Production process for extracting shikimic acid from anise
A kind of production technique, the technology of shikimic acid, applied in the production technique field of extracting shikimic acid, can solve problems such as low shikimic acid extraction rate, reach the effect that helps to generate and preserve, dissolution rate is high, improves extraction quantity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
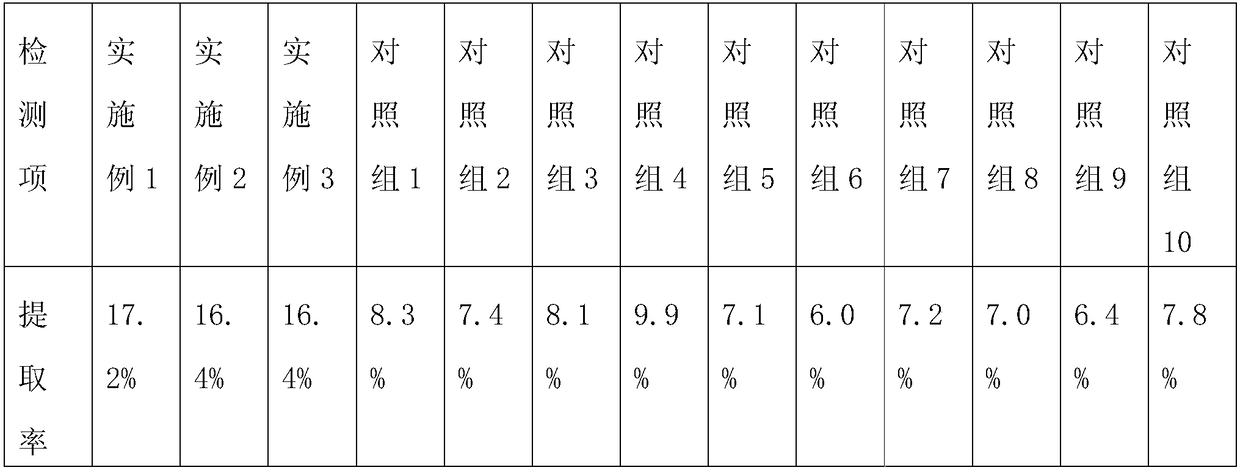
Embodiment 1
[0024] A production process for extracting shikimic acid from star anise includes the following steps:
[0025] (1) Pretreatment: Wash the star anise to remove impurities, crush it and pass it through an 80-mesh sieve for use;
[0026] (2) Pre-fermentation: Add glucose and soybean protein to the pretreated star anise in step (1), then add water of 3 times the quality of the star anise, stir evenly, add fermenting bacteria, and ferment at 25°C for 2 days; the fermentation The bacteria are composed of Rhizopus, Trichoderma, Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus niger, Escherichia coli, and Lactobacillus plantarum; the number of viable bacteria in the step (2) is 5×10 10 cfu / g. The mass ratio of star anise to glucose and soybean protein is 100:1:5;
[0027] (3) Post-fermentation: After the star anise fermented before step (2) is sterilized under infrared rays, Lactobacillus plantarum is added and fermented for 1 d, the pH of the star anise is 5, and then kept at 100°C for 1 hour;
[0028] (4)...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A production process for extracting shikimic acid from star anise includes the following steps:
[0031] (1) Pretreatment: Wash the star anise to remove impurities, crush it and pass it through an 80-mesh sieve for use;
[0032] (2) Pre-fermentation: add glucose and soybean protein to the pretreated star anise in step (1), add water of 1 times the quality of the star anise, stir evenly, add fermenting bacteria, and ferment at 30°C for 1d; The bacteria are composed of Rhizopus, Trichoderma, Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus niger, Escherichia coli, and Lactobacillus plantarum; the number of viable bacteria of the fermentation bacteria in the step (2) is 1×10 10 cfu / g. The mass ratio of star anise to glucose and soybean protein is 100:5:1;
[0033] (3) Post-fermentation: After the star anise fermented before step (2) is sterilized under infrared rays, Lactobacillus plantarum is added and fermented for 2 days, the pH value of the star anise is 4, and then kept at 100°C for 2 hours...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A production process for extracting shikimic acid from star anise includes the following steps:
[0037] (1) Pretreatment: Wash the star anise to remove impurities, crush it and pass it through an 80-mesh sieve for use;
[0038] (2) Pre-fermentation: add glucose and soybean protein to the pretreated star anise in step (1), then add 2 times the quality of the star anise water, stir evenly, add fermenting bacteria, and ferment at 28°C for 1 d; The bacteria are composed of Rhizopus, Trichoderma, Aspergillus oryzae, Aspergillus niger, Escherichia coli, and Lactobacillus plantarum; the number of viable bacteria in the step (2) of the fermentation bacteria is 3×10 10 cfu / g. The mass ratio of the star anise to glucose and soy protein is 100:3:3;
[0039] (3) Post-fermentation: After the star anise fermented before step (2) is sterilized under infrared light, Lactobacillus plantarum is added and fermented for 1 d, the pH value of the star anise is 5, and then kept at 100°C for 2 hour...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com