Pretreatment method and quantitative detection method for endogenous sugar phosphate compound in plant sample
A phosphate sugar, endogenous technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, affecting the accuracy of quantification, damage to the mass spectrometer, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the signal response of the mass spectrometer, ensuring the accuracy, and improving the detection sensitivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
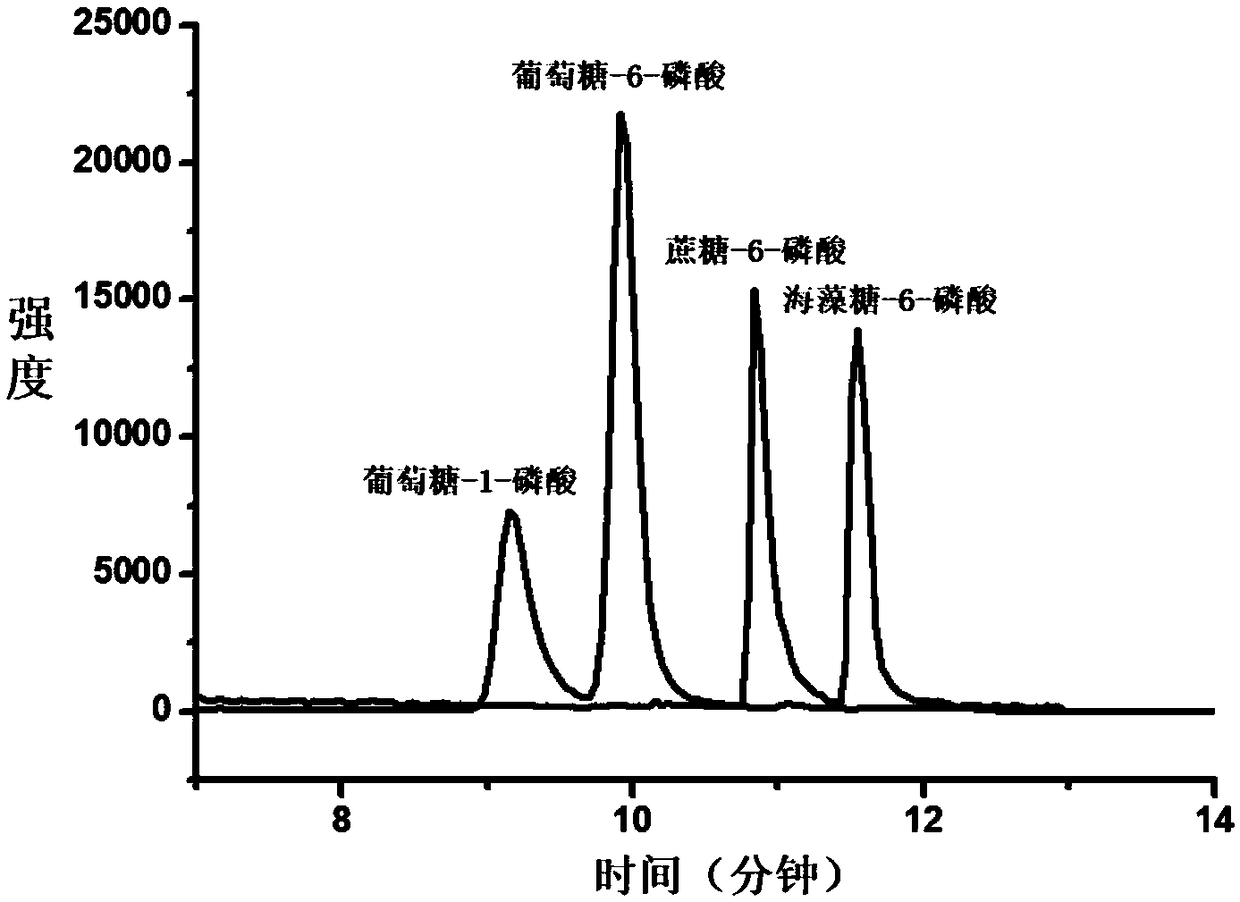
[0040] In this example, four standard substances were used as analytes to verify their chromatographic separation. Prepare mixed standards of glucose-1-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, sucrose-6-phosphate, and trehalose-6-phosphate, each standard 0.2ng dissolved in 300 μL of 50 mM borate buffered saline (pH 6.8); Add 180 μL of 8-DMQ DMSO solution (0.014 mM) to the resulting solution, then place it at room temperature to shake for 40 minutes, centrifuge (10000×g) for 5 minutes to take the supernatant; then take 2 μL of the supernatant to pass through the HILIC column for mass spectrometry analysis .
[0041] As shown in Figure 1, the two pairs of isomers are well separated, have good chromatographic retention behavior, and the chromatographic peak shape is good.
Embodiment 2
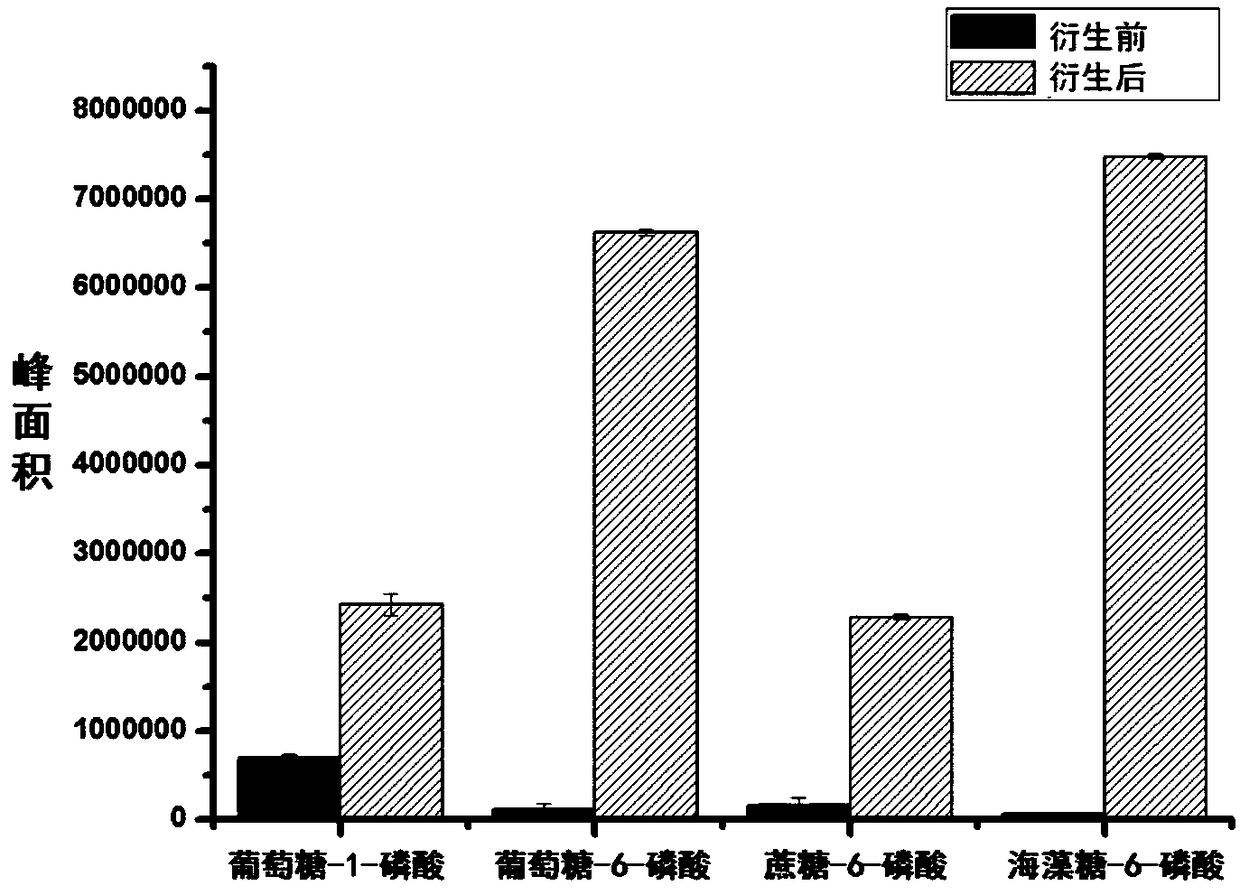
[0043] In this example, four standard substances were used as analytes to verify the improvement of sensitivity before and after derivatization.
[0044] First, prepare mixed standards of glucose-1-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, sucrose-6-phosphate, and trehalose-6-phosphate, and dissolve 0.2 ng of each standard in 300 μL of 50 mM borate buffered saline solution (pH 6.8 ); add 180μL of 8-DMQ DMSO solution (0.014mM) to the resulting solution, then place it at room temperature to shake for 40min, centrifuge (10000×g) for 5min to get the supernatant; then take 2μL of the supernatant to pass through the HILIC column Enter mass spectrometry.
[0045] In addition, prepare mixed standards of glucose-1-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate, sucrose-6-phosphate, and trehalose-6-phosphate, and dissolve 0.2 ng of each standard in 480 μL of 50 mM borate buffered saline (pH 6.8 ); after that, 2 μL of the resulting solution was passed through a HILIC chromatographic column for mass spectrometry ...
Embodiment 3
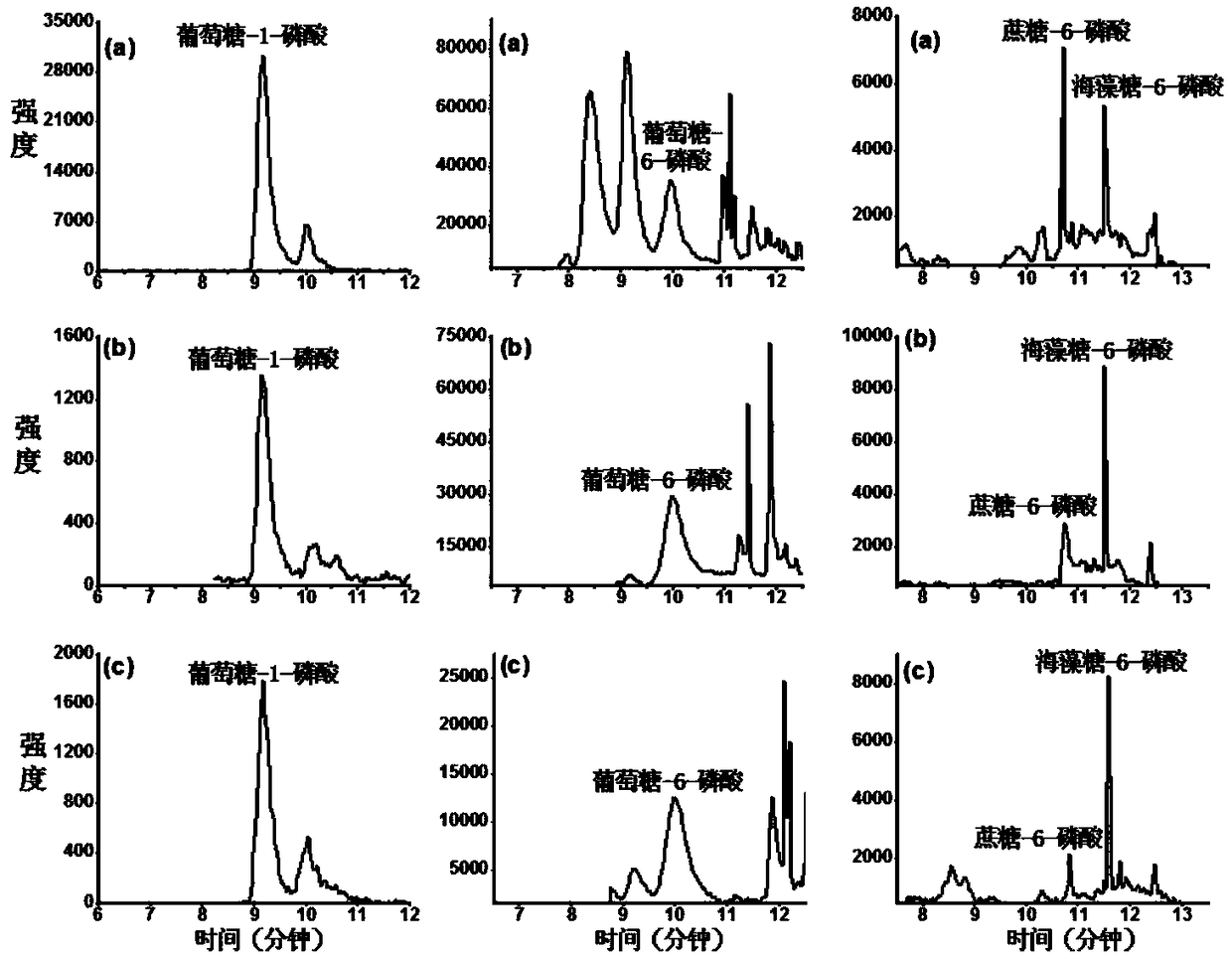
[0048] A pretreatment method for endogenous phosphate sugar in a plant sample, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0049] 1) Accurately weigh 1mg of rice leaves, 5mg of rice roots, and 10mg of Arabidopsis leaves and grind them into powder with liquid nitrogen as plant samples;
[0050] Add the isotope internal standard [ 13 C 6 ] Phosphate-6-glucose 25ng and 0.25mL iced chloroform / acetonitrile 3:7 (v / v) were mixed evenly; after vortex mixing, placed in a refrigerator at -20°C for extraction for 2 hours, and vortexed occasionally; after that, Add 0.2mL of ice water and vortex for 3min. After centrifugation (10000×g) for 5min, take out the upper aqueous phase and put it in another centrifuge tube; add 0.2mL of ice water again to repeat the above steps, and combine the two extracts to obtain the sample extraction solution;
[0051] 2) Blow dry the sample extraction solution obtained above under nitrogen, then reconstitute with 200 μL of 50 mM boric acid buffered saline so...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com