body region 202, the N-type carrier barrier region 010, the N-type substrate 001, and the second N-type semiconductor region 004. When the potential of the emitter second electrode 500 is higher than that of the collector first electrode When the potential of the electrode 502 is constant, the P-N-N diode is forward-biased, and at this time, a current flows from the emitter second electrode 500 to the collector first electrode 502 to form a reverse conduction.
[007...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com