A kind of preservation method of solanacearum phage
A preservation method and technology of R. solanacearum, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, preservation of microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of short preservation time, large titer drop, unsatisfactory effect, etc., and achieve reasonable operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] 1. Acquisition of R. solanacearum: From naturally occurring tobacco plants, the dilution coating separation method is used to isolate, and a single colony is picked for 3-5 times of purification to obtain wild R. solanacearum.
[0016] 2. Screening of non-toxic strains: wild R. solanacearum isolated from naturally occurring tobacco plants, after more than 20 generations of continuous culture, pick colonies with poor fluidity and carry out pathogenicity measurement. The measurement results show that the strain loses its pathogenicity to tobacco. The pathogenicity is a mutant strain of the virulent R. solanacearum, named RSsw326-2.
[0017] 3. Determination of pathogenicity: Pick a single colony of the mutant strain obtained by subculture and shake it in NB liquid medium (28°C, 180rpm) to a concentration of about 10 8 CFU / mL, using root irrigation to inoculate 5 true leaves of tobacco seedlings, 30 days after the inoculation treatment, the inoculated tobacco was the same ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2 Determination of the host range of avirulent strains:
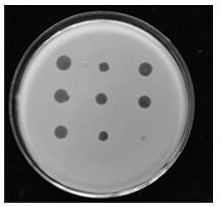
[0024] The host range of avirulent strains was determined using the spot method. The specific operation is:
[0025] Take 1mL log phase R. solani ( Ralstonia solanacearium ) culture into the CPG semi-solid medium, mix well and pour it onto the pre-prepared CPG solid agar plate, after solidification, take 0.5 μL phage stock solution dropwise onto the surface of the plate, dry it, and incubate it upside down at 28°C overnight. 2d Observe the formation of plaques. The results showed that the strain could be parasitized by R. solanacearum phage ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0027] (1) Inoculate the strain RSsw326-2 on a CPG plate, turn it upside down, and culture it at 28°C for 24-48 hours to make it grow a single colony.
[0028] (2) Pick a single colony of the strain RSsw326-2 in a Erlenmeyer flask filled with 100mL NB medium, and culture it at 28°C with shaking at 180rpm until the concentration is about 10 8 cfu / ml.
[0029] (3) Add 1mL of phage stock solution, mix well, let stand for 15min, shake overnight at 28°C and 130rpm, and culture to completely lyse the bacteria.
[0030] (4) Centrifuge the co-cultivation solution at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes, and filter the supernatant with a 0.45 μm filter membrane to obtain the phage stock solution.
[0031] (5) Take the cultured phage stock solution, measure its titer and record it for future use.
[0032] (6) The phage stock solution (2.29*10 10 PFU / mL) do the following: ①Store the stock solution at room temperature; ②Store the stock solution at 4°C; ③Store the stock solution at -20°C; ④Store t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com