Corrosion-resistant zirconium-tantalum-niobium-hafnium alloy and preparation method thereof
A technology for corroding zirconium and tantalum and niobium, which is applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as the impact on the life of nuclear materials and nuclear waste storage containers, and achieve the effect of simple preparation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] (1) According to the percentage by weight of zirconium, niobium, tantalum and hafnium, tantalum: 0.1%, niobium: 0.5%, hafnium: 0.1%, and the remaining zirconium is compressed into industrial-grade sponge zirconium, zirconium-tantalum master alloy and zirconium-niobium master alloy to obtain monolithic electrode;
[0018] (2) welding the monolithic electrode group obtained in the step (1) into a consumable electrode;
[0019] (3) Carry out vacuum consumable smelting to the consumable electrode that described step (2) obtains, the voltage of vacuum consumable smelting is 33V, and the vacuum degree of vacuum consumable smelting is 5 * 10 -3 Pa, the current of vacuum consumable smelting is 185A, the melting coefficient of vacuum consumable smelting is 0.95kg / (kA·min), smelting twice, and the corrosion-resistant zirconium-niobium-tantalum-hafnium alloy is obtained.
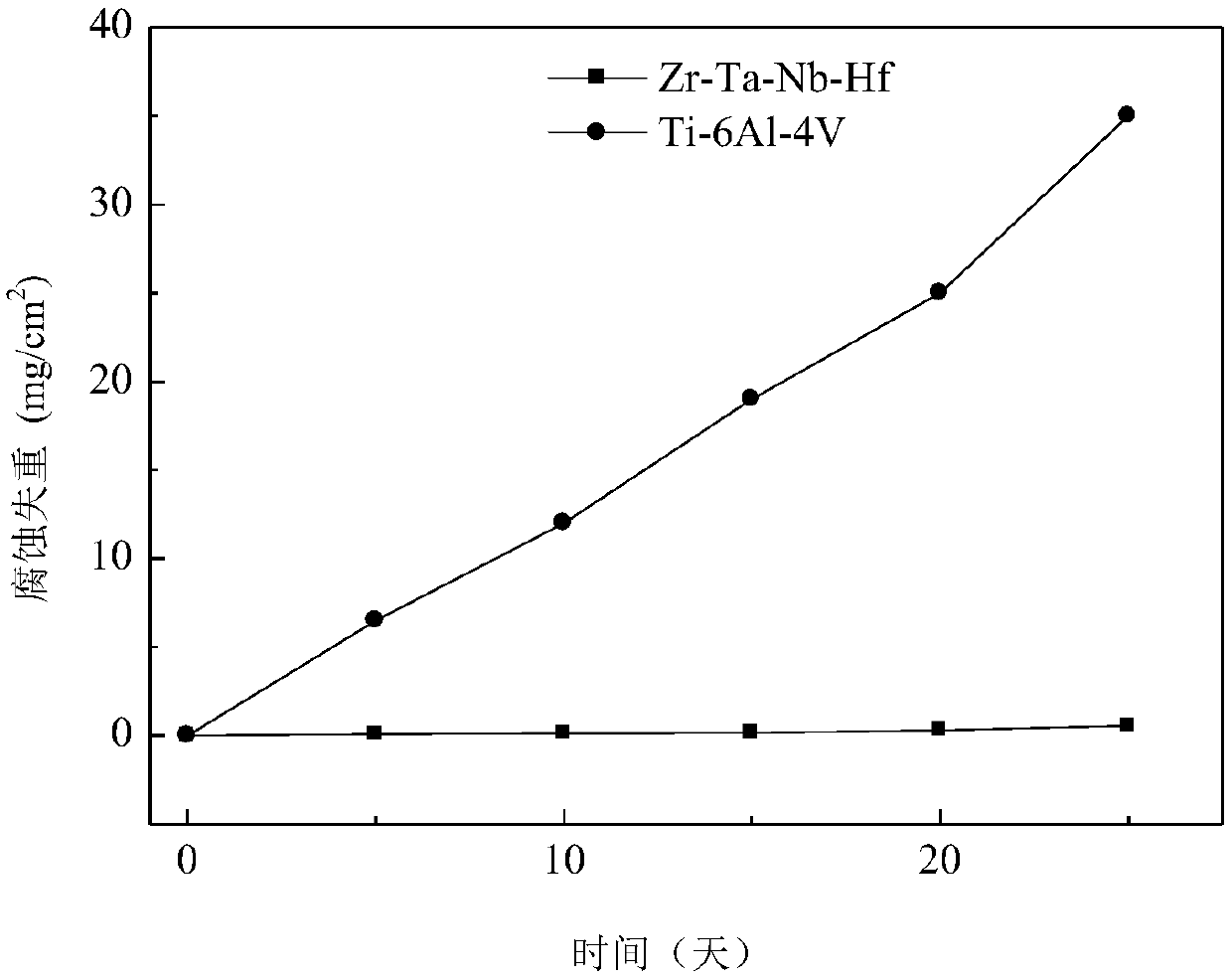
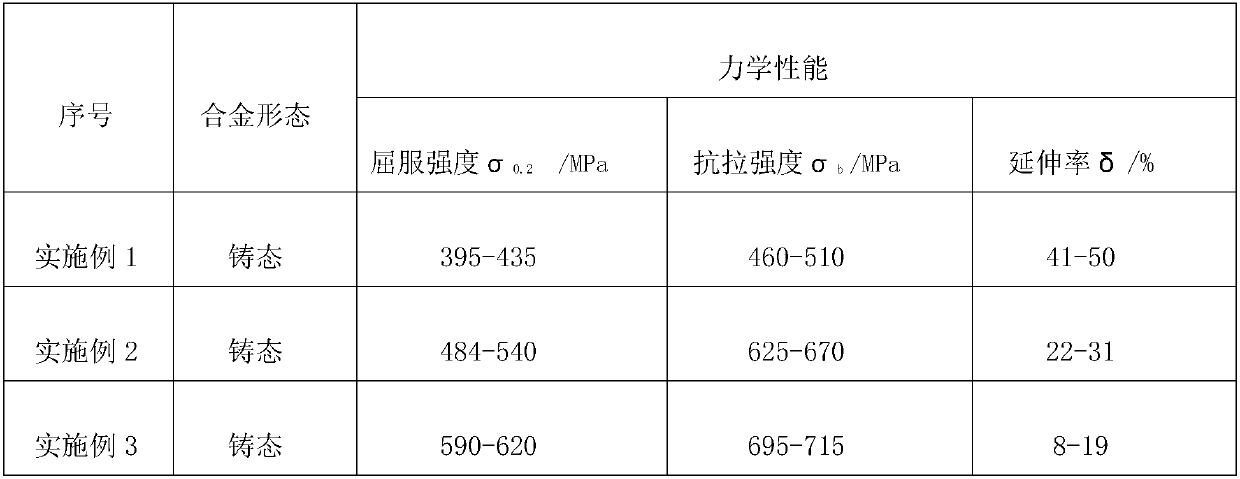
[0020] The corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the prepared corrosion-resistant zirconium-niob...
Embodiment 2
[0023] (1) According to the percentage by weight of zirconium, niobium, tantalum and hafnium, tantalum: 5%, niobium: 1.75%, hafnium: 2.5%, and the remaining zirconium is compressed into industrial-grade sponge zirconium, zirconium-tantalum master alloy and zirconium-niobium master alloy to obtain monolithic electrode;
[0024] (2) welding the monolithic electrode group obtained in the step (1) into a consumable electrode;
[0025] (3) Carry out vacuum consumable smelting to the consumable electrode that described step (2) obtains, the voltage of vacuum consumable smelting is 33V, and the vacuum degree of vacuum consumable smelting is 5 * 10 -3 Pa, the current of vacuum consumable smelting is 185A, the melting coefficient of vacuum consumable smelting is 0.95kg / (kA·min), smelting 3 times, and the corrosion-resistant zirconium-niobium-tantalum-hafnium alloy is obtained.
[0026] The corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the prepared corrosion-resistant zirconium-nio...
Embodiment 3
[0028] (1) According to the percentage by weight of zirconium, niobium, tantalum and hafnium, tantalum: 10%, niobium: 3%, hafnium: 5%, and the remaining zirconium is compressed into industrial-grade sponge zirconium, zirconium-tantalum master alloy and zirconium-niobium master alloy to obtain monolithic electrode;
[0029] (2) welding the monolithic electrode group obtained in the step (1) into a consumable electrode;
[0030] (3) Carry out vacuum consumable smelting to the consumable electrode that described step (2) obtains, the voltage of vacuum consumable smelting is 33V, and the vacuum degree of vacuum consumable smelting is 5 * 10 -3 Pa, the current of vacuum consumable smelting is 185A, the melting coefficient of vacuum consumable smelting is 0.95kg / (kA·min), smelting 3 times, and the corrosion-resistant zirconium-niobium-tantalum-hafnium alloy is obtained.
[0031] The corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the prepared corrosion-resistant zirconium-niobium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com