Non-destructive testing method for lithium precipitation of lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery, non-destructive testing technology, applied in the direction of secondary battery testing, secondary battery repair/maintenance, electrical measurement, etc., can solve problems such as complex calculation process and mathematical model, to improve stability and accuracy, avoid Potential safety hazards, detection methods are simple and easy to implement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
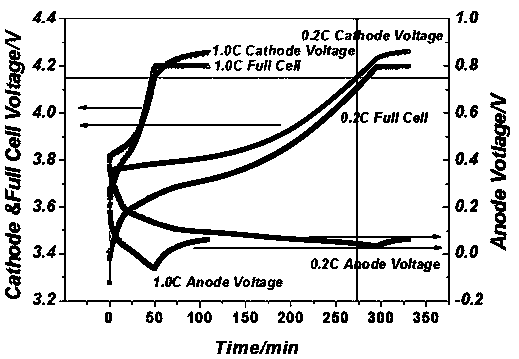
[0035] The three-electrode constant current and constant voltage charging test is carried out on the lithium-ion battery to be tested in this embodiment, and the obtained three-electrode charging curve is shown in the attached figure 1 shown. attached by figure 1 It can be seen that during the charging process, the precipitation of metal lithium occurs at the end of constant current charging; during the constant voltage process, with the elimination of polarization, the potential of the negative electrode rises, causing the metal lithium precipitated on the surface of the negative electrode to re-embed into the negative electrode of the battery, thus Not conducive to detection and analysis. In the constant current process, the precipitation of metal lithium has a precipitation boundary rate. When the charge rate is greater than the limit rate, the lithium battery will precipitate metal lithium; when the charge rate is less than the limit rate, the lithium battery will not pre...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The detection method of lithium battery analysis lithium in the present embodiment is:
[0044] S01, at 20°C, charge the lithium-ion battery under test with a constant current of 1.0C to a voltage of 4.0V;
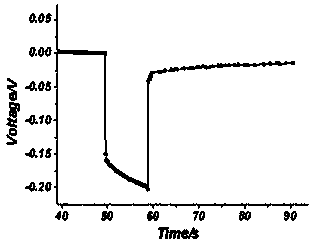
[0045] S02, after the constant current charging is completed, perform intermittent electrochemical excitation on the lithium-ion battery to be tested at 20°C, and measure the voltage of the lithium-ion battery to be tested during the intermittent electrochemical excitation process; intermittent electrochemical excitation method A constant current pulse electrochemical excitation is carried out every 3 minutes for the lithium-ion battery to be tested, the constant current pulse current is 2.0C, and the constant current pulse electrochemical excitation time is 10s.
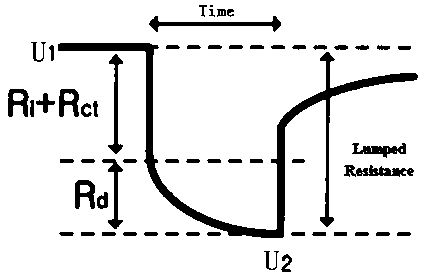
[0046] S03, during the above constant current pulse electrochemical excitation process, record the voltage U of the lithium battery before the excitation 1 and the voltage U of the lithium battery after ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The detection method of lithium battery analysis lithium in the present embodiment is:
[0050] S01, at 20°C, charge the lithium-ion battery under test with a constant current of 1.5C to a voltage of 4.0V;
[0051] S02, after the constant current charging is completed, perform intermittent electrochemical excitation on the lithium-ion battery to be tested at 20°C, and measure the voltage of the lithium-ion battery to be tested during the intermittent electrochemical excitation process; intermittent electrochemical excitation method A constant current pulse electrochemical excitation is carried out every 3 minutes for the lithium-ion battery to be tested, the constant current pulse current is 3.0C, and the constant current pulse electrochemical excitation time is 10s.
[0052] S03, during the above constant current pulse electrochemical excitation process, record the voltage U of the lithium battery before the excitation 1 and the voltage U of the lithium battery after ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com