Cerium-containing neodymium-iron-boron magnet and heat treatment processs and application thereof
A neodymium-iron-boron and heat treatment technology, which is applied in the manufacture of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc., can solve the problems of the comprehensive performance decline of cerium-containing neodymium-iron-boron magnets, so as to ensure the comprehensive magnetic performance of the magnets, reduce cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] A low-cost NdFeB magnet with high cerium content, which is prepared by sintering process with components: praseodymium neodymium (Pr-Nd): 29kg, cerium (Ce): 3kg, niobium (Nb): 0.2kg , boron (B): 1kg, aluminum (Al): 0.8kg, copper (Cu): 0.12kg, cobalt (Co): 0.2kg, iron (Fe): 65.68kg.
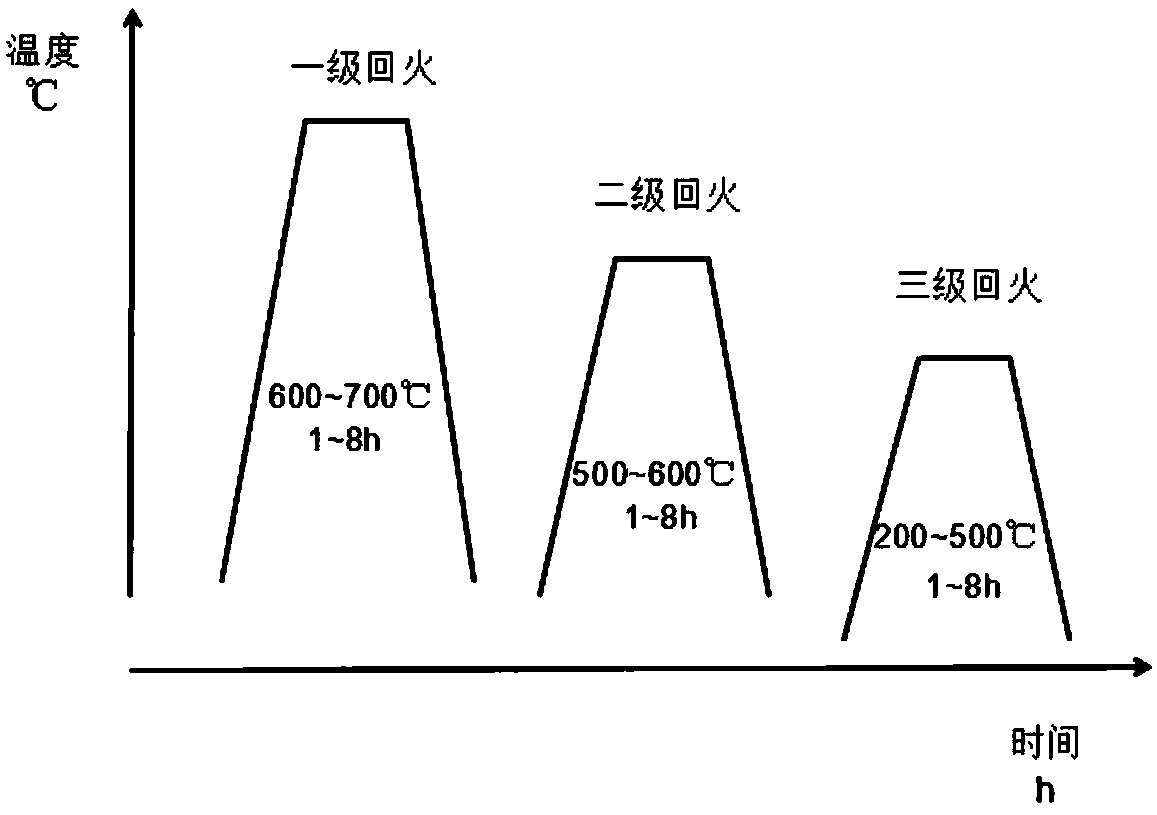
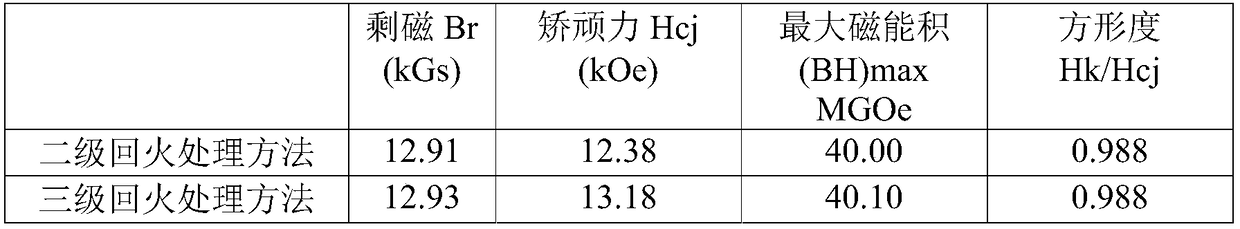
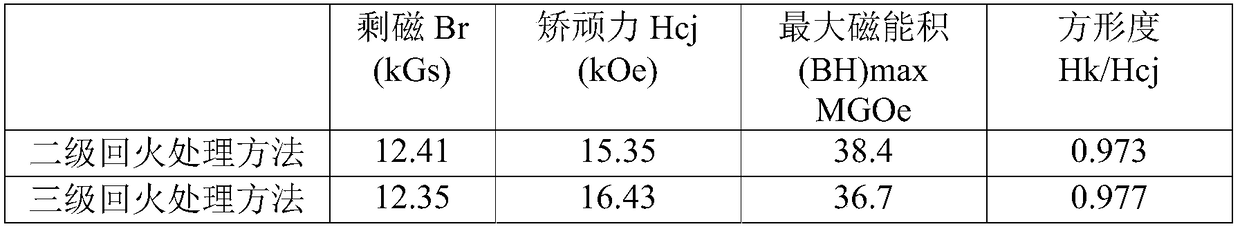
[0048]In the vacuum sintering furnace, firstly, the sintered NdFeB magnet is subjected to the primary tempering process, the heating rate is first 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 590°C, the heating rate is reduced to 2°C / min, and the temperature is raised to the first-stage tempering The temperature is 645°C, the temperature is kept for 3 hours, and the vacuum degree is 0.8 Pa. After the end, the vacuum degree is filled with nitrogen and air-cooled to room temperature. Then perform secondary tempering, the heating rate is first 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 485°C, the heating rate is reduced to 2°C / min, the temperature is raised to the secondary tempering temperature of 535°C,...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A low-cost NdFeB magnet with high cerium content, which is prepared by sintering the following components: praseodymium neodymium (Pr-Nd): 22.2kg, cerium (Ce): 8kg, dysprosium (Dy): 1.2 kg, holmium (Ho): 0.4kg, gallium (Ga): 0.2kg, niobium (Nb): 0.2kg, boron (B): 1kg, aluminum (Al): 0.4kg, copper (Cu): 0.15kg, cobalt (Co): 0.2 kg, zirconium (Zr): 0.1 kg, iron (Fe): 65.95 kg.
[0055] In the vacuum sintering furnace, firstly, the sintered NdFeB magnet is subjected to the primary tempering process, the heating rate is first 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 590°C, the heating rate is reduced to 2°C / min, and the temperature is raised to the first-stage tempering The temperature is 640°C, the temperature is kept for 3 hours, and the vacuum degree is 0.8 Pa. After the end, the vacuum degree is filled with nitrogen and air-cooled to room temperature. Then perform secondary tempering, the heating rate is first 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 485°C, the heating rate ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A low-cost NdFeB magnet with high cerium content, which is prepared by sintering process from the following components: praseodymium neodymium (Pr-Nd): 21kg, cerium (Ce): 11kg, niobium (Nb): 0.2kg , boron (B): 1kg, aluminum (Al): 0.8kg, copper (Cu): 0.12kg, cobalt (Co): 0.2kg, iron (Fe): 65.68kg.
[0062] In the vacuum sintering furnace, firstly, the sintered NdFeB magnet is subjected to the primary tempering process, the heating rate is first 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 590°C, the heating rate is reduced to 2°C / min, and the temperature is raised to the first-stage tempering The temperature is 645°C, the temperature is kept for 3 hours, and the vacuum degree is 0.8 Pa. After the end, the vacuum degree is filled with nitrogen and air-cooled to room temperature. Then perform secondary tempering, the heating rate is first 8°C / min, the temperature is raised to 485°C, the heating rate is reduced to 2°C / min, the temperature is raised to the secondary tempering tempe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com