Multi-functional arthrobacter Fp64 for controlling soil phosphorus loss and application thereof
A technology of soil phosphorus and Arthrobacter, which is applied in the direction of soil conditioning materials, applications, and microbial-based methods. It can solve the problems of few microbial research results, reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria, prevent disease outbreaks, and reduce the number.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The screening of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0021] (1) Source of strain
[0022] The Arthrobacter Fp64 of the present invention is isolated and screened from the soil of a protected agricultural greenhouse, and the sampling depth is 20-40 cm.
[0023] (2) Primary screening
[0024] The primary screening of bacterial strains adopts PAOs screening medium, and the formula is: sodium citrate 4g, NaCl 0.5g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 2.5g, CalCl 2 0.25g, MgSO 4 0.25g, Na 2 HPO 4 12.8g, KH 2 PO 4 3g, maltose 0.01g, toluidine blue 0.025g, agar 20g, no need to adjust pH, sterilize at 110°C for 20min. The culture temperature was 28°C.
[0025] The preliminary screening steps are as follows: (1) Prepare several test tubes containing 9ml water and several shake flasks containing 100ml water, autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes, and cool down for later use; (2) Each 10g soil sample is filled into 100ml In the shaking flask of bacterial water, the shaker was shaken for 30 min...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Phosphorus removal effect and other characteristic identification of embodiment 2 joint bacillus Fp64
[0032] 1. Phosphorus removal effect
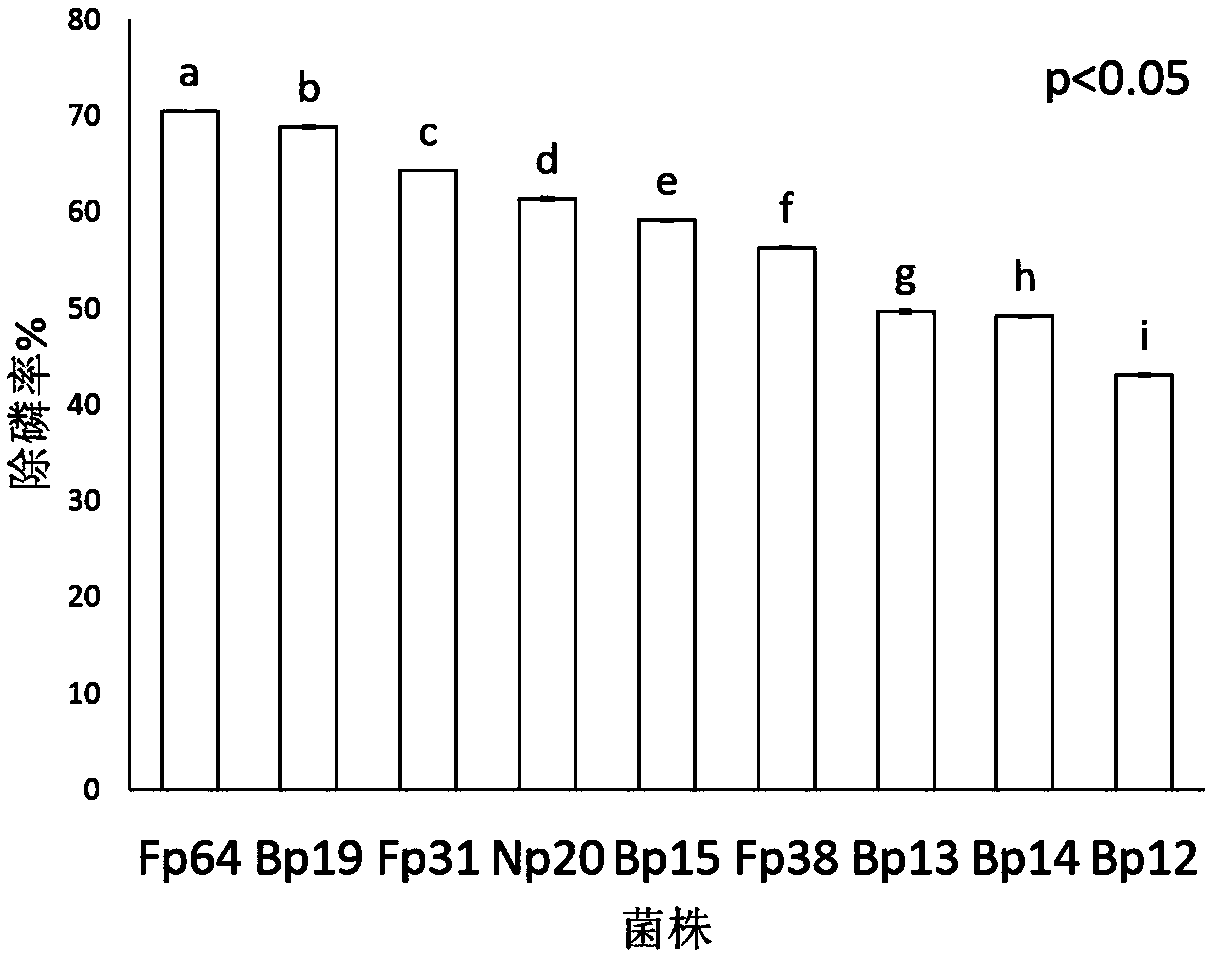
[0033]Arthrobacter Fp64 of the present invention and 8 bacterial strains (Bacillus subtilis Bp19, Rhodococcus rhodochrous Fp31, Microbacterium esteraromaticum Np20, Bacillus subtilis Bp15, Arthrobacter keyseri Fp38, Bacillus subtilis Bp13, Bacsubus methylp14, 2acillus trophicus Bp13) obtained by rescreening in Example 1 To compare the phosphorus removal rate, the experimental results are as follows figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that the phosphorus removal rate of Arthrobacter Fp64 in the present invention is 70.52% in a nutrient solution containing a final concentration of 10mg / L phosphorus. have significant advantages.
[0034] 2. Determination of salt tolerance
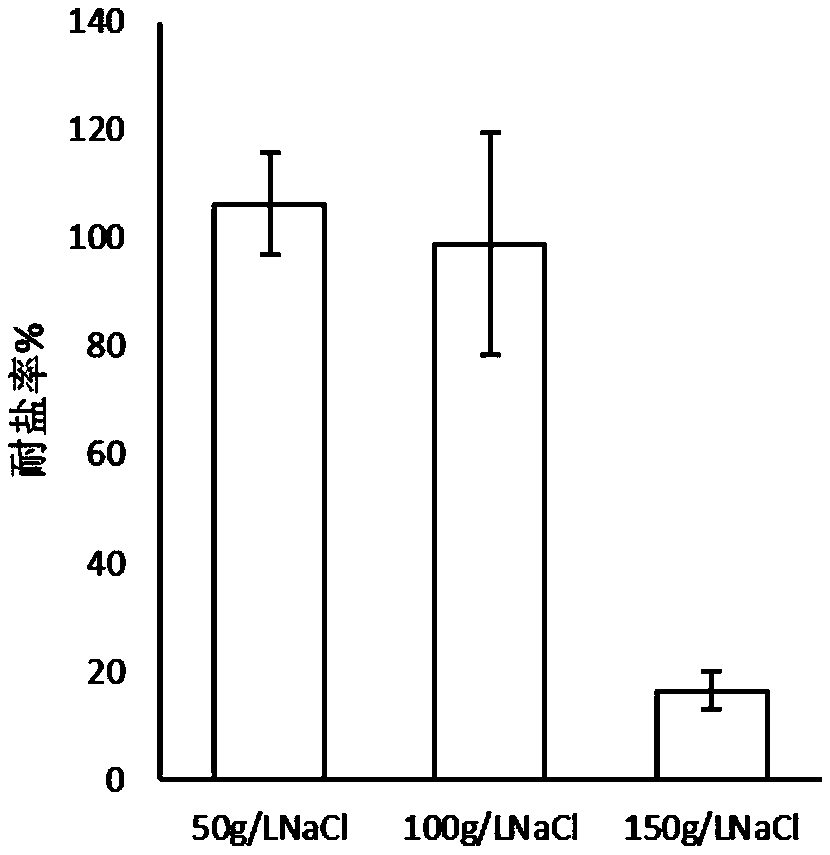
[0035] After the Arthrobacter Fp64 shaker of the present invention is activated, it is inoculated into LB liquids added with 50, 100 and 150 g / L NaCl ...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Soil adaptability of embodiment 3 Arthrobacter Fp64 and the effect measurement of reducing soil phosphorus loss
[0039] Cucumber seedlings were planted in a permeable pot with a diameter of 12 cm and a height of 30 cm. The potting soil was collected from the soil within 1 m of the greenhouse soil layer (the soil available phosphorus content was 49.55 mg / kg). The potting test was carried out immediately after the fresh soil was obtained. The treatment group was mixed with 20ml concentration of 1×10 8 / ml Arthrobacter Fp64 sterile water suspension soil, control group mixed with 20ml sterile water soil, five biological replicates were established. Measure the maximum water-holding capacity of the soil, water quantitatively and not exceed the water-holding capacity, and cultivate under the conditions of 25-28°C and 14-16h light.
[0040] In the treatment group and the control group, soil at a depth of 20 cm was collected at the time of inoculation and 30 days after cultiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com