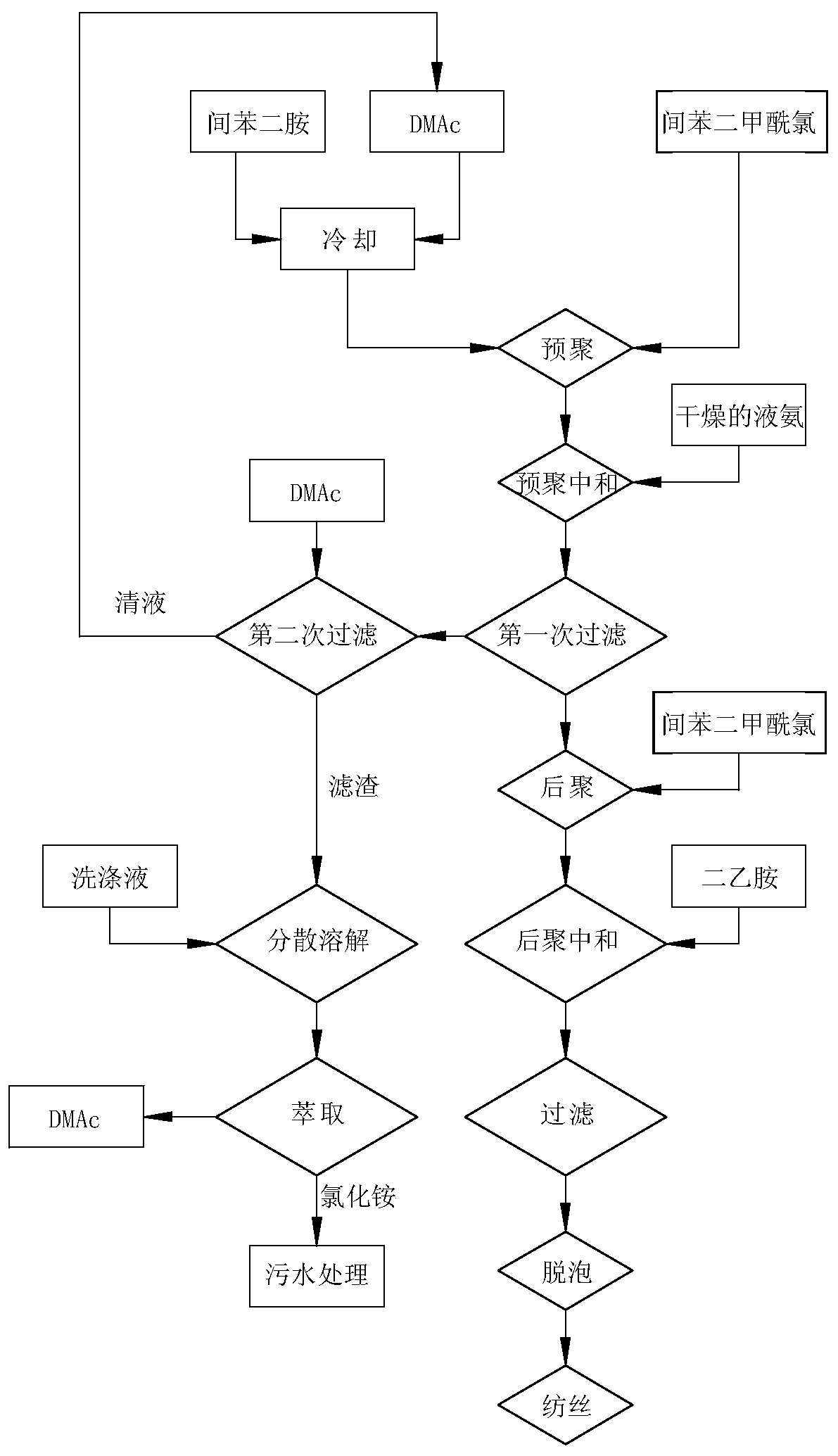
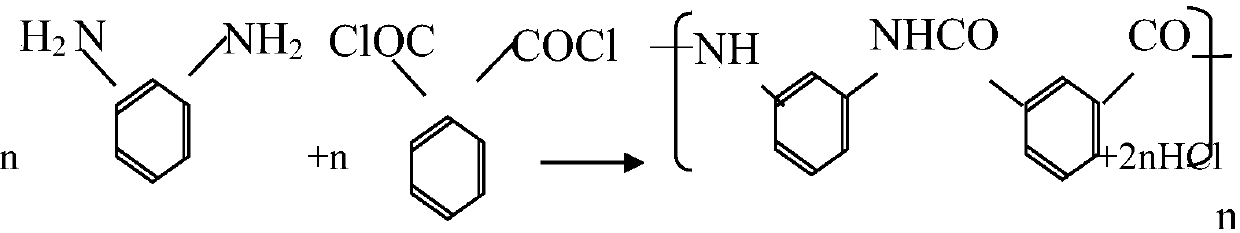An energy-saving and environment-friendly meta-aramid polymerization process
An energy-saving, environmentally friendly, polymerization process technology, applied in the direction of single-component synthetic polymer rayon, single-component polyamide rayon, textile and papermaking, etc., can solve the problem of large energy consumption and equipment corrosion, affecting the quality of DMAc, spinning The spinnability of the silk solution has a great influence on the problems such as reducing the economic burden and waste of resources, avoiding the large-scale production of HCl gas, and avoiding the high temperature decomposition of DMAc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1 (comparative example)
[0052] Add 60 parts by weight of anhydrous DMAc to a jacketed reactor equipped with a stirring paddle and a thermometer, and record the liquid level in the reactor as a. Add 6.25 parts by weight of flaky or molten m-phenylenediamine under the protection of nitrogen, and stir to dissolve. Put -15°C ice-salt water into the jacket, cool the solution to -10-0°C, and gradually add 11.16 parts by weight of powdered or molten isophthaloyl chloride while stirring to carry out prepolymerization. Speed, temperature and flow of cooling water in the jacket, so that the reaction temperature is controlled within the range of 0-10°C. Continue to stir for 15-20 minutes after the addition of the above-mentioned acid chloride, and gradually introduce dry ammonia gas for pre-polymerization and neutralization. During the pre-polymerization and neutralization process, control the addition rate of ammonia gas to keep the temperature within the range of 0...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Add 60 parts by weight of anhydrous DMAc to a jacketed reactor equipped with a stirring paddle and a thermometer, and record the liquid level in the reactor as a. Under the protection of nitrogen, add 6.25 parts by weight of flaky or molten m-phenylenediamine, stir to dissolve, pass -15°C ice-salt water into the jacket, cool the solution to -10~0°C, and stir Gradually add 11.16 parts by weight of powdery or molten isophthaloyl chloride for prepolymerization, and control the reaction temperature within the range of 0-10°C by controlling the feeding rate, the temperature and the flow rate of cooling water in the jacket. Continue stirring for 15-20 minutes after the addition of the above-mentioned acid chlorides, and gradually introduce dry ammonia gas for prepolymerization and neutralization, and control the addition rate of ammonia gas to keep the temperature within the range of 0-10°C. Stir and neutralize until the pH value is 6.0, stop adding ammonia, and continue stir...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Add 60 parts by weight of anhydrous DMAc to a jacketed reactor equipped with a stirring paddle and a thermometer, and record the liquid level in the reactor as a. Add 6.25 parts by weight of flaky or molten m-phenylenediamine under the protection of nitrogen, and stir to dissolve. Put -15°C ice-brine into the jacket, cool the solution, and gradually add 11.16 parts by weight of powdered or molten isophthaloyl chloride while stirring for prepolymerization. By controlling the feeding speed, the cooling water in the jacket Adjust the temperature and flow rate of the prepolymerization reaction. Continue stirring for 15-20 minutes after the addition of the above-mentioned acid chlorides, and gradually feed dry ammonia gas for prepolymerization and neutralization. Control the rate of adding ammonia to keep the pre-polymerization neutralization temperature within the range of 0-10°C. Stir and neutralize until the pH value is 6.0, stop adding ammonia, and continue stirring fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com