Low-drive-voltage lithium niobateelectrooptical modulator and manufacturing method thereof
An electro-optical modulator, low driving voltage technology, applied in the fields of instruments, optics, nonlinear optics, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the driving voltage of the modulator, the modulation efficiency is not high, increasing the driving voltage of the electro-optical modulator, etc., to reduce the driving voltage. , the effect of improving the modulation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
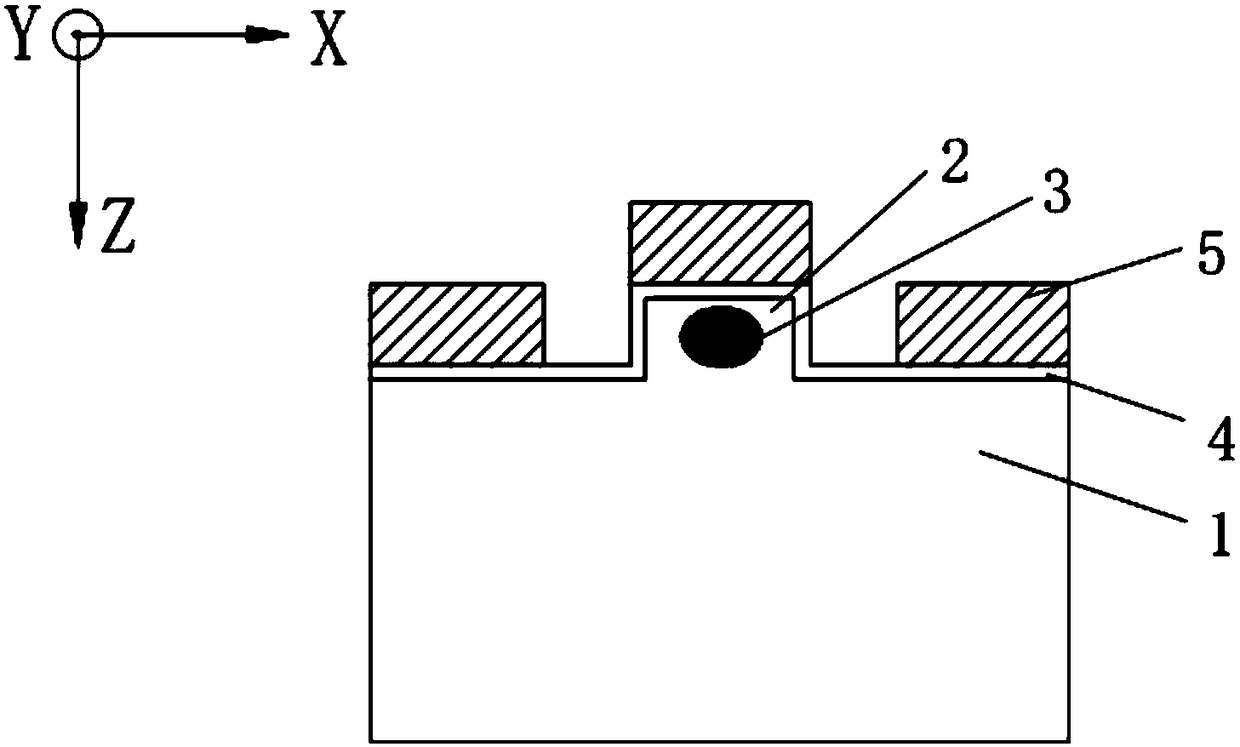
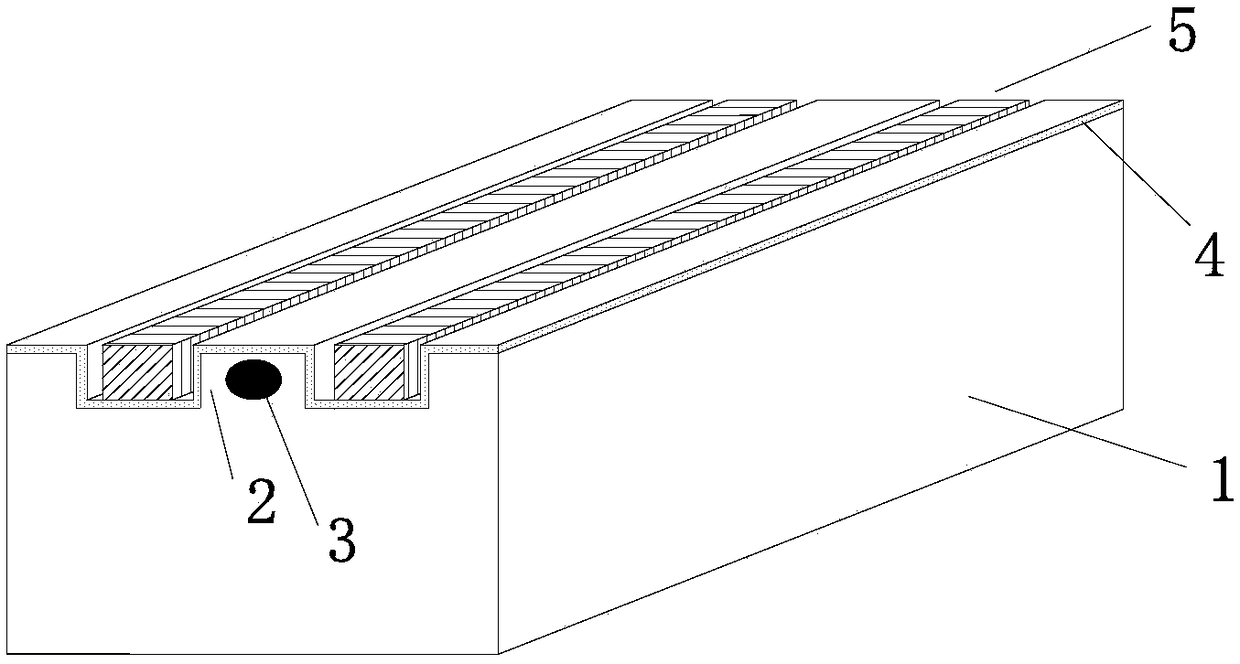
[0088] figure 2 and image 3 It is the first embodiment of the low driving voltage lithium niobate electro-optic modulator proposed by the present invention, which is a high modulation bandwidth (or high modulation rate) lithium niobate phase modulator. For lithium niobate electro-optic modulators with high modulation bandwidth (or high modulation rate), traveling wave electrode structure is often used, and silicon dioxide film is often added as a buffer layer to achieve speed matching and impedance matching, and improve device modulation bandwidth ( or modulation rate).
[0089] The lithium niobate electro-optic modulator provided in this embodiment includes: a lithium niobate wafer 1 , a ridge structure 2 , an optical waveguide 3 , a silicon dioxide film 4 , and a modulation electrode 5 .
[0090] The lithium niobate wafer 1 is a lithium niobate single crystal material, the tangential direction of the crystal is X-cut and Y-cut, and the thickness is 0.1 mm to 2 mm.
[00...
Embodiment 2
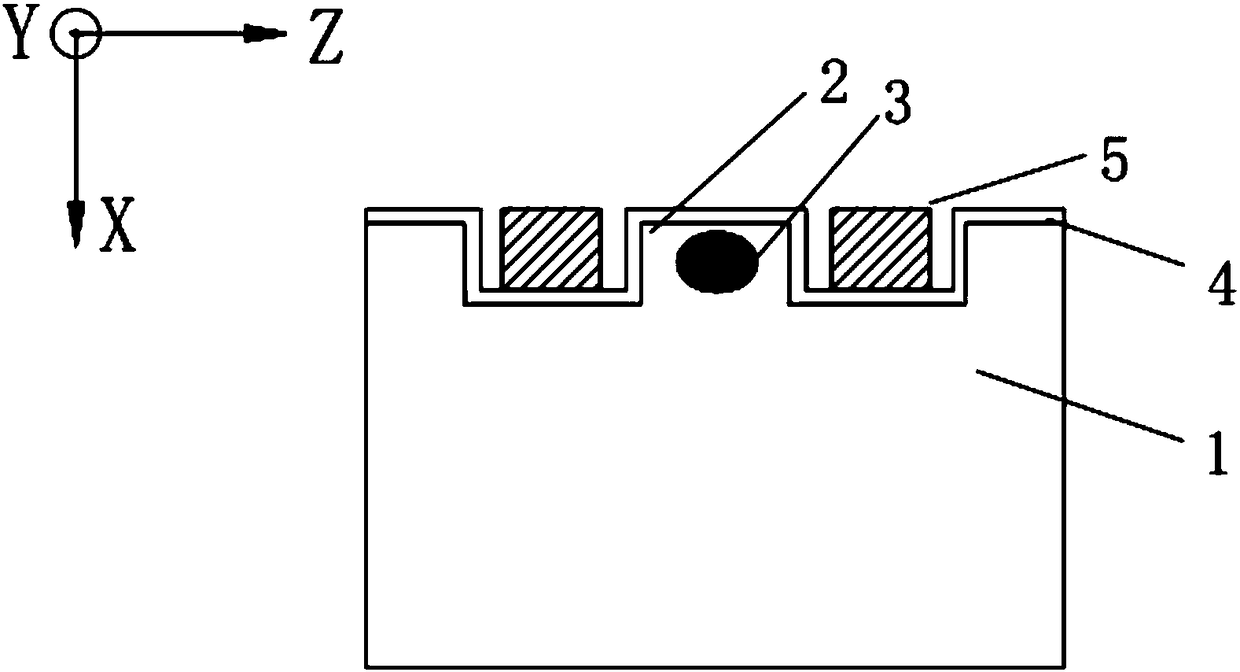
[0103] Figure 4 and Figure 5 It is the second embodiment of the low driving voltage lithium niobate electro-optic modulator proposed by the present invention, which is a high modulation bandwidth (or high modulation rate) lithium niobate intensity modulator. For lithium niobate electro-optic modulators with high modulation bandwidth (or high modulation rate), traveling wave electrode structure is often used, and silicon dioxide film is often added as a buffer layer to achieve speed matching and impedance matching, and improve device modulation bandwidth ( or modulation rate).
[0104] The lithium niobate electro-optic modulator provided in this embodiment includes: a lithium niobate wafer 1 , a ridge structure 2 , an optical waveguide 3 , a silicon dioxide film 4 , and a modulation electrode 5 .
[0105] The lithium niobate wafer 1 is a lithium niobate single crystal material, the tangential direction of the crystal is X-cut and Y-cut, and the thickness is 0.1 mm to 2 mm. ...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Figure 6 and Figure 7 It is the third embodiment of the low driving voltage lithium niobate electro-optic modulator proposed by the present invention, which is a phase modulator with high modulation bandwidth (or high modulation rate) based on lithium niobate thin film. By thinning the lithium niobate wafer and making the lithium niobate thin film on the low dielectric constant substrate wafer, it is beneficial to improve the modulation bandwidth (or modulation rate) of the lithium niobate electro-optic modulator, and the lithium niobate thin film is made The ridge structure is beneficial to reduce the driving voltage of the device while maintaining the high modulation bandwidth (or high modulation rate) of the lithium niobate electro-optic modulator provided in this embodiment.
[0119] The lithium niobate electro-optic modulator provided in this embodiment includes: a base wafer 6 , a lithium niobate thin film 7 , a ridge structure 2 , an optical waveguide 3 , and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com