Preparation method of artificial skin with controllable drug release
An artificial skin and drug technology, applied in the field of artificial skin and drug controlled release, can solve the problems of complex process, difficult cell adhesion, affecting wound healing efficacy, etc., and achieve the effect of improving in vivo biological effects and promoting blood vessel regeneration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
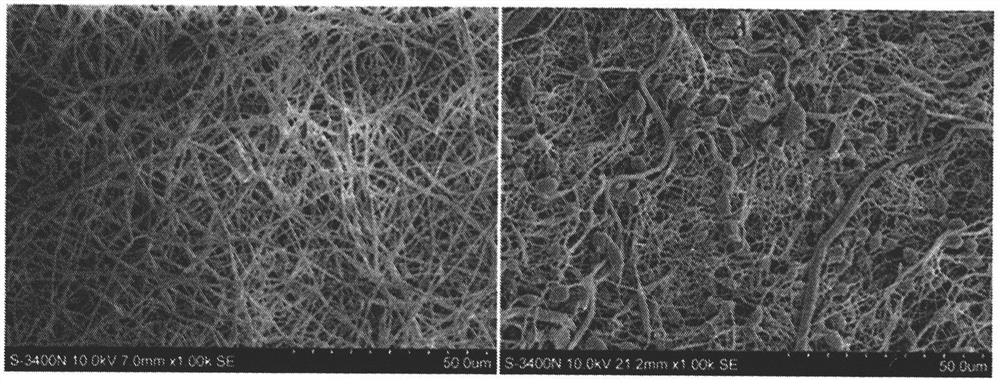
[0046] Embodiment 1: Preparation of artificial skin, observation by scanning electron microscope, confirmation of microsphere morphology (preparation method effect test).
[0047] Use dichloromethane / dimethylformamide solution, the volume ratio of dichloromethane / dimethylformamide is 5:1, configure 20% polycaprolactone solution, prepare three-dimensional porous material by freeze-drying method, cross-link and fix, Dry and set aside. First, immerse in a fibronectin solution, incubate in a 37°C incubator for 18 hours, rinse with pure water for 3 times, the fibronectin is 5 mg / ml, and the pH is 7.5. Then, immerse in platelet endothelial growth factor (VEGF) solution, 37 ° C, 12h, rinse once with pure water, platelet endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is 1 mg / ml, pH7.5. Finally, immerse in acetone for 5 minutes. After drying, its structure was observed by scanning electron microscope ( figure 1 ).
Embodiment 2
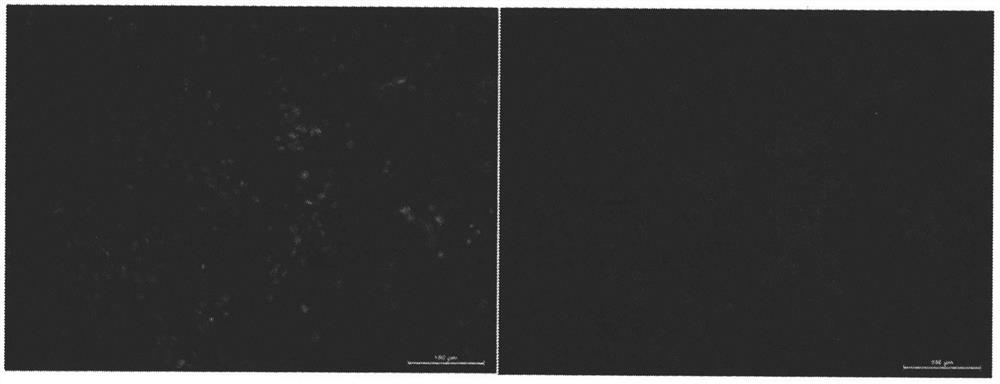
[0048] Example 2: Inoculate cells into artificial skin, and observe the morphology and distribution of cells in artificial skin with a fluorescence microscope (biological safety and compatibility testing).
[0049] The primary mouse dermal fibroblasts were isolated and cultured. When they were cultured to the fifth generation, they were digested with trypsin, diluted, and suspended by pipetting to prepare a fibroblast suspension with a concentration of about 10×10 5 / ml. The cell suspension was inoculated into the sterilized artificial skin, and cultured in the cell box until the 8th day. First, fix with 10% paraformaldehyde solution, then use rhodamine-labeled phalloidin (R415, Molecular Probes) to stain the fibrous actin in the cytoplasm respectively, and use 4′,6-diamidine Cell nuclei were stained blue with 2-phenylindole (DAPI). Finally, the slides were sealed with anti-fluorescence quenching mounting reagent and stored in the dark. Observe and take pictures with a fluor...
Embodiment 3
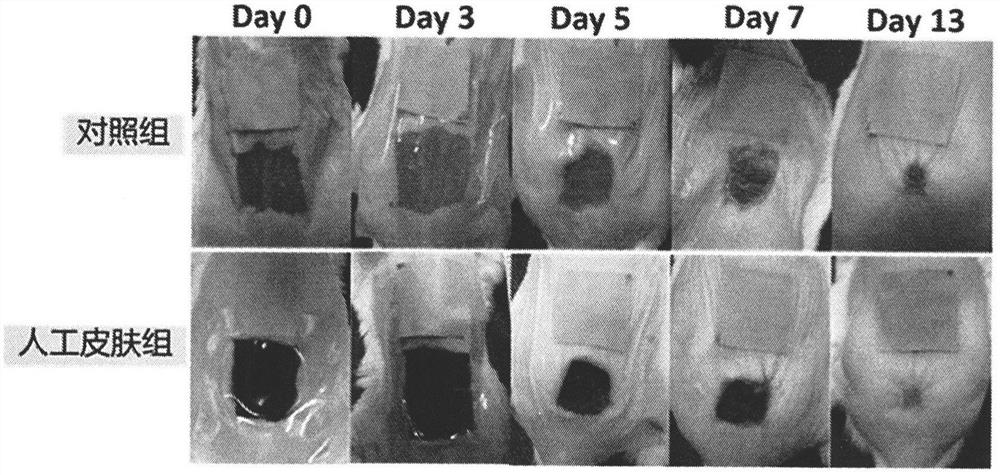
[0050] Embodiment 3: Using animal experiments, detect the effect of the artificial skin on the wound healing speed of mice (detect the curative effect of the artificial skin at the level of the animal body).
[0051] In the first step, the experimental mice are anesthetized. The experimental mice were injected intraperitoneally with 0.8% pentobarbital for anesthesia. Anesthetics were used at a dose of 0.02 mg / g body weight. In the second step, hair removal cream was used to remove the hair on the back of the mouse, and disinfected with alcohol; a full-thickness skin defect wound was made on the back of the mouse to ensure that the size and depth of each mouse wound were basically the same. The third step is to cover the wound with the prepared artificial skin graft, take pictures of the wound, and calculate the wound healing rate. On the 0th, 3rd, 5th, 7th, and 13th day after artificial skin transplantation, a Canon digital camera was used perpendicular to the wound surface....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com