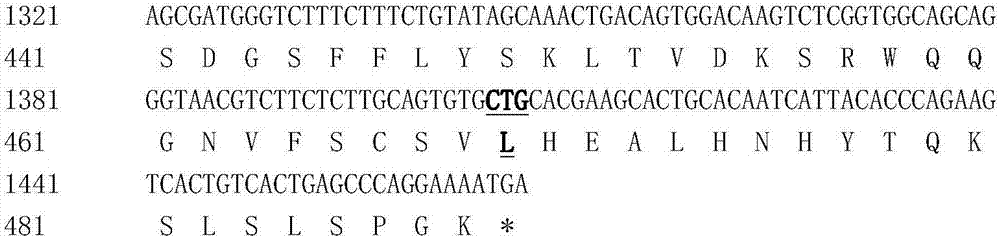High-glycosylation human growth hormone fusion protein and preparation method and purpose thereof
A technology of human growth hormone and fusion protein, which is applied in the field of highly glycosylated human growth hormone fusion protein and its preparation, can solve the problems of poor biological activity and short half-life, and achieve improved biological activity, fast onset of action, and simple purification steps Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] IgG Fc variant
[0054] non-lytic Fc variant
[0055] The Fc element is derived from the Fc fragment of the constant region of immunoglobulin IgG, which plays an important role in the immune defense to eliminate pathogens. The effector function of Fc-mediated IgG exerts two mechanisms: (1) Binding to cell surface Fc receptors (FcγRs), digesting pathogens by phagocytosis or lysis or killing cells through the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) pathway , or (2) binding to C1q of the first complement component C1, triggering the complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) pathway, thereby lysing the pathogen. For therapeutic application in humans, when the hGH-L-CTP-vFc fusion protein binds to hGH receptors on the surface of target cells, the Fc region of the fusion protein preferably does not have adverse effector functions and thus does not dissolve Or remove these target cells. Therefore, the Fc region of hGH-Fc must be insoluble, preferably inactive for bind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com