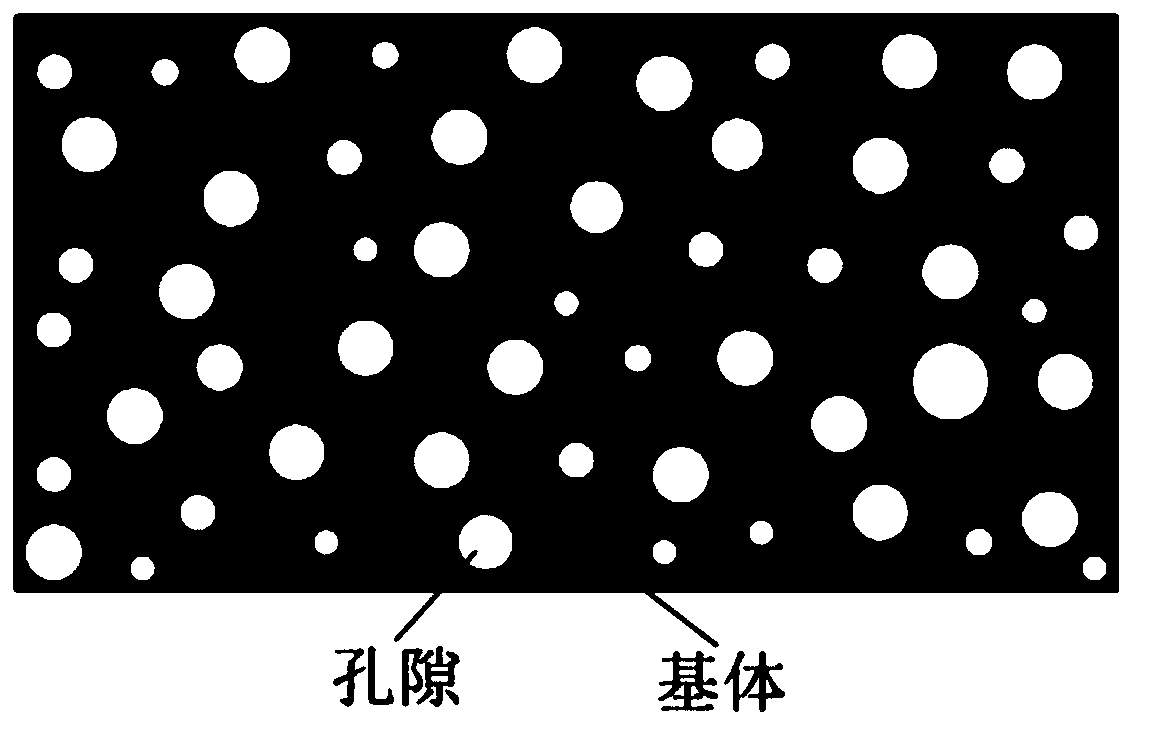
Carbon fiber brake pad material with porous structure and preparation method of carbon fiber brake pad material
A porous structure, carbon fiber technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, friction linings, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problem that carbon fibers cannot effectively transmit loads, affect the strength and wear resistance of composite materials, and the friction coefficient and wear rate fluctuations are relatively high. Large and other problems, to achieve the effect of increasing the effective bonding area, improving the tensile strain capacity, and reducing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
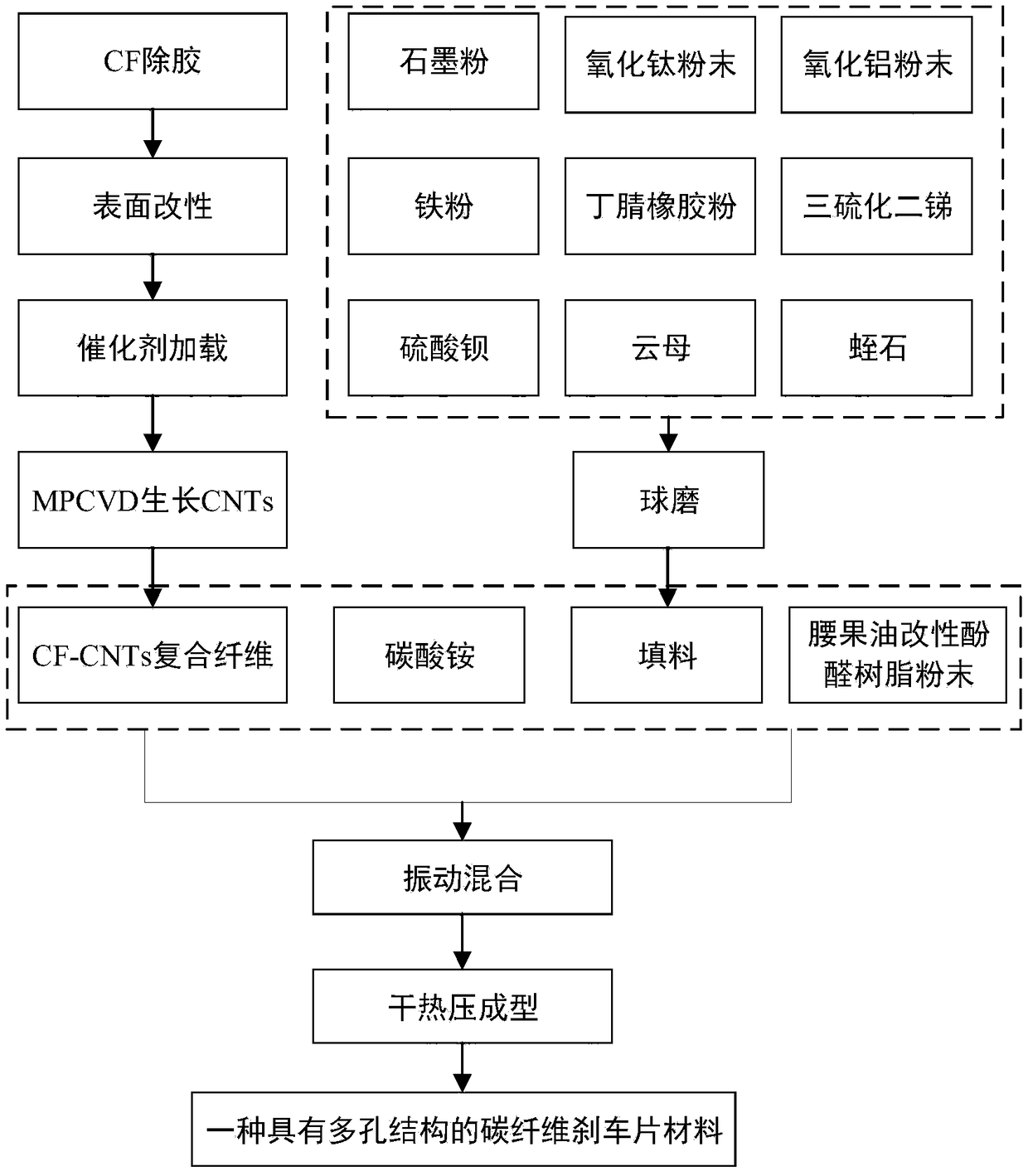
[0034] A carbon fiber brake pad material with a porous structure, which uses carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fibers and fillers as a matrix, uses cashew nut oil modified phenolic resin as a binder, and is obtained by adding pore-forming agent ammonium carbonate and adopting a dry hot pressing molding process The fillers include graphite, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, iron, nitrile rubber, antimony trisulfide, barium sulfate, mica, and vermiculite; the components and mass percentages in the adhesive and the matrix are: cashew nut oil modified phenolic 15% resin, 22% carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fiber, 6% graphite, 2% titanium oxide, 2% aluminum oxide, 2% iron, 15% nitrile rubber, 6% antimony trisulfide, 16% barium sulfate, 6% of mica, 8% of vermiculite; the mass percentage of the pore-forming agent ammonium carbonate is 16% of the total mass of the binder and the matrix.
[0035] The preparation method of the above-mentioned carbon fiber brake pad material wi...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A carbon fiber brake pad material with a porous structure, which uses carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fibers and fillers as a matrix, uses cashew nut oil modified phenolic resin as a binder, and is obtained by adding pore-forming agent ammonium carbonate and adopting a dry hot pressing molding process The fillers include graphite, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, iron, nitrile rubber, antimony trisulfide, barium sulfate, mica, and vermiculite; the components and mass percentages in the adhesive and the matrix are: cashew nut oil modified phenolic 10% resin, 28% carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fiber, 5% graphite, 2% titanium oxide, 3% aluminum oxide, 3% iron, 15% nitrile rubber, 6% antimony trisulfide, 15% barium sulfate, 6% of mica, 7% of vermiculite; the mass percentage of the pore-forming agent ammonium carbonate is 18% of the total mass of the binder and the matrix.
[0046] The preparation method of the above-mentioned carbon fiber brake pad material wi...
Embodiment 3
[0056] A carbon fiber brake pad material with a porous structure, which uses carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fibers and fillers as a matrix, uses cashew nut oil modified phenolic resin as a binder, and is obtained by adding pore-forming agent ammonium carbonate and adopting a dry hot pressing molding process The fillers include graphite, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, iron, nitrile rubber, antimony trisulfide, barium sulfate, mica, and vermiculite; the components and mass percentages in the adhesive and the matrix are: cashew nut oil modified phenolic 8% resin, 30% carbon fiber-carbon nanotube composite fiber, 5% graphite, 2% titanium oxide, 3% aluminum oxide, 3% iron, 15% nitrile rubber, 6% antimony trisulfide, 15% barium sulfate, 6% of mica, 7% of vermiculite; the mass percentage of the pore-forming agent ammonium carbonate is 20% of the total mass of the binder and the matrix.
[0057] The preparation method of the above-mentioned carbon fiber brake pad material wit...
PUM
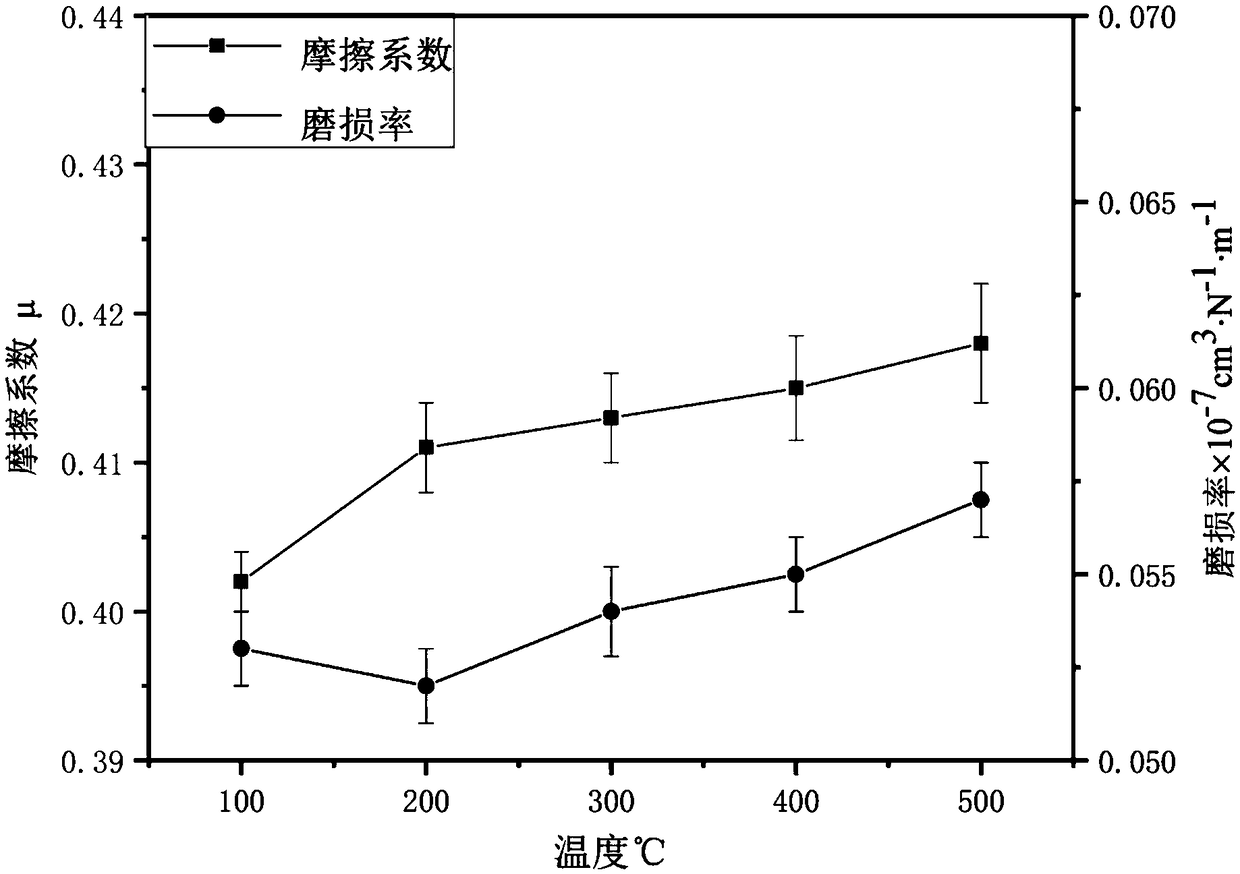
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| friction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com