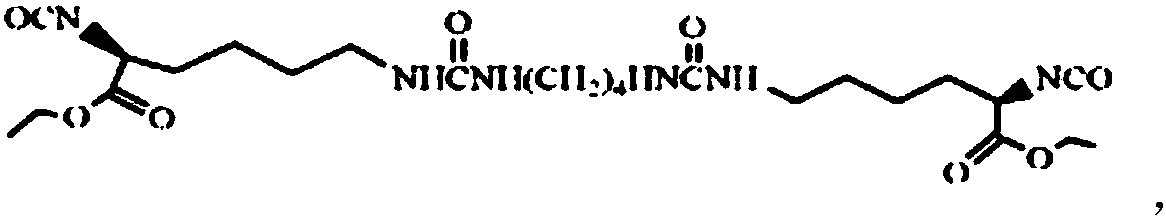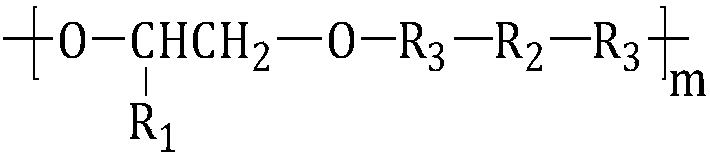Preparation method and application of high-biocompatibility biodegradable bone filling material
A technology of filling materials and compounds, used in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problem of not improving the in vitro degradation performance of PPDO
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Preparation of Diisocyanate Chain Extender LBL Containing Urea Structure
[0076] Under dry nitrogen protection and mechanical stirring, add 1,4-butanediamine dropwise to L-lysine diisocyanate (-NCO:-NH 2 =8:1, molar ratio), after reacting at room temperature for 2h, add four times the volume of n-hexane to the reaction product, after stirring evenly, obtain a white solid by suction filtration, wash with n-hexane repeatedly until the filtrate IR detects that there is no -NCO absorption Peak (2270cm -1 ), vacuum-dried to constant weight to obtain white powder LBL.
Embodiment 2
[0078] Under the protection of dry nitrogen, 6.5g (5mmol) terminal dihydroxypolyethylene glycol phosphorylcholine compound (PC-(OH) 2 ,M n =1300) and 60.0g (25mmol) polydioxanone (PPDO, M n =2400) were mixed, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) was added to dissolve (0.5g / mL), the temperature of the reaction system was raised to 80°C, and a DMF solution (1.0g / mL) of LBL (30.6mmol) was added dropwise, After the dropwise addition, keep the temperature and continue the reaction for 4.0 hours, lower to room temperature, then add DMF to make a solution with a concentration of about 10%, settle with 8 times the volume of glacial ether, and dry the obtained solid under vacuum at 35°C to obtain high biocompatibility and biodegradability Polyurethane urea;
[0079] Dissolve the polyurethane urea in dioxane, control the mass volume concentration to 60%, stir the solution at 40° C. for 12 hours to obtain a homogeneous solution, put it into a mold (polytetrafluoroethylene) and freeze-dry to obt...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Under the protection of dry nitrogen, 6.5g (5mmol) terminal dihydroxypolyethylene glycol phosphorylcholine compound (PC-(OH) 2 ,M n =1300) and 48.0g (20mmol) polydioxanone (PPDO, M n =2400) were mixed, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) was added to dissolve (0.5g / mL), the temperature of the reaction system was raised to 85°C, a DMF solution (1.0g / mL) of LBL (25.8mmol) was added dropwise, After the dropwise addition, keep the temperature and continue the reaction for 3.5 hours, lower to room temperature, then add DMF to make a solution with a concentration of about 10%, settle with 8 times the volume of glacial ether, and dry the obtained solid under vacuum at 35°C to obtain high biocompatibility and biodegradability Polyurethane urea;
[0082] Dissolve the polyurethane urea in dioxane, control the mass volume concentration to 60%, stir the solution at 40° C. for 12 hours to obtain a homogeneous solution, put it into a mold (polytetrafluoroethylene) and freeze-dry to obtain ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com