Pluripotent stem cells directional differentiation method
A technology of human pluripotent stem cells and directed differentiation, applied in the field of directed differentiation, can solve problems such as no successful cases reported, and achieve the effects of orderly blood differentiation process, low cost, and easy control of culture conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
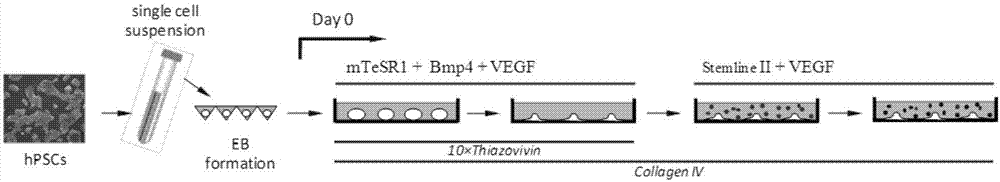
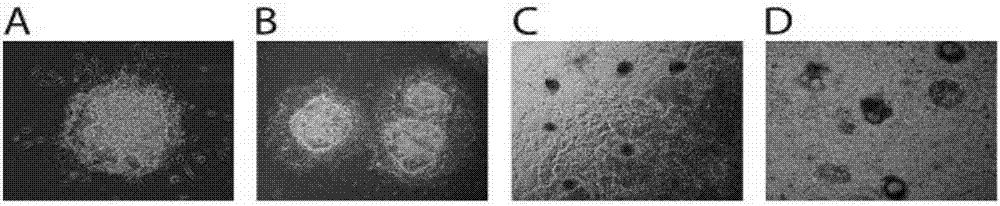
[0045] (1) Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) were routinely cultured in serum-free mTeSR1 medium lined with Matrigel. After hPSCs were passaged at short intervals for 3–5 times, cells in the exponential growth phase were trypsinized into single-cell suspensions. After centrifugation, the cells were resuspended with mTeSR1 medium containing 1 μM Thiazovivin, and the single cell suspension was added to the AggreWell culture plate to form EBs. Each AgreeWell400 culture well had one million cells. Each EB contains 200-500 cells.
[0046] (2) EBs were cultured for 24 hours under standard hPSCs culture conditions (5% carbon dioxide, 21% oxygen, 37°C, humidified environment), and then the EBs were pipetted out carefully, and hVEGF containing 50ng / mL 165 , 2ng / mL hBMP4 and 10μM Thiazovivin mTeSR1 culture medium suspended, added to the mouse or human collagen IV (0.5μg / cm 2 ) on plastic culture plates. The culture density of EBs is 15-20 per square centimeter. Addition of Activi...
Embodiment 2
[0051] This example provides a method for expanding the scale of cell culture. The steps are the same as in Example 1, except that the cells are treated with trypsin during the second to fourth days of differentiation, and then re-plated on the culture plate coated with collagen IV or On the petri dish, incubate for 1 h under the standard culture environment. Then gently pipet and aspirate the cells that are still in suspension or in a semi-adsorbed state to remove residual undifferentiated hPSCs. The adsorbed cell part can continue to be cultured in the original culture dish according to the above conditions, or be seeded in a new collagen IV-coated culture dish at a density of 10,000 cells per square centimeter. The method of this embodiment can expand the scale of the whole cell culture about ten times.
experiment example 1
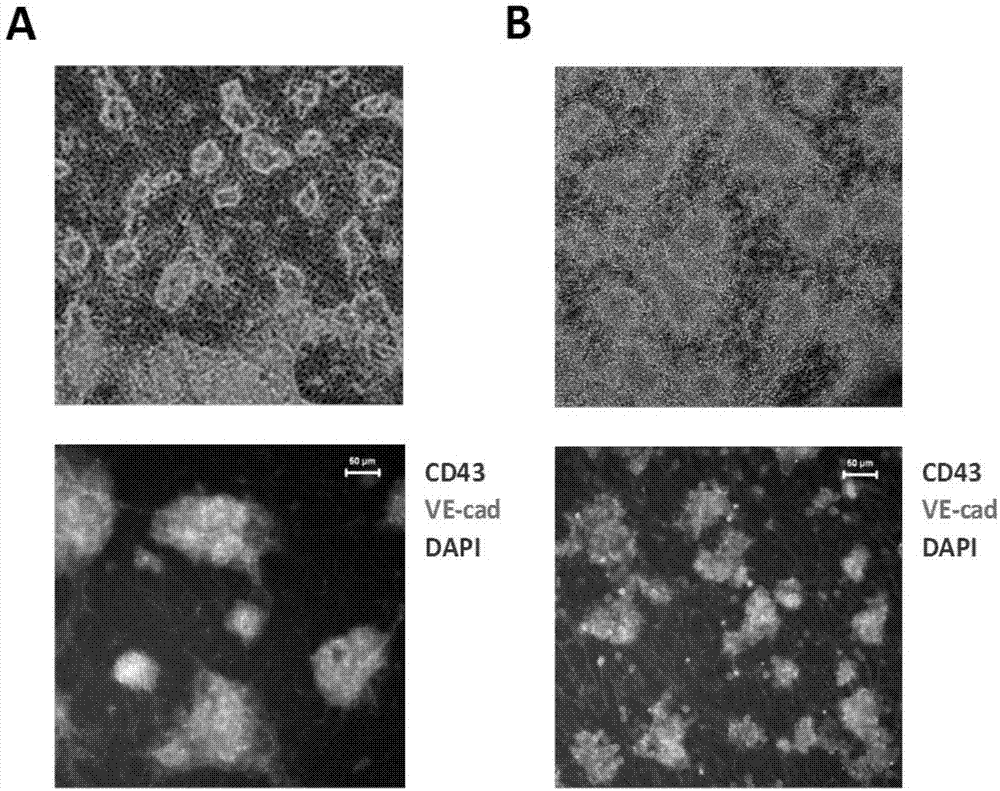
[0053] To analyze blood progenitor cells generated during differentiation, whole cells or sorted cells at different stages of differentiation were added to a culture medium containing the human cytokines SCF, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-6, and EPO. Colony analysis was performed in serum-free methylcellulose medium. The earliest blood progenitors appear on the fourth day of differentiation. Most blood cells with blood colony forming ability are present in the suspension cell fraction. Essentially all blood progenitors are present on CD43 + cell population (see Figure 6 ). CD43 + cells and CD43 - Compared with cells, many blood cell-related genes are highly expressed (see Figure 7 ). In the early stages of differentiation, erythroid progenitors and multipotent progenitors (CFU-E, BFU-E and CFU-Mix) are the main hematopoietic progenitors generated. At the later stage of differentiation (differentiation day 14 to 16), the multipotent progenitor cells were well maintained due...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com