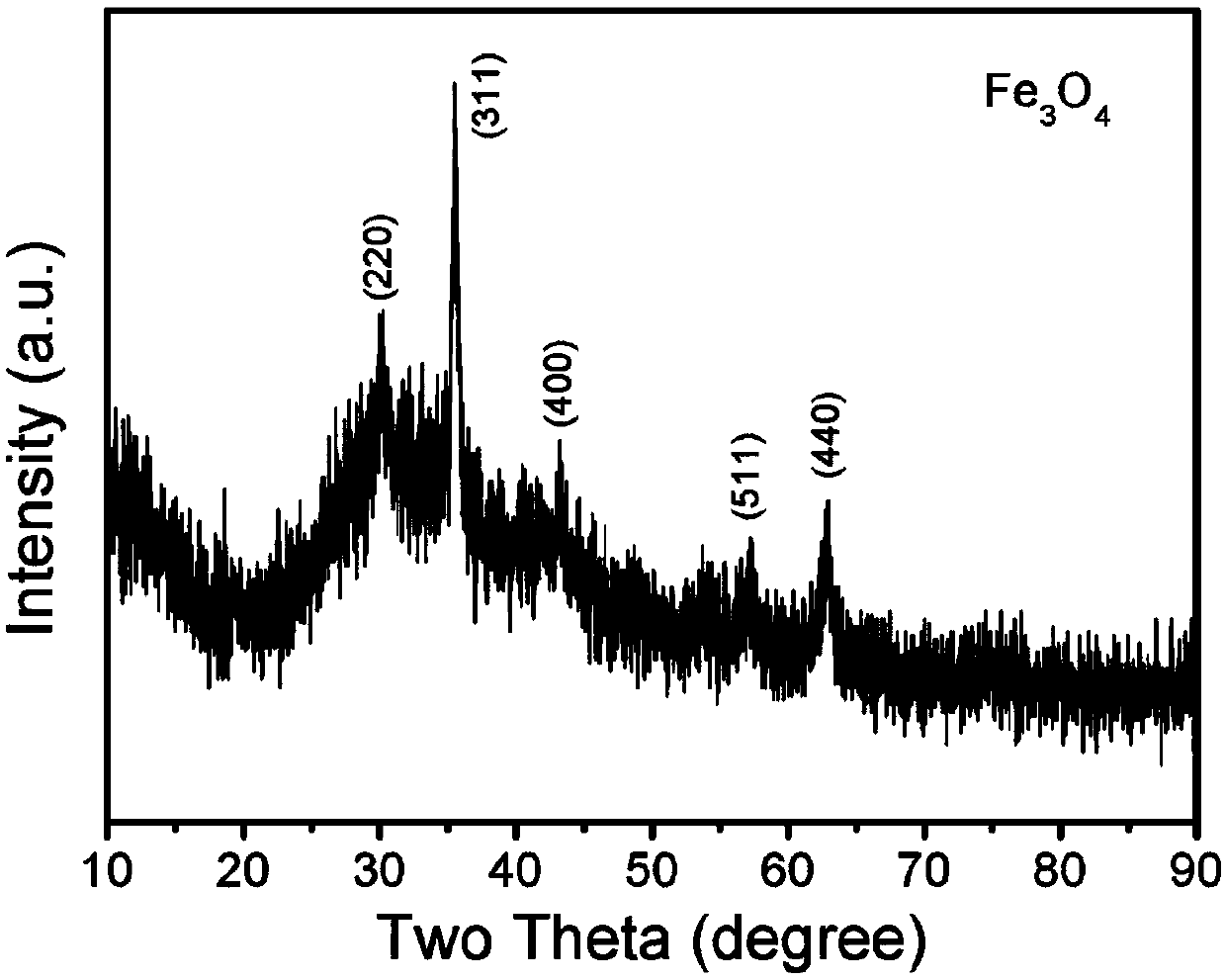
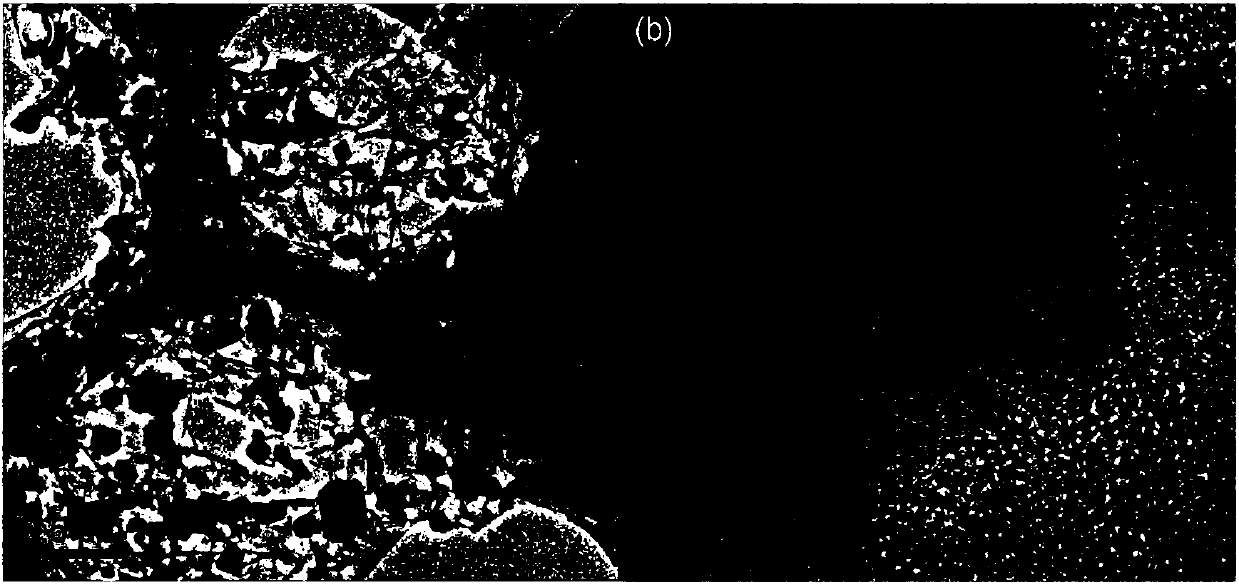
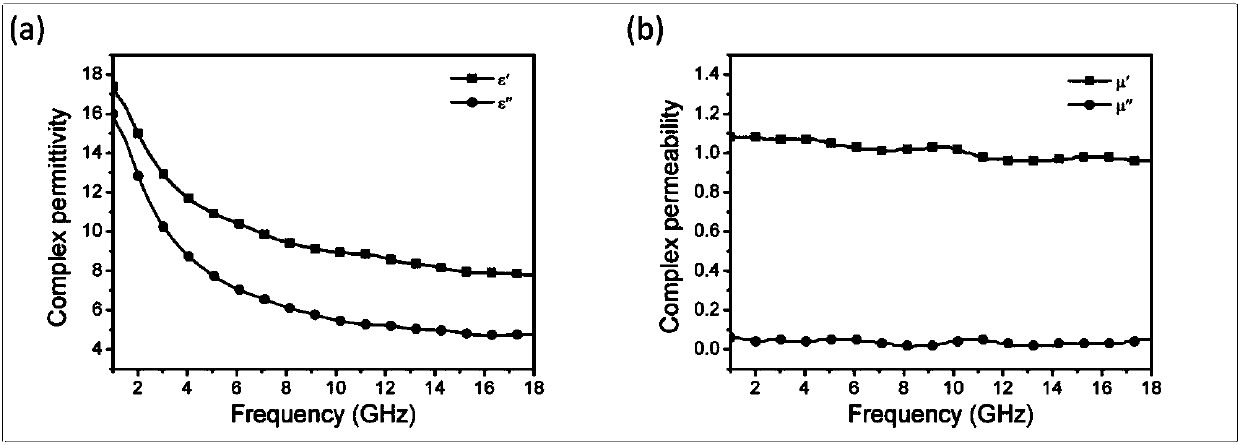
Preparation method of graphene-supported iron oxide nanoparticle composite wave-absorbing agent
A technology of ferric oxide and nanoparticles, which is applied in the field of wave absorbing materials, can solve the problems of difficulty in uniform distribution of graphene, easy agglomeration of ferric oxide nanoparticles, and difficult control of product purity, and achieves uniform distribution and good absorption. Wave properties, the effect of simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Weigh 3.592g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 4g of anhydrous glucose, and 26g of sodium chloride, dissolve the mixture in 300ml of deionized water and stir magnetically for 4 hours to obtain a uniform mixed solution. The resulting solution is processed by a spray dryer to obtain a composite material precursor powder. Take 10g of precursor powder and place it in the ark, put the ark into the constant temperature zone of the tube furnace, pass through 400ml / min Ar for 20min to exhaust the air, then use 100ml / min Ar as the protective atmosphere, and raise the temperature at a heating rate of 10℃ / min Heat at 700°C for 2 hours to carbonize glucose and reduce ferric nitrate. After the reaction, cool to room temperature under the protection of Ar atmosphere to obtain the first-step calcined product. Put the calcined product of the first step into a tube furnace, use 400ml / min air as the calcining atmosphere, and raise the temperature to 250°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, keep ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Weigh 2.694g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 4g of anhydrous glucose, and 26g of sodium chloride, dissolve the mixture in 300ml of deionized water and stir it magnetically for 4 hours to obtain a uniform mixed solution. The resulting solution is processed by a spray dryer to obtain a composite material precursor powder. Take 10g of precursor powder and place it in the ark, put the ark into the constant temperature zone of the tube furnace, pass through 400ml / min Ar for 20min to exhaust the air, then use 100ml / min Ar as the protective atmosphere, and raise the temperature at a heating rate of 10℃ / min Heat at 700°C for 2 hours to carbonize glucose and reduce ferric nitrate. After the reaction, cool to room temperature under the protection of Ar atmosphere to obtain the first-step calcined product. Put the calcined product of the first step into a tube furnace, use 400ml / min air as the calcining atmosphere, and raise the temperature to 250°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, ke...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Weigh 1.796g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, 4g of anhydrous glucose, and 26g of sodium chloride, dissolve the mixture in 300ml of deionized water and stir it magnetically for 4 hours to obtain a uniform mixed solution. The resulting solution is processed by a spray dryer to obtain a composite material precursor powder. Take 10g of precursor powder and place it in the ark, put the ark into the constant temperature zone of the tube furnace, pass through 400ml / min Ar for 20min to exhaust the air, then use 100ml / min Ar as the protective atmosphere, and raise the temperature at a heating rate of 10℃ / min Heat at 700°C for 2 hours to carbonize glucose and reduce ferric nitrate. After the reaction, cool to room temperature under the protection of Ar atmosphere to obtain the first-step calcined product. Put the calcined product of the first step into a tube furnace, use 400ml / min air as the calcining atmosphere, and raise the temperature to 250°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, ke...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Effective absorption bandwidth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com