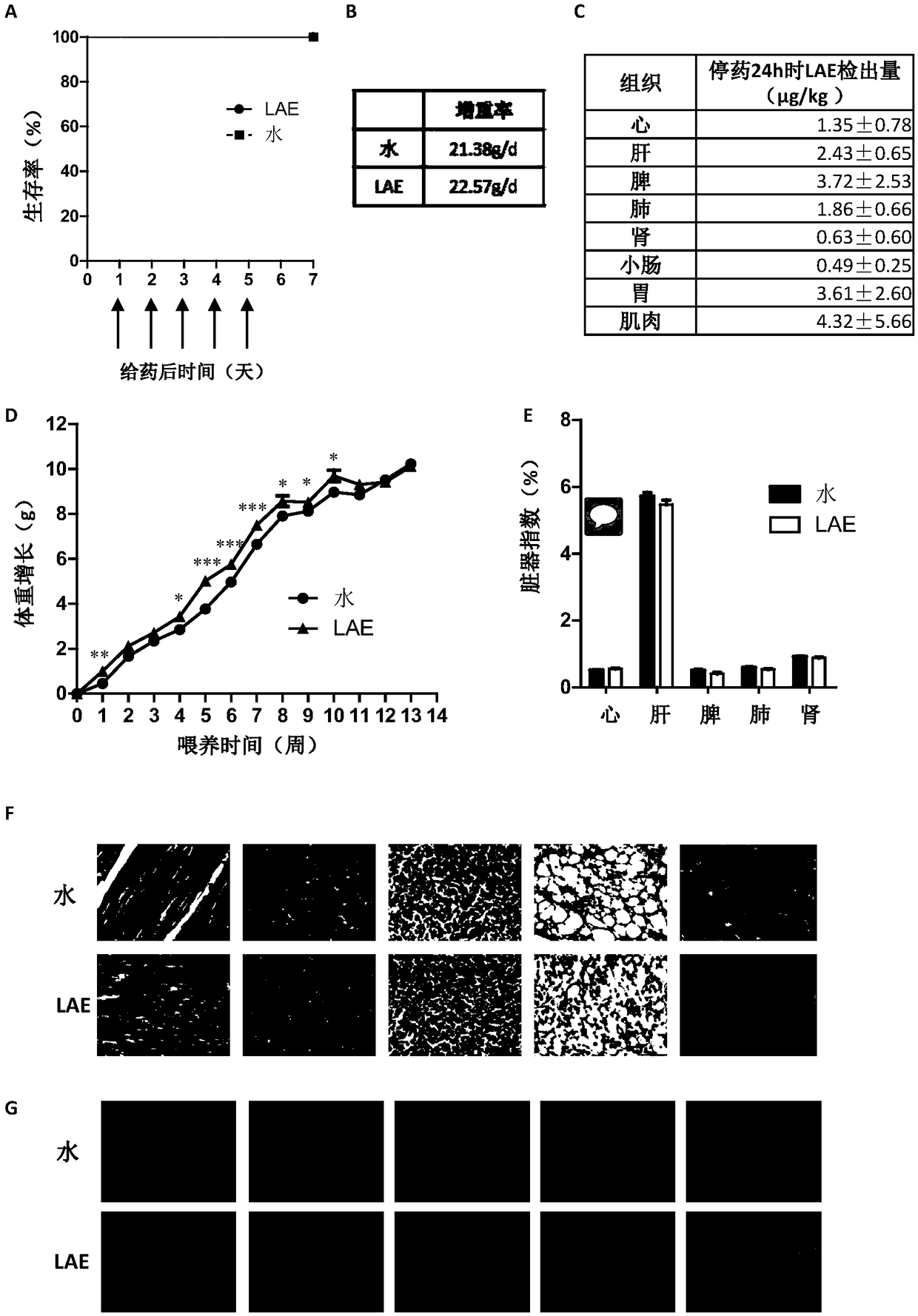
Application of ethyl lauroylarginate as feed additive
A technology of use and feed, applied in the field of use of lauroyl arginine ethyl ester as a feed additive, can solve the problems of unresearched LAE's independent bacteriostatic effect and uninstructed, and reduce the risk of infection with Riemerella anatipestifer , small toxic side effects, no effect on survival
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Embodiment one: micro-broth dilution method measures LAE to bacterium minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
[0057] Principle and purpose: According to the micro-broth dilution method stipulated by CLSI, after co-incubating the drug and bacteria in a 96-well plate for 24 hours, the minimum drug concentration at which bacterial growth is inhibited is the minimum inhibitory concentration of the drug.
[0058] Methods: LAE and bacteria (the clinical isolate of Riemerella anatipestifer RA‐11, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213, and Escherichia coli ATCC 25922) were diluted with tryptone soy broth (TSB) and cultured. Added to the 96-well plate, and set up blank control medium CK1 without bacteria, medium CK2 added with LAE (1000 μg / ml) and control medium CK3 without drug LAE but containing normal growth of bacteria. The 96-well plate was incubated in a 37 °C incubator for 24 h, and then the absorbance value at 625 nm of each well was measured. OD of blank control medium CK1...
Embodiment 2
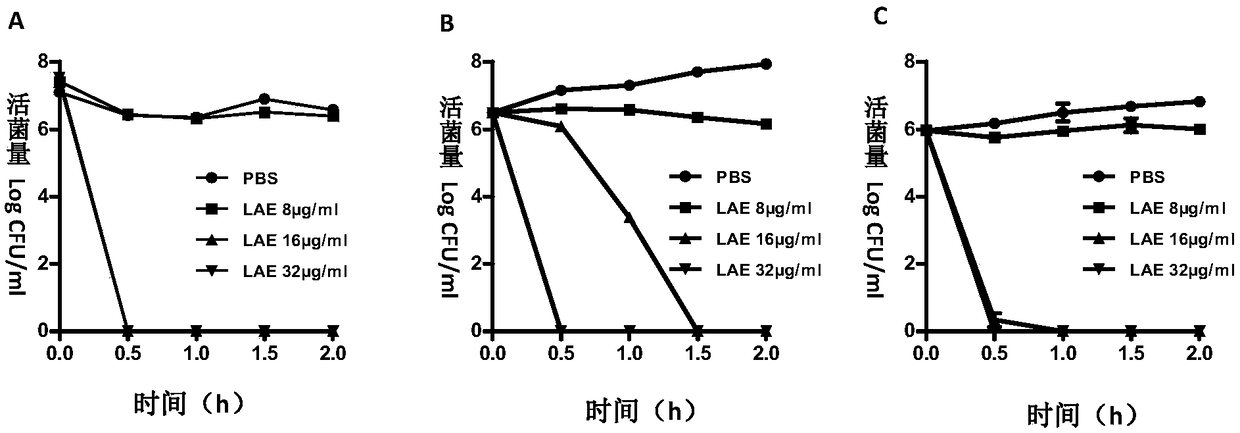
[0063] Embodiment two: LAE is to the mensuration of effective bactericidal time of bacteria
[0064] Principle and purpose: Drugs and bacteria are co-incubated, and a part of the samples are taken out at regular intervals for bacterial plate counting, so as to obtain the growth curve of the bacteria under the action of the drug, which is the time-killing curve of the drug.
[0065] Method: The bacteria in the logarithmic phase were mixed with different concentrations of LAE solutions, samples were taken at 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, and 2 hours after the addition of the drug, and the 10-fold serial dilution points were placed on the TSA plate, and cultured at 37°C for 18‐ 24h. Calculate the bacterial concentration of each dosing group at each time point by the number of colonies, and draw as follows figure 1 Bacterial survival curves are shown.
[0066] Result analysis: at a concentration of 16 μg / ml, LAE can completely kill Riemerella anatipestifer and Escherichia coli within 30 minu...
Embodiment 3
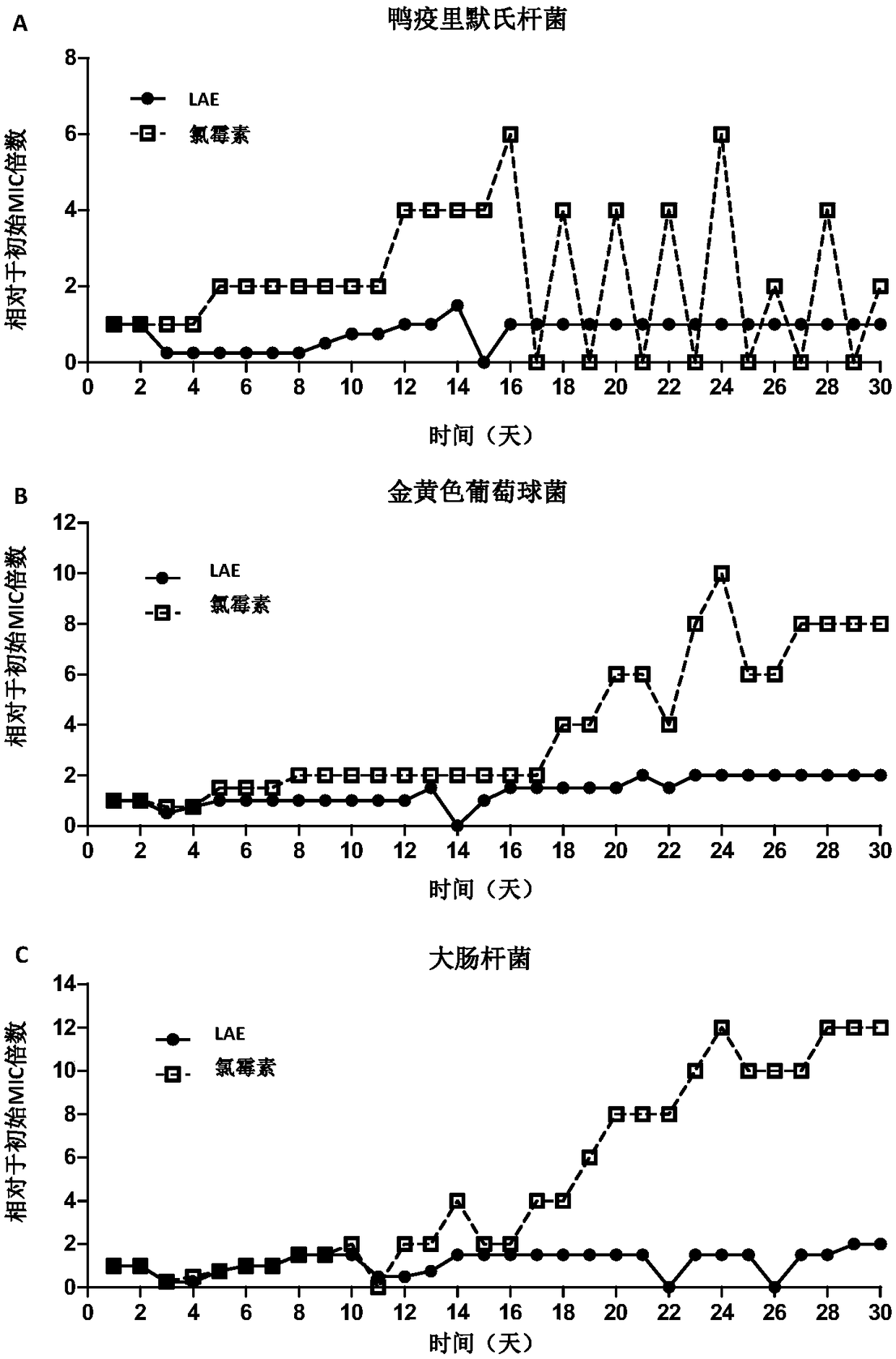
[0067] Example 3: LAE-induced bacterial drug resistance experiment
[0068] Principle and purpose: Bacteria can be induced to produce drug-resistant bacteria at sub-inhibitory concentrations, and the drug-induced bacteria can be detected by long-term transfer of bacteria cultured with sub-inhibitory concentrations of drugs to fresh drug-containing media Ability to generate resistance mutations.
[0069] Method: The bacteria in the logarithmic phase were mixed with the LAE solution in a glass test tube, sealed with a cotton plug, and placed in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C and 220 rpm for 24 hours. Afterwards, check the MIC of the drug every 24 hours, and add the bacterial solution with the highest drug concentration (that is, the highest drug concentration lower than the MIC) that can cultivate a turbid bacterial solution to fresh cultures containing different drug concentrations at a ratio of 1:100. In Kiri, culture at 37°C, 220rpm for 24h and last for 30 days. Chlo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com