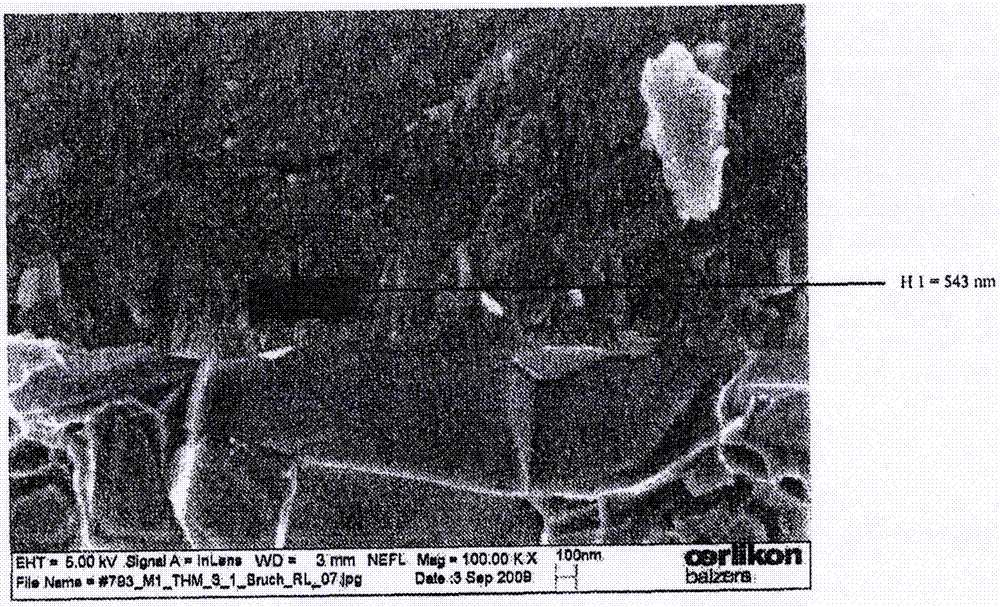
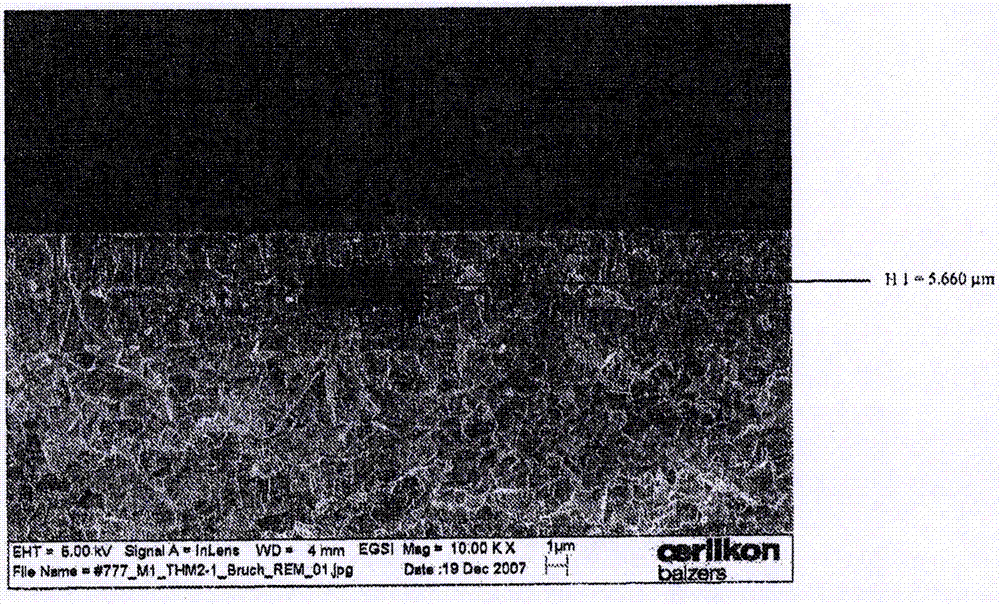
Method for producing cubic zirconia layers
A zirconia and cubic technology, applied in the field of preparing zirconia layers, can solve the problems of difficulty in controlling the crystal structure of the synthesis layer, target poisoning, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0156] Step (A)
[0157] First of all, the outside of the coating system is cleaned of the substrate on which the coating or layer system is to be applied. It depends on the substrate material and its production method. In most cases, wet chemical treatment, heat removal in a specific atmosphere or other methods known to those skilled in the art will be performed. In this case, wet chemical treatment is performed.
[0158] Step (B)
[0159] After placing the workpiece in the clamping device that provides this action and the holder in the vacuum processing device, the processing chamber is evacuated to a pressure of about 0.01 Pa.
[0160] Step (C)
[0161] Then, in a first vacuum pretreatment step, a radiant heater-assisted low-voltage arc plasma is between a cathode chamber with a hot cathode separated by a partition and the anode-connected workpiece in an argon-hydrogen atmosphere Ignition, wherein the method step is characterized by the following parameters:
[0162] ...
Embodiment 2
[0189] In another method variant, layers are now produced in which alloy targets produced by powder-metallurgy are used (in the example, 2 pieces at a time) with a composition of 85 at % Zr and as a typical stabilizer 15 at% yttrium (Y) to synthesize the functional layer (see also Table 2). For the production of intermediate or carrier layers, 2 elemental Zr targets are additionally used:
[0190] First, as described in Example 1, substeps (A)-(D) were repeated.
[0191] First, for comparison, layers without stabilizer were reproduced (steps E1 and F1). In this regard, the two Zr(85at%) / Y(15at%) targets were again replaced by two elemental Zr targets, i.e. 4 Zr targets were run to produce the interlayer.
[0192] Step (E2a)
[0193] This is done with the following parameters:
[0194]
[0195] Step (F2a)
[0196] Then a pure Zr-O layer (without Y) was deposited as a layer for which no Zr-Y target was used, i.e. 4 Zr targets were still run and as in example 1 only oxyge...
Embodiment approach
[0270] According to one embodiment, an advantage of the method of the invention is that the materials present separately will become alloyed with each other during operation in oxygen and in nitrogen-oxygen mixtures under the action of a spark moving on the target. Because the temperature at the bottom point of the spark can reach several thousand degrees Celsius, high melting point materials such as Zr can therefore be melted together with different concentrations of stabilizers, such as 1at%-25at% Y on the target surface just before being transformed into the gas phase molten.
[0271] Doing this method in argon will result in a lot of sputtering. These materials with different melting temperatures combine well with each other in oxygen or nitrogen-oxygen mixtures as reactive gases. The alloying process at the target surface provides greater freedom in the selection of starting materials for target production, since powders with an average particle size of 1 µm or lower to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com