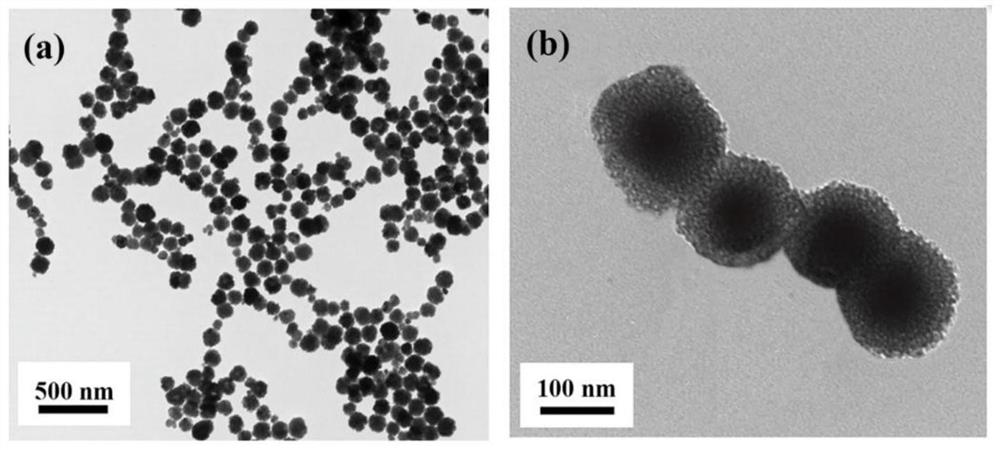
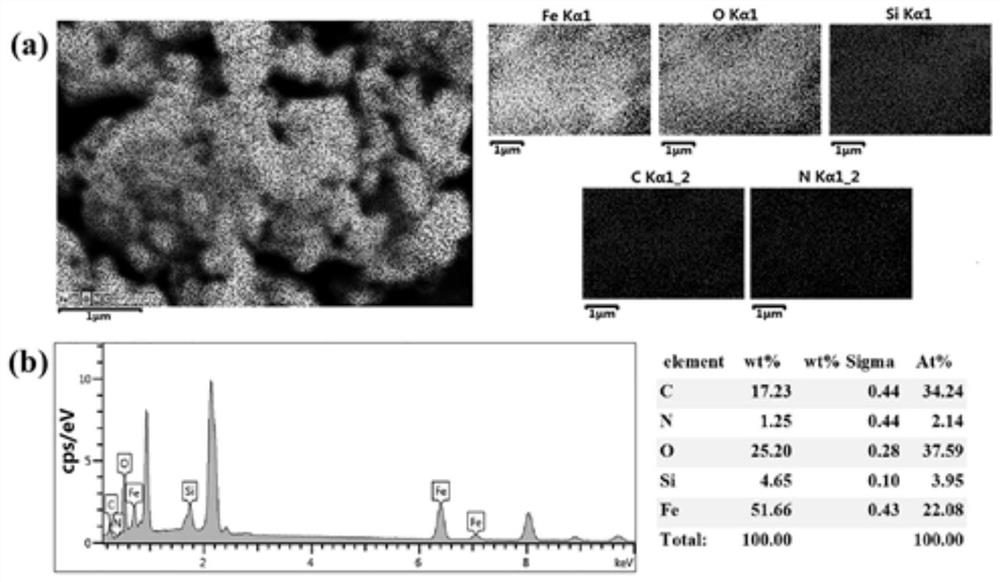
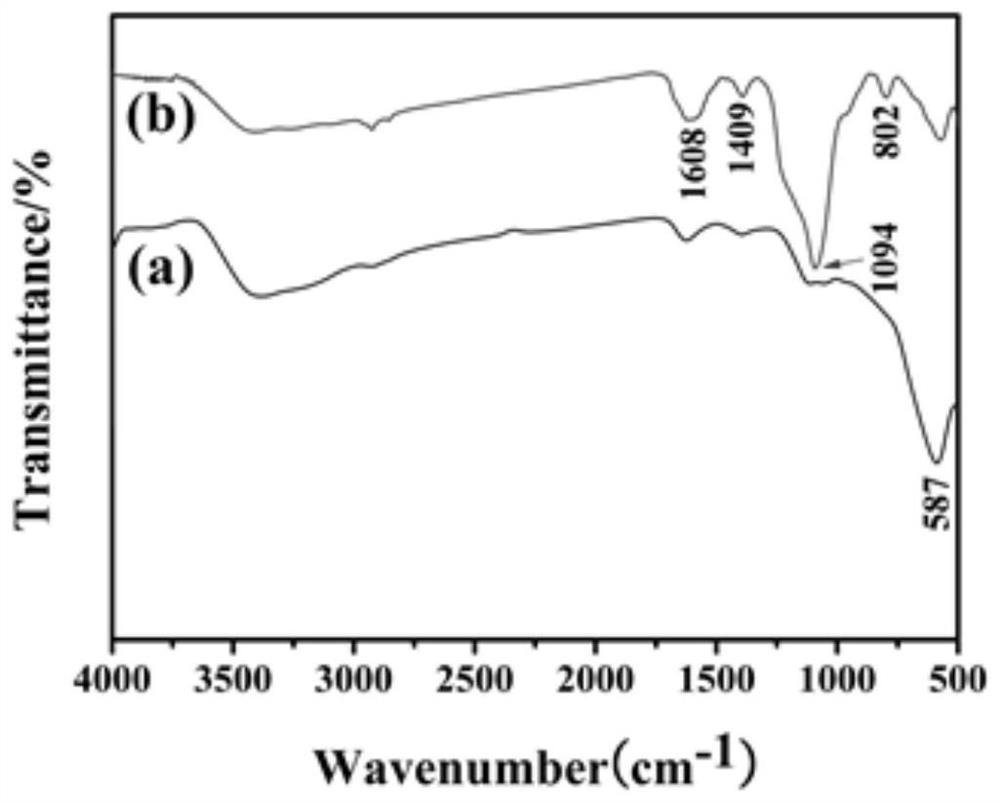
A blood lead removal instrument for removing blood lead in vitro
A technology of blood and blood lead, which is applied in the field of biomedical instruments, can solve problems such as inability to enter red blood cell lead ions, impossibility and poor removal of lead ions, and severe blood lead poisoning, so as to overcome unclear removal principles, relieve illness, compose simple effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] 1) Preparation of magnetic ferroferric oxide (Fe 3 o 4 NPs)
[0043] Weigh ferric chloride hexahydrate (1.35g, 5mmol) and fully dissolve it in 30mL of ethylene glycol solution. Sodium acetate (NaAc, 3.6 g) and polyethylene glycol-2000 (PEG-2000 1.0 g) were added with stirring. Stirring was continued for 30 min, and the solution was transferred to a high-temperature reactor at 200° C. for 72 h. After natural cooling, it was washed with deionized water and ethanol solution several times in sequence, and dried under vacuum at 60°C.
[0044] 2) Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 / aminated mesoporous silica composites using polylysine as template (MMS / P NPs)
[0045] Dissolve 100 mg sodium lauroyl sarcosinate into 10 mL citric acid / sodium citrate buffer solution (0.1 M, pH 5.2) at room temperature, and add 150 μL ε-polylysine (20 wt %) to the solution. At this point, the solution immediately becomes an emulsion, generating polylysine / sodium lauroyl sarcosinate composite micel...
Embodiment 2
[0055] 1) Preparation of magnetic ferric oxide
[0056] Synthesis of ferric oxide nanoparticles (FeO) by hydrothermal method 3 o 4 NPs). The specific method is as follows: Weigh ferric trichloride hexahydrate (1.35 g, 5 mmol), and fully dissolve it in 40 mL of ethylene glycol solution. Sodium acetate (NaAc, 1.8 g) and sodium citrate trihydrate (Na 3 Cit 0.2g). Stirring was continued for 1 h, and the solution was transferred to a high-temperature reactor at 200° C. for 20 h. After natural cooling, it was washed with deionized water and ethanol solution several times in sequence, and dried under vacuum at 60°C.
[0057] 2) Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 / rich aminated mesoporous silica composites (MMS / H NPs) using hyperbranched polyamide (PAMAM) as template
[0058] Will Fe 3 o 4 NPs solution (3mg / mL, 50mL) was mixed evenly with 9mL hydrazine hydrate, and treated with ultrasound for 30min. The mixture was transferred to a three-neck flask, and 70 mL of deionized water was...
Embodiment 3
[0064] 1) Preparation of magnetic ferric oxide
[0065] Synthesis of ferric oxide nanoparticles (FeO) by hydrothermal method 3 o 4 NPs). The specific method is as follows: Weigh ferric trichloride hexahydrate (1.35 g, 5 mmol), and fully dissolve it in 40 mL of ethylene glycol solution. Sodium acetate (NaAc, 1.8 g) and sodium citrate trihydrate (Na 3 Cit 0.2g). Stirring was continued for 1 h, and the solution was transferred to a high-temperature reactor at 200° C. for 20 h. After natural cooling, it was washed with deionized water and ethanol solution several times in sequence, and dried under vacuum at 60°C.
[0066] 2) Preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 / rich aminated mesoporous silica composites using chitosan as template
[0067] Will Fe 3 o 4 NPs solution (3mg / mL, 50mL) was mixed evenly with 9mL hydrazine hydrate, and treated with ultrasound for 30min. The mixture was transferred to a three-neck flask, and 70 mL of deionized water was added. Then 90 mg TEOS was added,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com