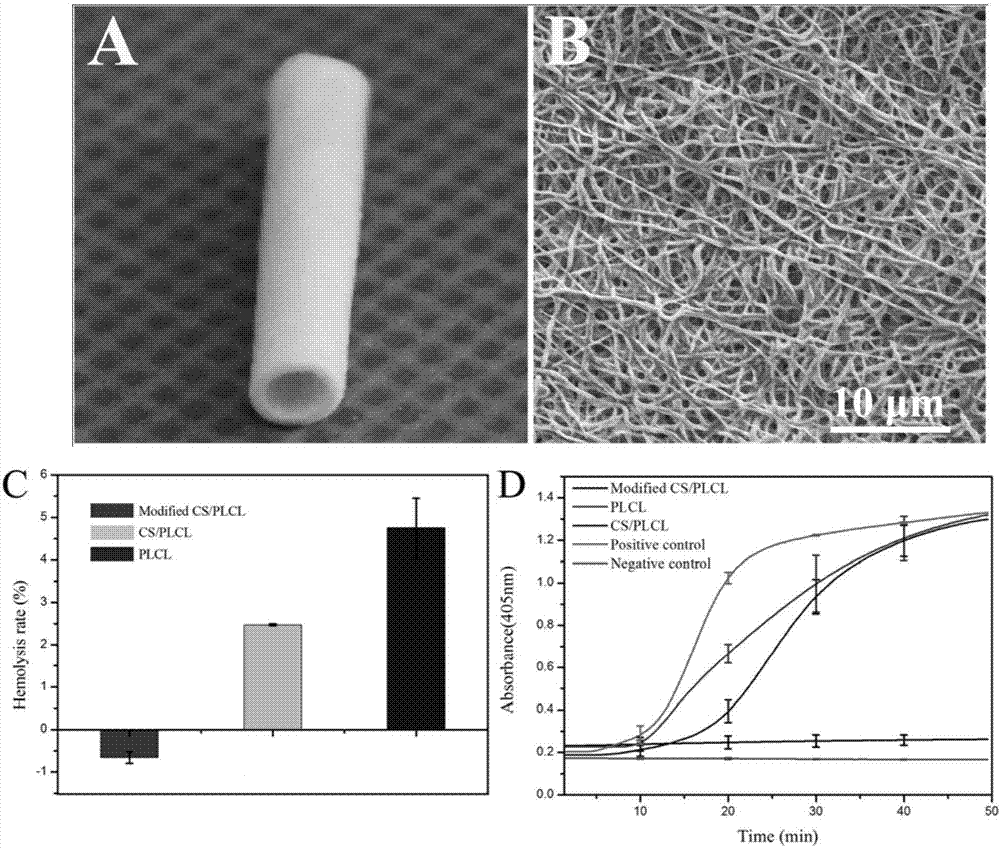
Tissue engineering nanofiber intravascular stent and preparation method thereof
A nanofiber and tissue engineering technology, applied in the field of tissue engineering nanofiber vascular stent and its preparation, can solve the problems of postoperative embolism, intimal hyperplasia, and long-term patency reduction, so as to improve anticoagulant performance and promote adhesion , Promote the effect of transportation and discharge of metabolic waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Dissolve chitosan in trifluoroacetic acid / hexafluoroisopropanol solution under normal temperature conditions, stir and prepare a 6% (w / v) homogeneous solution, and dissolve PLCL in hexafluoroisopropanol under normal temperature conditions , stirred to prepare a 6% (w / v) homogeneous solution, then mixed the two evenly at a volume ratio of 1:2, and carried out electrospinning with the roller as the receiving device (electrostatic voltage: 12kV, spinning rate: 2mL / h, acceptance height: 15cm), dry the stent to remove residual solvent;
[0026] (2) Take dextran sulfate equivalent to chitosan in step (1) and dissolve it in an aqueous acetic acid solution with a mass fraction of 0.175%, and immerse the tubular stent in (1) in the above solution for 1 hour at room temperature , taking out the scaffold, washing it with deionized water, and freeze-drying to obtain the nanofiber scaffold.
Embodiment 2
[0028] (1) Dissolve polylysine in deionized water at normal temperature, stir to prepare a 6% (w / v) homogeneous solution, dissolve PLCL in hexafluoroisopropanol at normal temperature, and stir to prepare 6% (w / v) homogeneous solution, and then mix the two evenly at a volume ratio of 1:2, and use the roller as the receiving device to carry out electrospinning (electrostatic voltage: 12kV, spinning rate: 2mL / h, receiving height: 15cm), dry the bracket to remove residual solvent;
[0029] (2) Take chondroitin sulfate equal to the amount of polylysine in step (1) and dissolve it in an aqueous solution of acetic acid with a mass fraction of 0.175%. Under normal temperature conditions, immerse the tubular support in (1) in the above solution After 1 hour, the scaffold was taken out, washed with deionized water, and freeze-dried to obtain the nanofiber scaffold.
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) Dissolve polyacrylamide in hexafluoroisopropanol at normal temperature, stir to prepare a 6% (w / v) homogeneous solution, dissolve PLCL in hexafluoroisopropanol at normal temperature, and stir to prepare 6% (w / v) homogeneous solution, and then the two were mixed uniformly at a volume ratio of 1:2, and the roller was used as a receiving device for electrospinning (electrostatic voltage: 12kV, spinning rate: 2mL / h, receiving Height: 15cm), dry the bracket to remove residual solvent;
[0032] (2) Dissolve the same amount of heparin as the polyacrylamide in step (1) in an aqueous acetic acid solution with a mass fraction of 0.175%, and immerse the tubular stent in (1) in the above solution for 1 hour at room temperature, and take out the stent , washed with deionized water, and freeze-dried to obtain the nanofiber scaffold.
[0033] Table 1: The stent aperture value that each implementation case obtains:
[0034]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com