Method for preparing gamma-aminobutyric acid by feeding substrate enzyme
A technology of aminobutyric acid and substrates, which is applied in the field of feeding substrate enzymes to prepare γ-aminobutyric acid, can solve the problems of low catalytic reaction stability, unfavorable industrial production, and prone to substrate inhibition, etc. Inhibition of substances, effective control, and good reproducibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
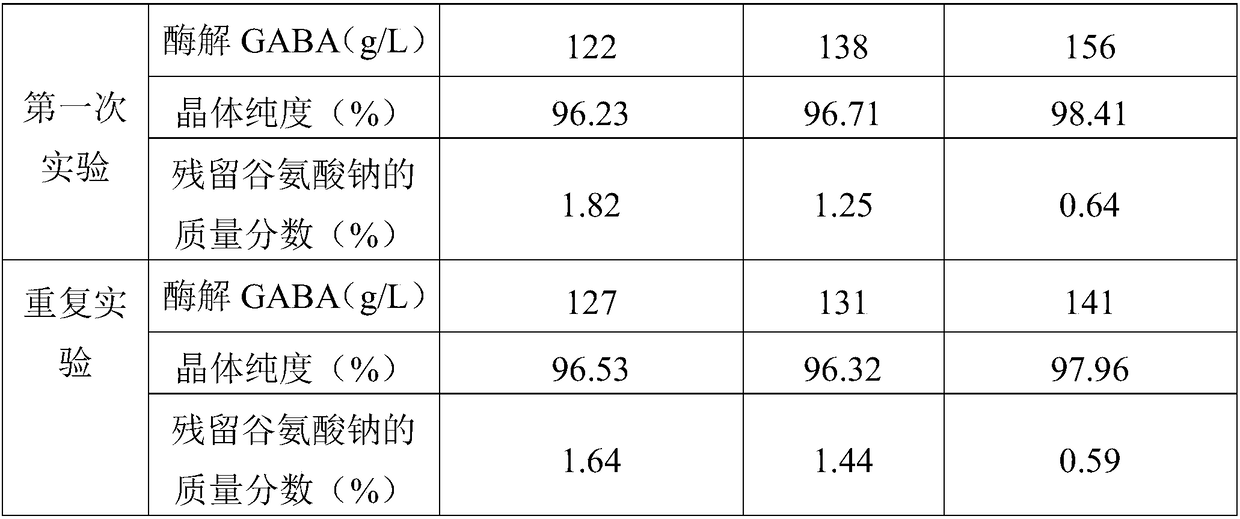
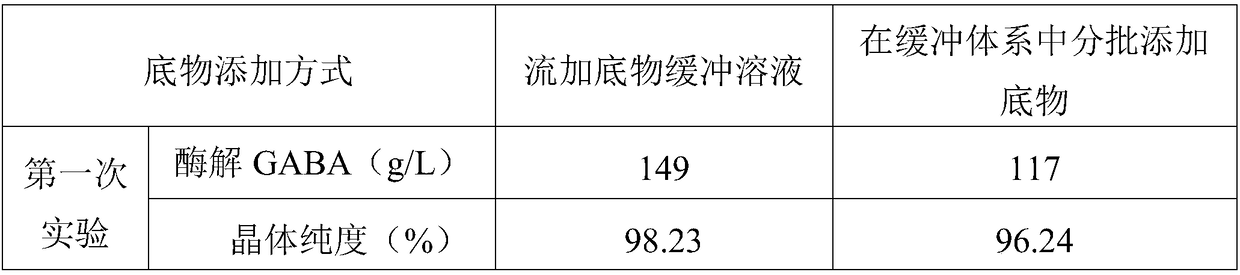
[0032] The invention discloses a method for preparing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by feeding substrate enzymes, respectively using citric acid-sodium citrate, acetic acid-sodium acetate and disodium hydrogen phosphate of 0.05mol / L and pH=4.5 -Three kinds of buffer solutions of citric acid dissolve the substrate sodium glutamate, prepare a mass fraction of 4% sodium glutamate solution; then adopt a membrane filter to filter the sodium glutamate solution to remove impurities and remove bacteria; After the enrichment culture, the bacterial slurry was obtained by membrane filtration; the bacterial slurry was divided into three parts, and transferred to three enzyme-catalyzed reaction tanks for stirring. The reaction temperature was controlled at 35°C, the pH was 4.5, and the stirring speed was adjusted to 100rpm, add three kinds of sodium glutamate solutions after impurity removal to the three reaction tanks continuously, control the concentration of residual sodium glutamate so...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The invention discloses a method for preparing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by feeding substrate enzymes. The substrate sodium glutamate is dissolved in a disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer solution of 0.05 mol / L and pH=4.5. Prepare sodium glutamate solutions with mass fractions of 2%, 4% and 6% respectively; then use a membrane filter to filter the sodium glutamate solution to remove impurities and eliminate bacteria; enrich and cultivate microorganisms, and pass through the membrane Filter to obtain the bacterial slurry; divide the bacterial slurry into 3 parts, and transfer to three enzyme-catalyzed reaction tanks for stirring respectively. Three kinds of sodium glutamate solutions with different mass fractions after impurity removal are added continuously in the internal flow, and the concentration of residual sodium glutamate solution is controlled between 10-45g / L. After each reaction for 36 hours, the bacterial cells are removed by membrane filtratio...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The invention discloses a method for preparing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by feeding substrate enzymes. The substrate sodium glutamate is dissolved in a disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer solution of 0.05 mol / L and pH=4.5. Prepare a sodium glutamate solution with a mass fraction of 4%; then use a membrane filter to filter the sodium glutamate solution to remove impurities and remove bacteria; enrich and cultivate the microorganisms, and obtain a bacterium slurry by membrane filtration after the end; Divide the slurry into 4 parts and transfer them to four enzyme-catalyzed reaction tanks for stirring respectively. Continuously add 4% sodium glutamate solution after removal of impurities in the tank, control the concentration of residual sodium glutamate solution between 10-45g / L, after each reaction for 36 hours, remove bacteria by membrane filtration, and obtain enzymolysis clear liquid , then detect the content of GABA prepared in four reaction tanks by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com