Method for optimizing thermal cycle and random vibration life of LCCC chip solder joint of car networking
A technology of random vibration and optimization methods, applied in design optimization/simulation, computer-aided design, special data processing applications, etc. The effect of cycle life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
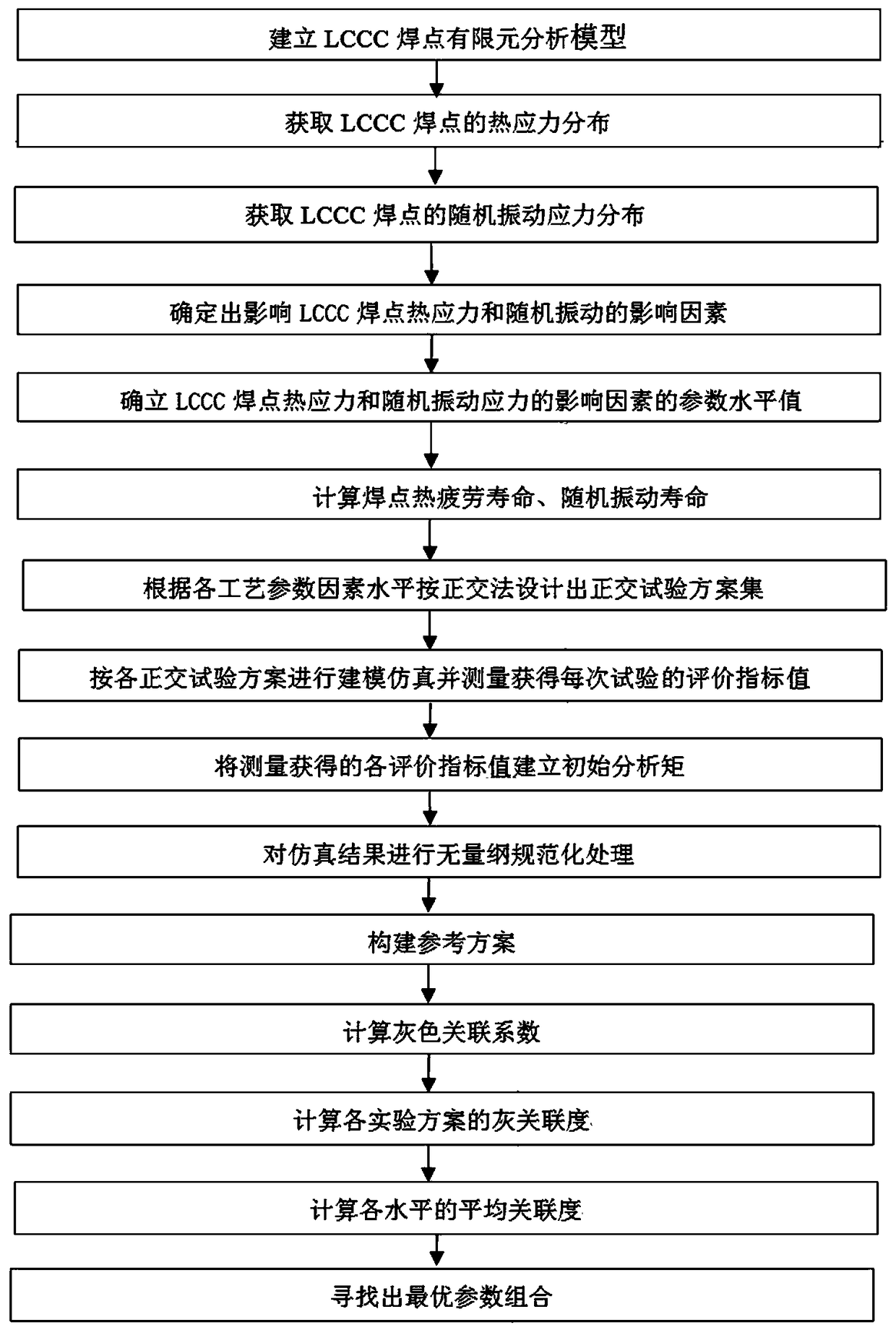
[0065] Such as figure 1 As shown, 1) establish the finite element analysis model of LCCC solder joint;
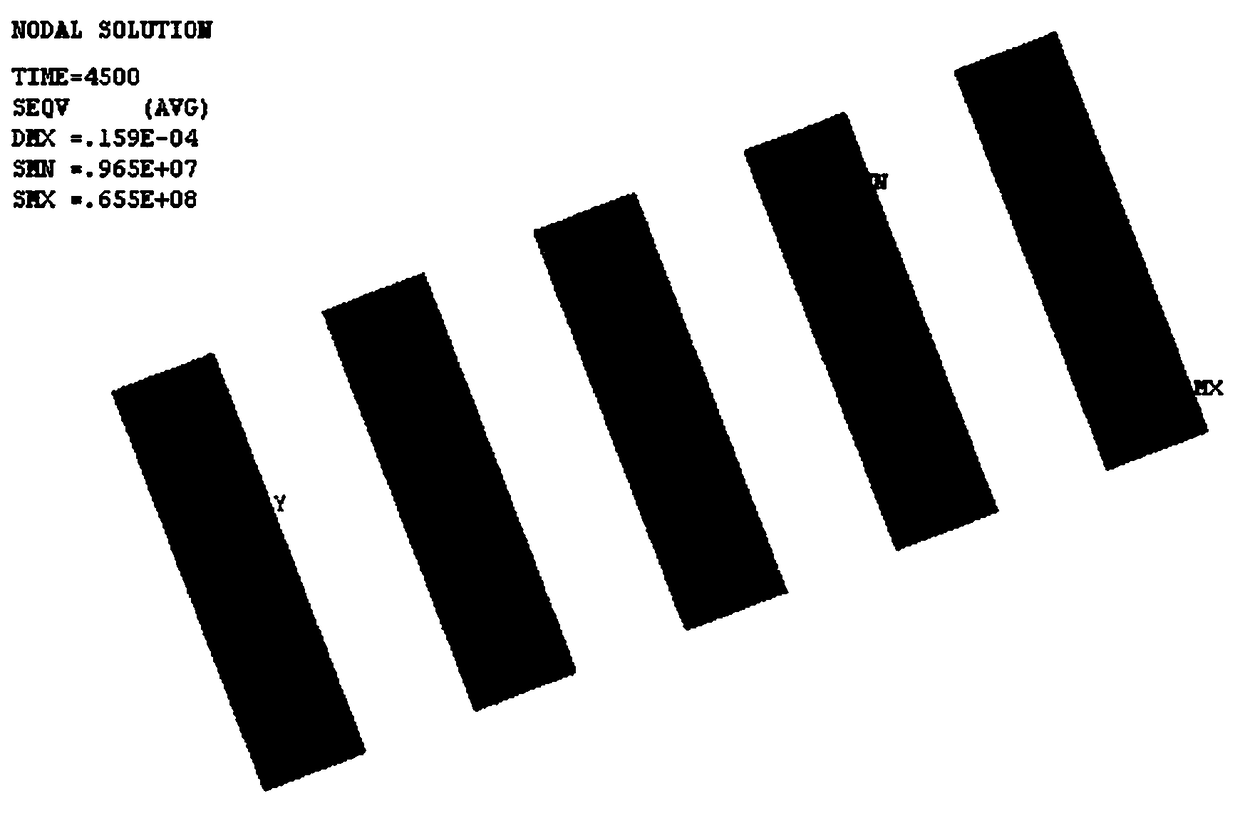
[0066] 2) Obtain the thermal cycle stress of the LCCC solder joints: apply constraints to the model built in step 1), perform analysis under temperature cycle loading conditions, and then use ANSYS software to simulate and analyze the model to obtain the stress distribution of the LCCC solder joints;
[0067] 3) Obtain the random vibration stress of the LCCC solder joint: impose constraints on the model built in step 1), perform analysis under random vibration loading conditions, and then use ANSYS software to simulate and analyze the model to obtain the stress distribution of the LCCC solder joint;
[0068] 4) Determine the influencing factors that affect the thermal cycle and random vibration of LCCC solder joints: specifically include LCCC pad width W, pad length L, gap height H, and stencil thickness T, so as to obtain a set of process parameters that can be optimized a...
test approach Y1
[0079] Test plan Y 1 :X 1 ={X 11 ,X 12 ,X 13 , X 14}={M 1 , N 1} (3)
test approach Y2
[0080] Test plan Y 2 :X 2 ={X 21 ,X 22 ,X 23 , X 24}={M 2 , N 2} (4)
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Gap height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com