Method for measuring trace elements of aluminum, chromium, copper, manganese, nickel and silicon in pure iron
A silicon element and trace technology, which is used in the preparation of test samples, thermal excitation analysis, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of impurity element content that cannot meet the detection requirements, high metrological verification cost, and difficulty in obtaining accurately. The effect of good application effect, avoidance of wrong analysis results, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The above-mentioned and other technical features and advantages of the present invention will be described in more detail below in conjunction with the embodiments.
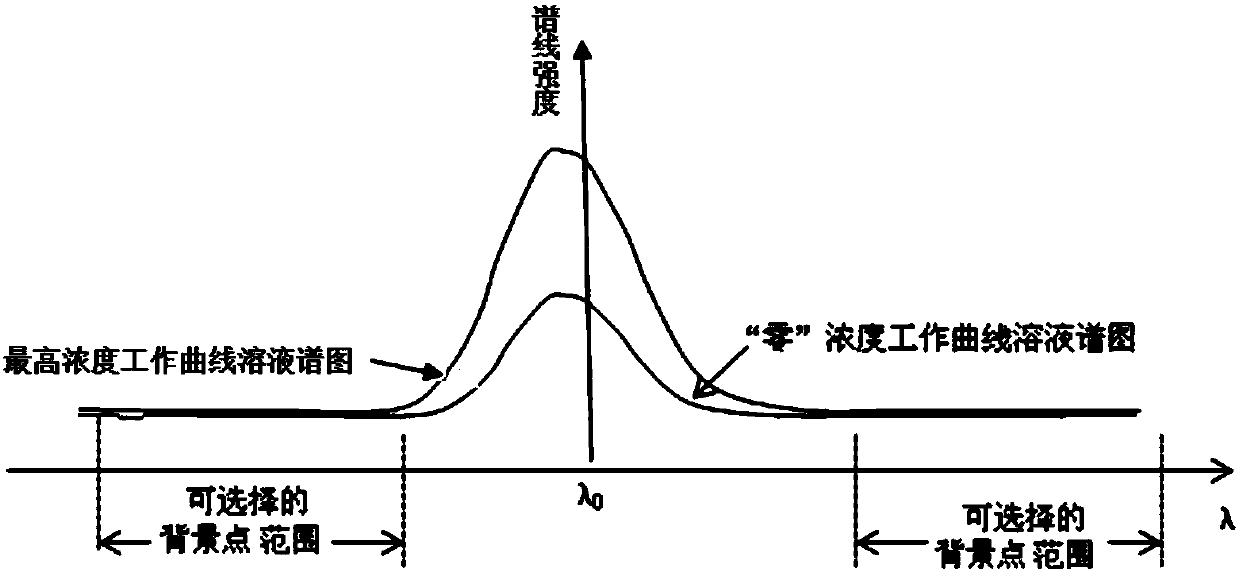
[0042] Determination of trace aluminum, chromium, copper, manganese, nickel and silicon elements in pure iron is measured on the following instrument: HJYULTIMA IIC inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer is used, and the working conditions of the instrument are as follows: incident power 1050W; reflected power< 10W; cooling air flow rate 15L / min; sample lifting volume 1.5mL / min; integration time 5s;
[0043] Analytical line wavelength λ of the analytical element 0 and background points are:
[0044] Al analysis line wavelength λ 0 396.152nm, background points -0.02267nm and +0.02954nm;
[0045] Cr analysis line wavelength λ 0 267.716nm, background points -0.01669nm and +0.02584nm or analysis line wavelength λ 0 359.348nm, background points -0.03120nm and +0.02291nm;
[0046] Cu analysis lin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com