Method for preparing retinal pigment epithelial cell slice by using autologous immunocyte
A technology of retinal pigment and autoimmunity, applied in the field of cell sheet preparation, can solve problems such as limited quantity, difficult source of RPE cells, unresolved social and ethical issues, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Example 1 Obtaining autologous immune cells from the patient's own peripheral blood
[0093] Obtaining autologous immune cells from the patient's own peripheral blood includes the following steps:
[0094] Firstly, the patient's own peripheral blood is diluted with normal saline, then added to the lymphocyte separation medium, centrifuged horizontally at room temperature, and stratified; Discard the supernatant and collect the autologous immune cells.
[0095] The detailed steps of this embodiment are:
[0096] Collect 50ml of the patient's own peripheral blood, and use TBD sample density separation medium (purchased from Tianjin Haoyang Huake Biology) to obtain autoimmune cells:
[0097] 1) Dilute 50ml of peripheral blood with normal saline at a ratio of 1:1. Carefully add the diluted blood to the same volume of lymphocyte separation medium to form obvious layers, and centrifuge horizontally at room temperature at 1200rpm / min for 20min. At this time, four layers ar...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 Dedifferentiation of autologous immune cells into pluripotent induced stem cells in vitro
[0100] The in vitro dedifferentiation of autologous immune cells into pluripotent induced stem cells includes the following steps:
[0101] After the immune cells obtained from RPMI (gibco) medium were cultured overnight, the cells were transfected with four kinds of lentiviruses respectively carrying transformation factors OCT4, SOX2, KLF4 and C-MYC, and the cells were constructed with transformation factors OCT4, The four plasmids of SOX2, KLF4 and C-MYC are ready for use after being sequenced correctly;
[0102] Using the lentiviral packaging kit, inoculate the lentiviral packaging cell line 293T in a culture dish, culture it, and use the obtained four plasmids with transformation factors OCT4, SOX2, KLF4 and C-MYC to transfect the lentiviral packaging cells respectively Line 293T, obtained recombinant pLent-OCT4 lentivirus, recombinant pLent-SOX2 lentivirus, recomb...
Embodiment 3I
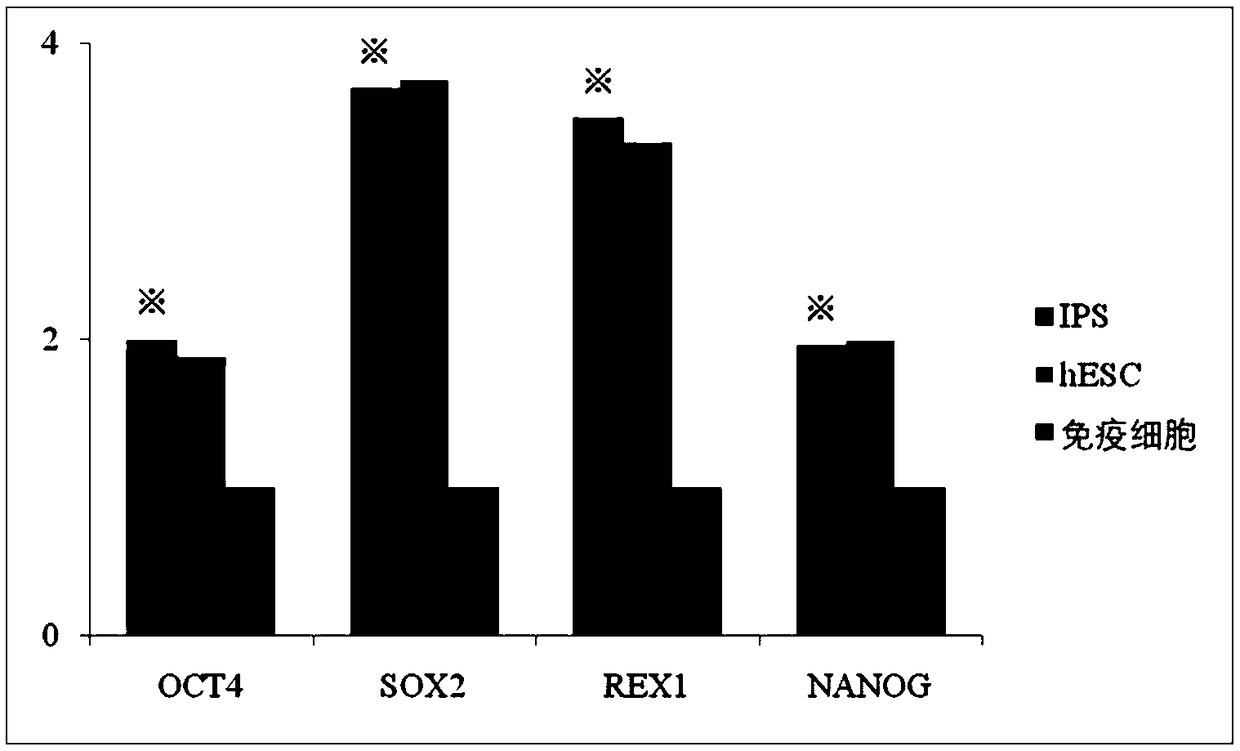
[0131] Identification of Example 3IPS (Induced Multi-Pluripotent Stem Cells)
[0132] The IPS cells obtained in Example 2 were subcultured to the 4th generation and then detected by fluorescent quantitative PCR.
[0133] In this example, the specific method: centrifuge to collect IPS cells into EP tubes, and use RNAisoTM Plus to lyse the cells to extract total RNA. Put the above-mentioned EP tube into a centrifuge at 4°C and centrifuge at 12000rpm for 10min, transfer the supernatant to a new EP tube, and discard the precipitate. An equal volume of chloroform solution was added to the supernatant, vortexed, and allowed to stand at room temperature for 7 minutes. Centrifuge at 4°C and 12000rpm for 15 minutes. At this time, the liquid in the EP tube is divided into three layers, and the white layer in the middle is the protein layer. Take the upper aqueous phase and transfer it to a new EP tube (RNA exists in the aqueous phase); add, etc. Add a volume of isopropanol to the tran...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Titer | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com