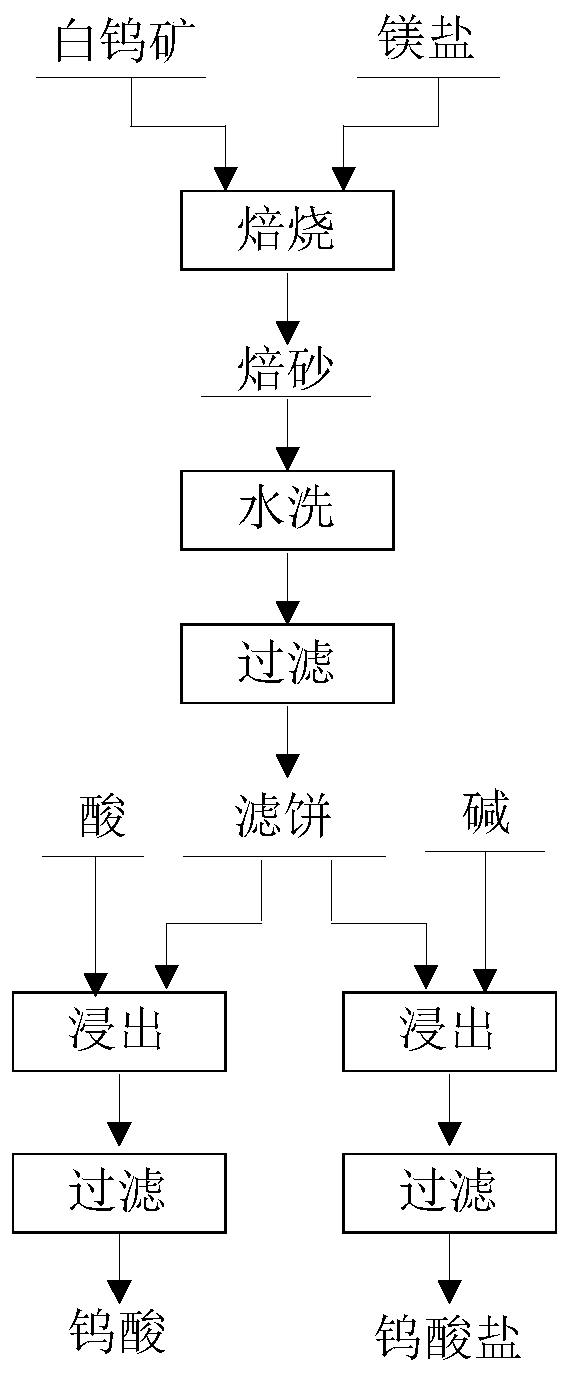
A method of processing scheelite
A technology of scheelite and magnesium salts, applied in the field of efficient leaching of tungsten in scheelite, can solve problems such as difficulty in extracting tungsten, reduce costs, avoid potential safety hazards, and improve leaching efficiency of tungsten ore
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
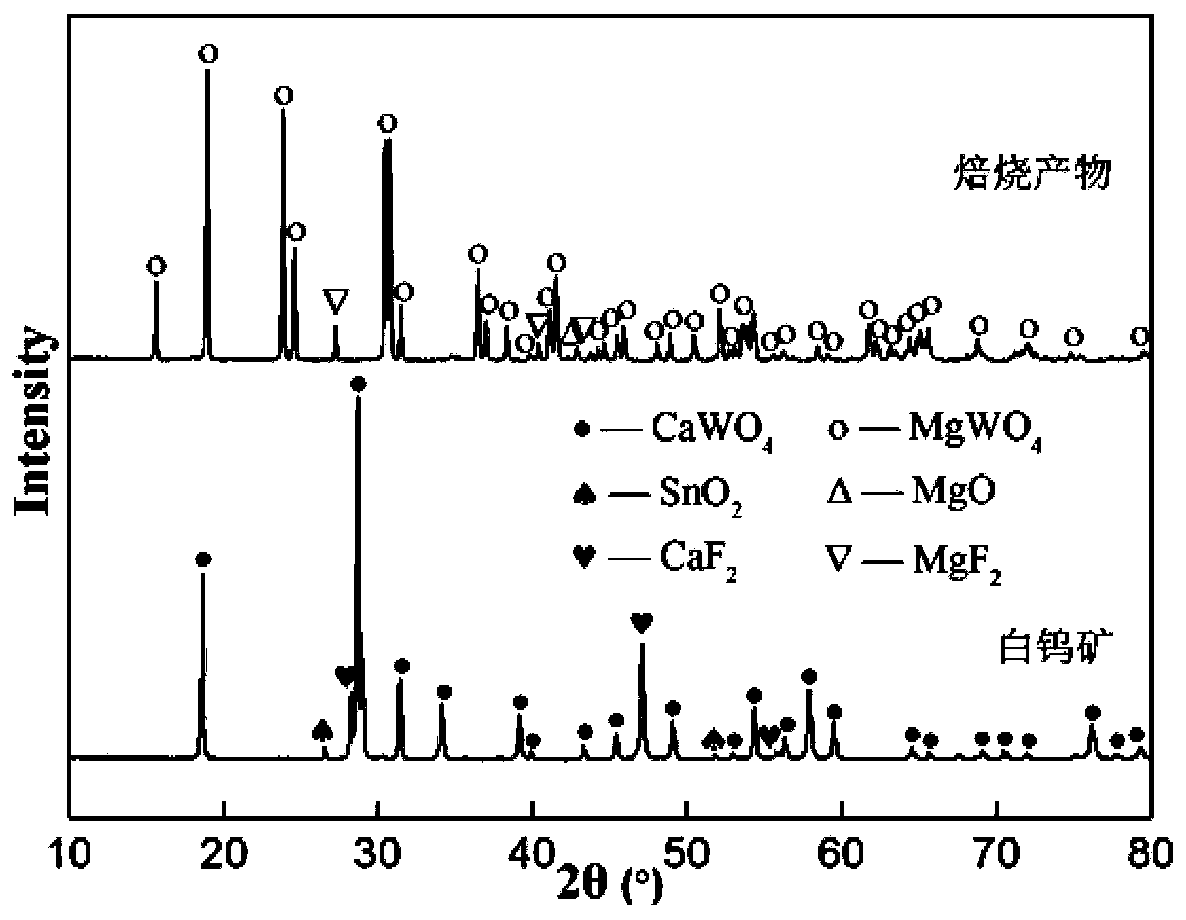
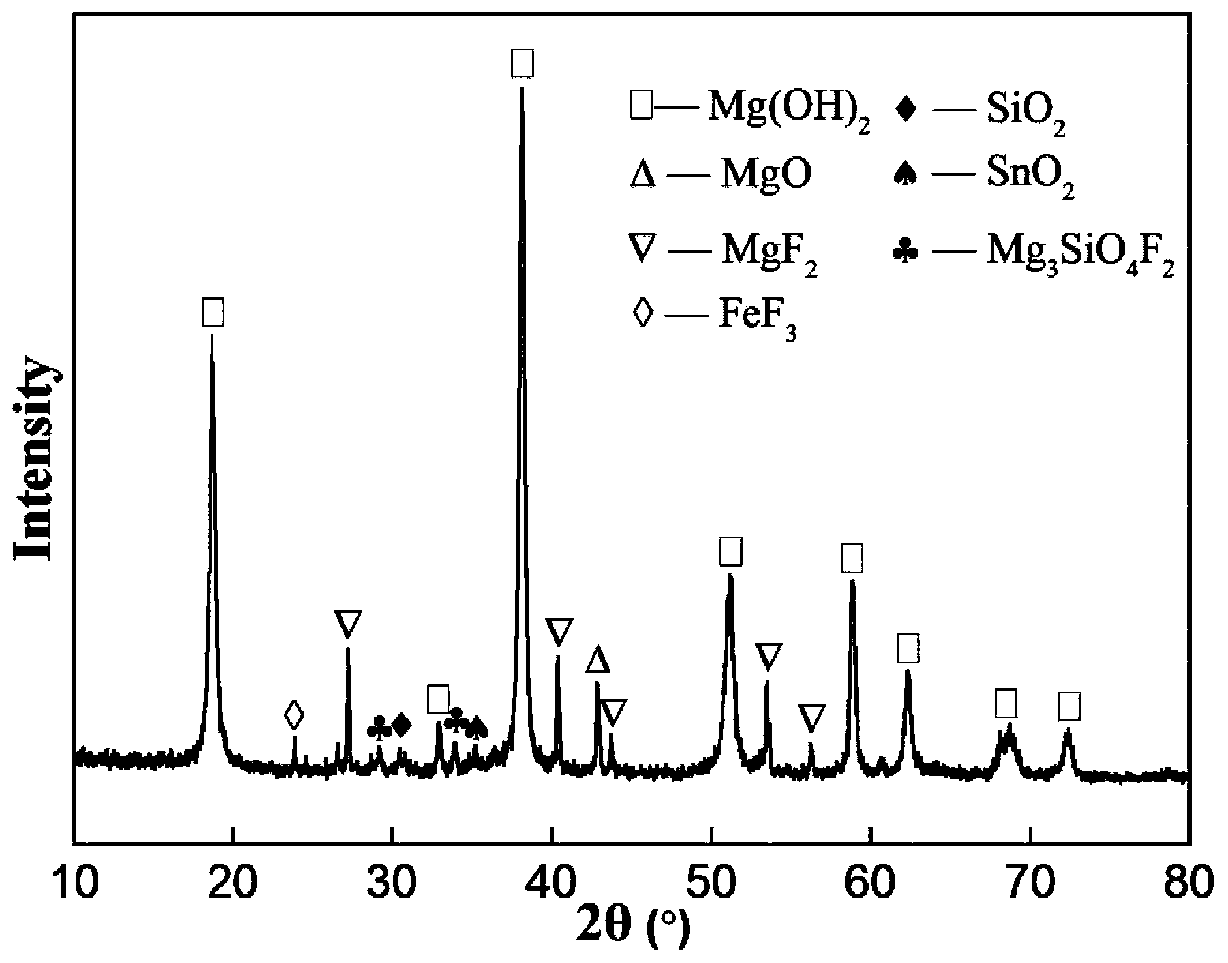
[0034] A certain scheelite contains WO 3 : 61.72%, the particle size is less than 200μm. Weigh 5g of the ore, add 4 times the theoretical amount of magnesium chloride, mix evenly, put it into a muffle furnace and roast at 670°C for 4 hours to obtain calcined sand; add 300mL deionized water to the calcined sand, stir at room temperature for 2 hours, filter, and wash to obtain Filter cake: Add 30 mL of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 6 mol / L to the filter cake, react at 60°C for 3 hours, and then filter to obtain tungstic acid, the extraction rate of metal W is 99.4%.
[0035] Control experiment: A certain scheelite contains WO 3: 61.72%, the particle size is less than 200μm. Weigh 5 g of the ore, add 30 mL of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 6 mol / L, react at 60° C. for 3 hours, and then filter to obtain tungstic acid. The extraction rate of metal W is 72.3%.
Embodiment 2
[0037] A certain scheelite contains WO 3 : 43.89%, the particle size is less than 200μm. Weigh 5g of the ore, add 3 times the theoretical amount of magnesium nitrate, mix evenly, put it into a muffle furnace and roast at 650 degrees for 6 hours to obtain calcined sand; add 200mL deionized water to the calcined sand, stir at room temperature for 3 hours, filter, wash, Obtain a filter cake; add 40 mL of nitric acid with a concentration of 3 mol / L to the filter cake, react at 80° C. for 4 hours, and then filter to obtain tungstic acid. The extraction rate of metal W is 98.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0039] A certain scheelite contains WO 3 : 26.45%, the particle size is less than 200μm. Weigh 5g of the ore, add 6 times the theoretical amount of magnesium nitrate, mix evenly, put it into a muffle furnace and roast at 670°C for 8 hours to obtain calcined sand; add 400mL deionized water to the calcined sand, stir at room temperature for 3 hours, filter, wash, Obtain a filter cake; add 40 mL of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 8 mol / L to the filter cake, react at 30° C. for 5 hours, and then filter to obtain tungstic acid. The extraction rate of metal W is 98.2%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com