Compounds for specifically and chemically marking 5-aldehyde uracil and marking method and application
A technology of aldehyde uracil and chemical labeling, which is applied in the field of chemical labeling and detection of epigenetic modified bases, and can solve the problem of low 5fU content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] [Example 1] Synthesis process and characterization of compound 1
[0037] Take 3,4-diaminobenzoic acid (3g, 19.7mmol) and ethyl cyanoacetate (7mL, 65.8mmol) in a 100mL round bottom flask, and stir at 180°C for 1h. After the reaction was completed, the reaction system was poured into 100 mL of diethyl ether to precipitate a solid, which was filtered under reduced pressure. The solid was chromatographed on a silica gel column and eluted with dichloromethane: methanol: acetic acid = 100:1:0.1 to obtain a white solid compound A ( 1 g, 25%). 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ12.92(s,1H),8.15(s,1H),7.83(d,J=8.4Hz,1H),7.61(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),4.46(s,2H).HRMS( ESI+)C 10 h 8 N 3 o 2 + [M+H] + calculated 202.06110, found 202.06082.
[0038] Concrete reaction route is as follows:
[0039]
[0040] Take compound A (290mg, 1.4mmol), 3-azidopropylamine (720mg, 7.2mmol) and HATU (1.1g, 2.9mmol) in a 25mL round bottom flask, add 10mL N,N-dimethylformamide and 5 drops of triethylamine w...
Embodiment 2
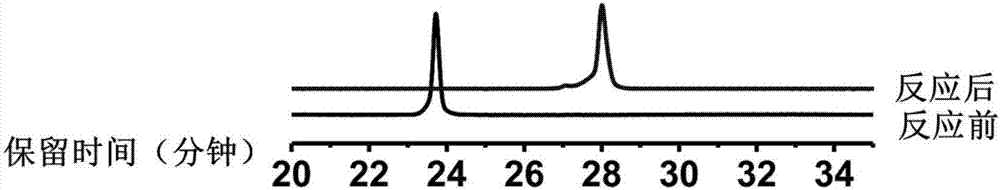
[0043] [Example 2] Compound 1 and 5fU monomer reaction route and characterization
[0044] Take 5-formyluracil (30mg, 0.12mmol) and compound 1 (33mg, 0.12mmol) in a 25mL round bottom flask, add 10mL of methanol and 5 drops of acetic acid, and stir the reaction at 50°C for 15h. After the reaction, the reaction system was evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure, and the solid was eluted by silica gel column chromatography with dichloromethane:methanol=50:1 to 15:1 to obtain compound B (36 mg, 60%) as a yellow solid. 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ13.39(s,1H),11.98(s,1H),8.95(s,1H),8.57(s,1H),8.36–7.90(m,2H),7.67(dd,J=78.5,12.8Hz ,2H),6.20(t,J=6.6Hz,1H),5.35(s,1H),4.99(s,1H),4.35–4.25(m,1H),3.90(dd,J=6.8,4.1Hz, 1H), 3.63(d, J=4.0Hz, 2H), 3.52–3.40(m, 4H), 2.37–2.11(m, 2H), 1.90–1.72(m, 2H). 13 C NMR (100MHz, DMSO-d 6 )δ167.04,162.12,149.76,143.38,142.24,138.00,135.09,129.33,123.61,122.04,118.71,116.68,111.55,107.86,100.39,88.68,86.20,71.21,61.86,49.06,40.78,37.22,28.94.HRMS...
Embodiment 3
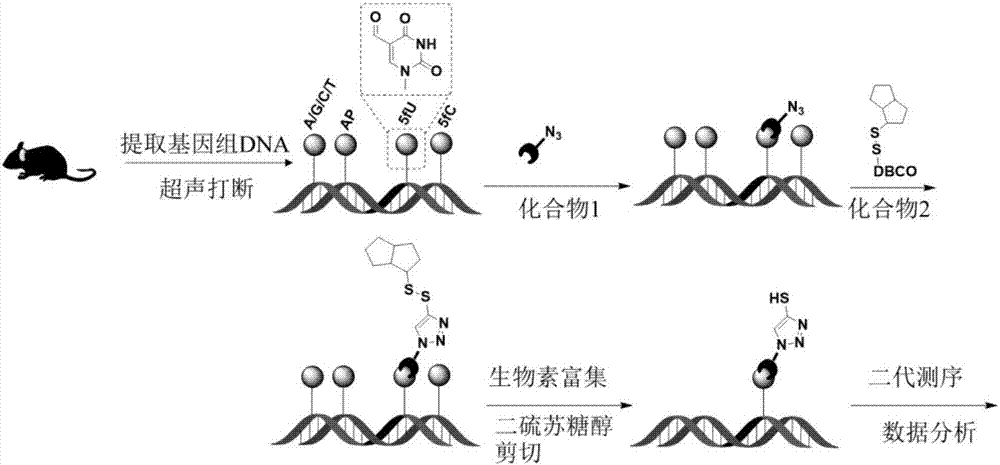
[0047] [Example 3] Marking of mouse genomic DNA
[0048] The extracted genomic DNA (gDNA) was disrupted by an ultrasonic instrument and dissolved in ultrapure water, and the gDNA was quantified by a Qubit Fluorometer quantifier. The labeling of genomic DNA is mainly divided into two steps, such as figure 1 As shown, the first step: Add 20 μL of gDNA (1 μg / μL), 5 μL of sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.0), 5 μL of compound 1 (250 mM dissolved in DMSO) and 20 μL of ultrapure water to a 1.5 mL EP tube , shake and centrifuge, put it into a shaking reactor, and react at 37°C for 12 hours. After the reaction, excess compound 1 was removed with a gel column. Step 2: Add 5 μL of DBCO-S-S-PEG to the product purified in the first step 3 -biotin, in the same way, after shaking and mixing, put it in a shaker at 37°C for 2 hours, and then use a gel column to remove excess small molecule compounds. The final purified mixture was made up to a volume of 100 μL with ultrapure water.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com