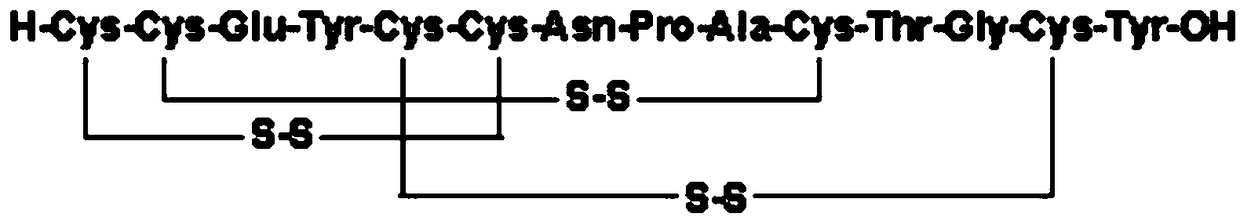
Pharmaceutical composition for preventing and treating intestinal type radiation sickness
A radiation sickness and composition technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem of intestinal radiation sickness that has not yet been seen in combination with FTY720 and linaclotide
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1 Establishment of mouse intestinal type radiation sickness model
[0066] 1. Selection and feeding of experimental animals
[0067] 50 male C57 / BL6 mice aged 6-8 weeks, weighing 20-25g. All mice were raised in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) grade animal room in a standardized animal center, fed with standard pellet feed, free to drink and eat, room temperature was (22±2)°C, and relative humidity was 40%-60%. After 7 days of adaptive feeding, they were used for experiments.
[0068] 2. The principle of making the model
[0069] Large doses of X-rays irradiating the abdomen of mice can cause gastrointestinal tissue damage and cause intestinal radiation sickness.
[0070] 3. Model preparation and standards
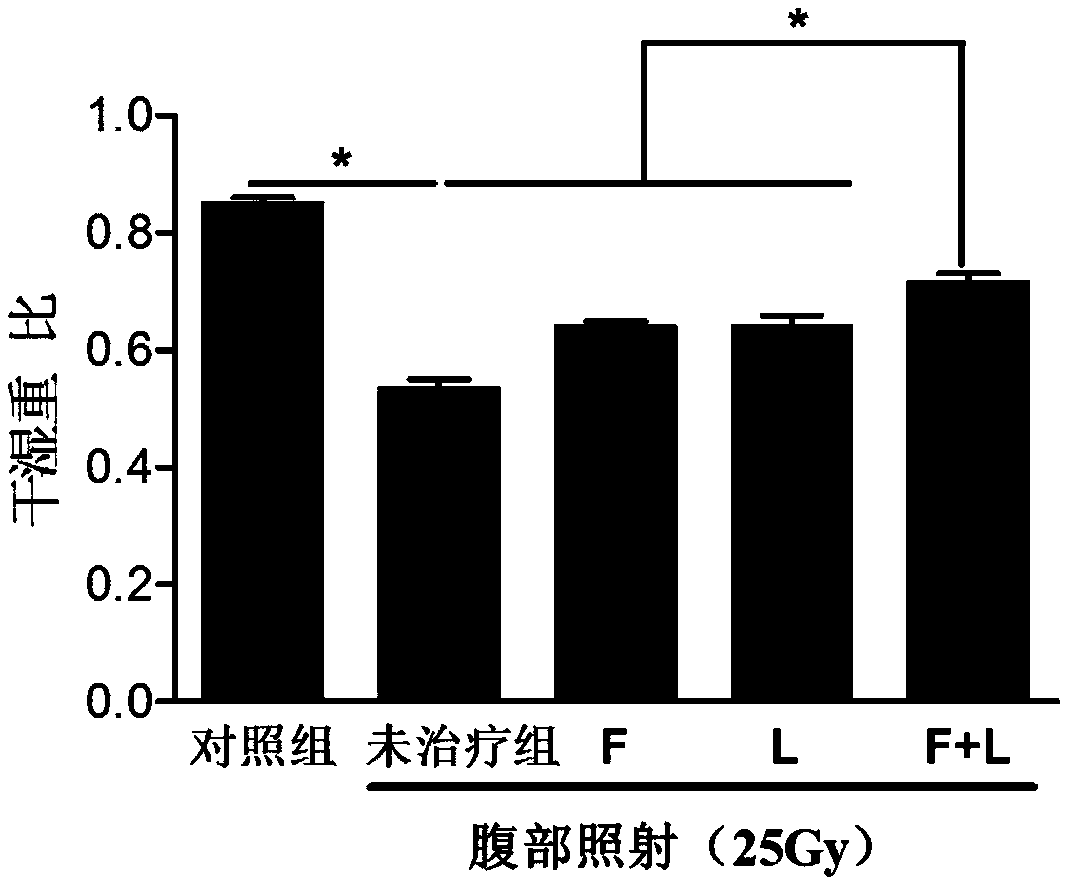
[0071] Shield the other parts of the mouse with a barrier device (such as a lead plate), expose the abdomen, give the mouse abdominal X-ray irradiation (25Gy), and detect a sharp decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood image, which means t...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2 The therapeutic effect of FTY720 and linaclotide on experimental animals
[0073]The model prepared above was used as the experimental object to verify the therapeutic effect of FTY720 and linaclotide on it.
[0074] 1. Administration method and specific route
[0075] Immediately after successful modeling, oral administration on an empty stomach, dose: FTY720, 1 mg / kg / time; linaclotide, 50 μg / kg / time, once a day for 10 days. The time interval between the two administrations is about 30 minutes.
[0076] 2. Section HE staining
[0077] 2.1 Materials
[0078] Mice were sacrificed and intestinal tissue removed.
[0079] 2.2 Slicing and staining
[0080] 2.3 Results
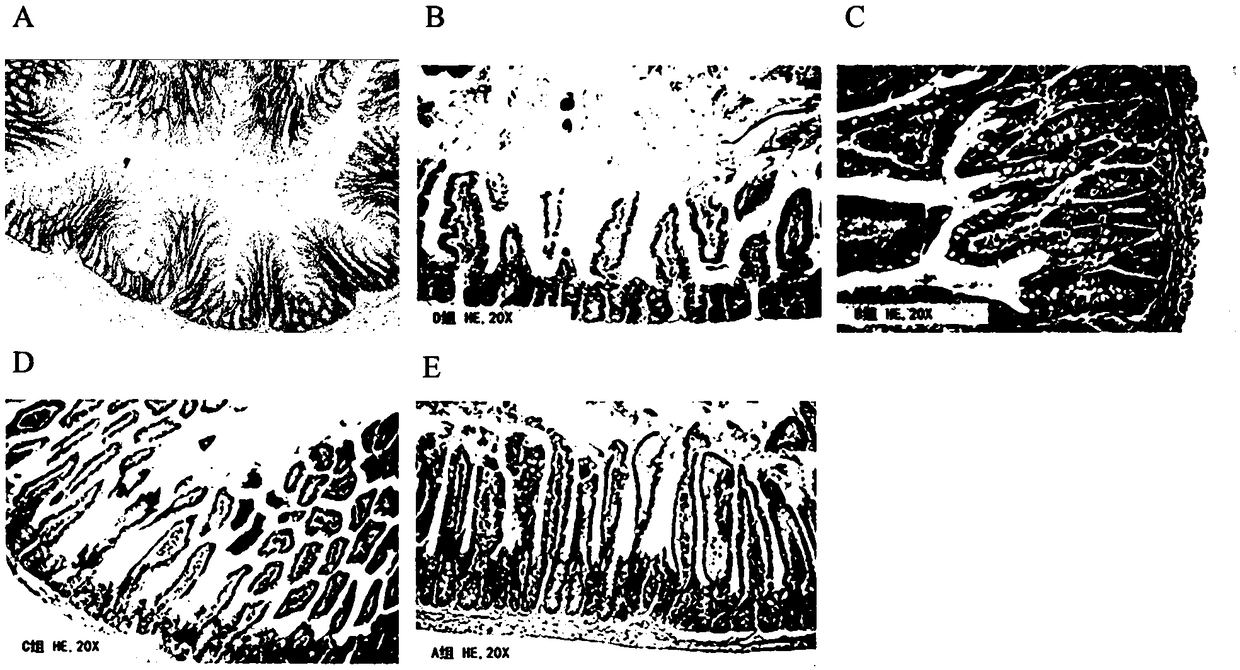
[0081] The result is as figure 2 As shown, severe intestinal tissue damage was seen in the untreated group, including epithelial-basement membrane separation in the intestinal mucosa, crypt cell edema, hyperemia, necrosis, and exposed villi. In the FTY720(F) treatment group and the linaclot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com